Abstract:
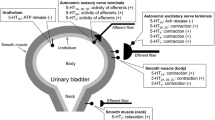
The multiple 5-hydroxytryptamine (5-HT, serotonin) receptor subtypes are distinguished. In this article, we described mainly the 5-HT4 receptor of four subtypes of functional 5-HT receptors, 5-HT1, 5-HT2, 5-HT3, and 5-HT4, recognized in the gastrointestinal tract. In-vivo microdialysis experiments determined that activation of the 5-HT4 receptor stimulated intestinal motor activity associated with a local increase in acetylcholine (ACh) release from the intestinal cholinergic neurons in the whole body of dogs. The 5-HT4 receptor-mediated response of ACh release in the antral, corporal, and fundic strips isolated from guinea pig stomach corresponds to the presence of 5-HT4 receptor in the myenteric plexus. In-vitro receptor autoradiograms of the stomach and colon indicate that the distribution of 5-HT4 receptors in human tissues is similar to that in the guinea pig, although density of 5-HT4 receptors in the myenteric plexus of human tissues is lower than that in guinea pig tissues. The 5-HT4 receptors located in the myenteric plexus may participate in gastrointestinal motility, and thus the 5-HT4 agonists and antagonists may be available for treatment of dysfunction of gastrointestinal motility.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Received: November 22, 1999 / Accepted: March 24, 2000
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Taniyama, K., Makimoto, N., Furuichi, A. et al. Functions of peripheral 5-hydroxytryptamine receptors, especially 5-hydroxytryptamine4 receptor, in gastrointestinal motility. J Gastroenterol 35, 575–582 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1007/s005350070056
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s005350070056