Background:
Background:
Cirrhotic patients frequently undergo various medical procedures, such as diagnostic gastrointestinal endoscopy, without taking breakfast. The aim of the present study was to clarify the effect of longer fasting (>12 h) on energy metabolism, and to test whether supplementation of an oral branched-chain amino-acid-enriched nutrient mixture (BCAA mixture), which contains various nutrients in addition to BCAA, could improve the catabolic state.
Methods:
Metabolic measurement was performed in 30 cirrhotic patients and 13 normal subjects, using indirect calorimetry.
Results:
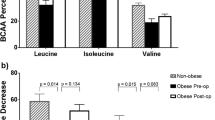
Compared with that in the normal subjects, the respiratory quotient (RQ) was significantly lower after an overnight fast in the cirrhotic patients, indicating accelerated fat oxidation and a catabolic state. In addition, RQ in cirrhotic patients (n= 7) decreased rapidly with longer fasting, whereas that in the normal subjects (n= 5) showed relatively stable values. These results indicate that special care should be taken with medical procedures that are carried out in patients who have fasted. The effect of oral glucose, a carbohydrate-rich snack (rice ball), and the BCAA mixture (each, 210 kcal) on RQ was studied in 6 normal subjects and 6 patients with liver cirrhosis after an overnight fast. Supplementation of the carbohydrate-rich snack and the BCAA mixture (210 kcal each) elevated RQ and blood glucose levels to a similar degree in the cirrhotic patients. Oral administration of glucose (210 kcal) led to significantly greater elevation of blood glucose levels than the other snacks, which may be unfavorable for cirrhotic patients, who frequently have glucose intolerance. In the 30 cirrhotic patients, supplementation with the BCAA mixture in the late evening significantly improved RQ in the early morning.
Conclusions:
Carbohydrate-rich meals are used as a late evening snack in cirrhotic patients, but our study indicates that supplementation with a BCAA mixture can also be used to reduce fat oxidation in the early morning, with results similar to those with carbohydrate-rich snacks.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Received: June 8, 2001 / Accepted: November 30, 2001
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nakaya, Y., Harada, N., Kakui, S. et al. Severe catabolic state after prolonged fasting in cirrhotic patients: effect of oral branched-chain amino-acid-enriched nutrient mixture. J Gastroenterol 37, 531–536 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1007/s005350200082
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s005350200082