Abstract
Purpose
Morphine is a powerful analgesic but its effect is often diminished owing to the development of tolerance. It has been suggested that morphine activates microglia through its action on the toll-like receptor 4 (TLR4) in the spinal cord, leading to suppression of the morphine effect. However, it has not been examined whether the development of morphine tolerance is affected by the deletion and mutation of the TLR4 gene.
Methods
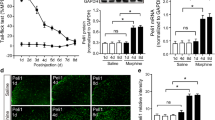
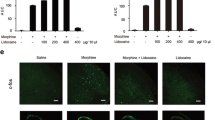
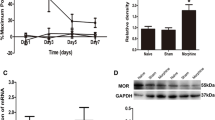
Mice were treated with morphine (60 mg/kg) or vehicle once daily for five consecutive days to induce morphine tolerance, which was assessed by the tail-flick test before and after the treatment period. The effect of the microglial inhibitor minocycline, and the effect of TLR4 mutation (C3H/HeJ mouse) and deletion (TLR4-knockout mouse) on the development of morphine tolerance were tested. The expression of the microglial activation marker, CD11b, in the spinal cords of TLR4-knockout and wild-type mice after morphine treatment for 5 days was assessed by reverse-transcription polymerase chain reaction.
Results
Minocycline attenuated the development of morphine tolerance in mice. Mutation or deletion of the TLR4 gene did not significantly affect the development of morphine tolerance. CD11b mRNA expression was increased after morphine treatment both in TLR4-knockout and wild-type mice.
Conclusion
Microglial activation caused by a mechanism independent of TLR4 is involved in the development of morphine tolerance. Further studies are necessary to clarify the cellular mechanisms of morphine-induced microglial activation.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Fukuda K. Opioids. In: Miller D, editor. Miller’s anesthesia. New York: Churchill Livingstone; 2009. p. 769–824.
Williams JT, Christie MJ, Manzoni O. Cellular and synaptic adaptations mediating opioid dependence. Physiol Rev. 2001;81:299–343.
Habibi-Asl B, Hassanzadeh K, Charkhpour M. Central administration of minocycline and riluzole prevents morphine-induced tolerance in rats. Anesth Analg. 2009;109:936–42.
Mika J, Wawrzczak-Bargiela A, Osikowicz M, Makuch W, Przewlocka B. Attenuation of morphine tolerance by minocycline and pentoxifylline in naive and neuropathic mice. Brain Behav Immun. 2009;23:75–84.
Narita M, Suzuki M, Narita M, Niikura K, Nakamura A, Miyatake M, Yajima Y, Suzuki T. mu-Opioid receptor internalization-dependent and -independent mechanisms of the development of tolerance to mu-opioid receptor agonists: comparison between etorphine and morphine. Neuroscience. 2006;138:609–19.
Raghavendra V, Tanga FY, DeLeo JA. Attenuation of morphine tolerance, withdrawal-induced hyperalgesia, and associated spinal inflammatory immune responses by propentofylline in rats. Neuropsychopharmacology. 2004;29:327–34.
Hutchinson MR, Zhang Y, Shridhar M, Evans JH, Buchanan MM, Zhao TX, Slivka PF, Coats BD, Rezvani N, Wieseler J, Hughes TS, Landgraf KE, Chan S, Fong S, Phipps S, Falke JJ, Leinwand LA, Maier SF, Yin H, Rice KC, Watkins LR. Evidence that opioids may have toll-like receptor 4 and MD-2 effects. Brain Behav Immun. 2010;24:83–95.
Poltorak A, He X, Smirnova I, Liu MY, Van Huffel C, Du X, Birdwell D, Alejos E, Silva M, Galanos C, Freudenberg M, Ricciardi-Castagnoli P, Layton B, Beutler B. Defective LPS signaling in C3H/HeJ and C57BL/10ScCr mice: mutations in Tlr4 gene. Science. 1998;282:2085–8.
Ogawa T, Asai Y, Hashimoto M, Takeuchi O, Kurita T, Yoshikai Y, Miyake K, Akira S. Cell activation by Porphyromonas gingivalis lipid A molecule through Toll-like receptor 4- and myeloid differentiation factor 88-dependent signaling pathway. Int Immunol. 2002;14:1325–32.
Chen ML, Bao F, Zhang YQ, Zhao ZQ. Effects of aquaporin 4 deficiency on morphine analgesia and chronic tolerance: a study at spinal level. J Mol Neurosci. 2010;42:140–4.
Roy A, Fung YK, Liu X, Pahan K. Up-regulation of microglial CD11b expression by nitric oxide. J Biol Chem. 2006;281:14971–80.
Zhang Y, Li H, Li Y, Sun X, Zhu M, Hanley G, Lesage G, Yin D. Essential role of toll-like receptor 2 in morphine-induced microglia activation in mice. Neurosci Lett. 2011;489:43–7.
Horvath RJ, Romero-Sandoval EA, De Leo JA. Inhibition of microglial P2X4 receptors attenuates morphine tolerance, Iba1, GFAP and mu opioid receptor protein expression while enhancing perivascular microglial ED2. Pain. 2010;150:401–13.
Zhou D, Chen ML, Zhang YQ, Zhao ZQ. Involvement of spinal microglial P2X7 receptor in generation of tolerance to morphine analgesia in rats. J Neurosci. 2010;30:8042–7.
Kettenmann H, Hanisch UK, Noda M, Verkhratsky A. Physiology of microglia. Physiol Rev. 2011;91:461–553.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by a Grant-in-Aid for Exploratory Research, No. 23659742, from the Japan Society for the Promotion of Science, Tokyo, Japan.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
About this article
Cite this article
Fukagawa, H., Koyama, T., Kakuyama, M. et al. Microglial activation involved in morphine tolerance is not mediated by toll-like receptor 4. J Anesth 27, 93–97 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00540-012-1469-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00540-012-1469-4