Abstract
Background
Protein p21Cip1/Waf1 is a cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor, which plays important roles in cell cycle arrest, senescence, and apoptosis. Interestingly, the nuclear and cytoplasmic p21 executes various functions in the cell. In this study, we investigated the prognostic impact of subcellular p21 expression in gastric cancer (GC).
Methods
Expressions of subcellular p21 was assessed by immunohistochemistry using a tissue microarray in a training cohort and it went into a second testing cohort and finally to a validating cohort. Prognostic and predictive role of subcellular p21 expression status was evaluated. We also studied the roles of subcellular p21 in GC cell migration and invasion.
Results
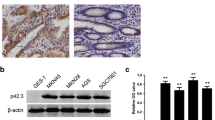
Nuclear and cytoplasmic p21 protein levels were significantly reduced and increased in GC lesions compared with adjacent non-cancerous tissues, respectively. Low nuclear p21 or high cytoplasmic p21 expression significantly correlated with shorter overall survival (OS), as well as with clinicopathologic characteristics in patients. Multivariate regression analysis showed that low nuclear and high cytoplasmic p21 expression, separately and together, were independent negative markers of OS. Finally, we found that nuclear p21 inhibits but cytoplasmic p21 promotes cell migration and invasion abilities.
Conclusions
These findings suggest that nuclear and cytoplasmic p21 protein expression in tumor are novel candidate prognostic markers in resectable human gastric carcinoma, and they exert distinct roles in cell migration and invasion.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Parkin DM, Bray F, Ferlay J, et al. Global cancer statistics, 2002. CA Cancer J Clin. 2005;55:74–108.
Gupta GP, Massague J. Cancer metastasis: building a framework. Cell. 2006;127:679–95.
Zhao X, Dou W, He L, et al. MicroRNA-7 functions as an anti-metastatic microRNA in gastric cancer by targeting insulin-like growth factor-1 receptor. Oncogene. 2013;32:1363–72.
Valastyan S, Weinberg RA. Tumor metastasis: molecular insights and evolving paradigms. Cell. 2011;147:275–92.
Peinado H, Olmeda D, Cano A. Snail, Zeb and bHLH factors in tumour progression: an alliance against the epithelial phenotype? Nat Rev Cancer. 2007;7:415–28.
Fidler IJ. The pathogenesis of cancer metastasis: the ‘seed and soil’ hypothesis revisited. Nat Rev Cancer. 2003;3:453–8.
Nguyen DX, Massague J. Genetic determinants of cancer metastasis. Nat Rev Genet. 2007;8:341–52.
Harper JW, Adami GR, Wei N, et al. The p21 Cdk-interacting protein Cip1 is a potent inhibitor of G1 cyclin-dependent kinases. Cell. 1993;75:805–16.
Cmielova J, Rezacova M. p21Cip1/Waf1 protein and its function based on a subcellular localization (corrected). J Cell Biochem. 2011;112:3502–6.
Rodriguez R, Meuth M. Chk1 and p21 cooperate to prevent apoptosis during DNA replication fork stress. Mol Biol Cell. 2006;17:402–12.
Komiya T, Hosono Y, Hirashima T, et al. p21 expression as a predictor for favorable prognosis in squamous cell carcinoma of the lung. Clin Cancer Res. 1997;3:1831–5.
Zirbes TK, Baldus SE, Moenig SP, et al. Prognostic impact of p21/waf1/cip1 in colorectal cancer. Int J Cancer. 2000;89:14–8.
Ferrandina G, Stoler A, Fagotti A, et al. p21WAF1/CIP1 protein expression in primary ovarian cancer. Int J Oncol. 2000;17:1231–5.
Lu X, Toki T, Konishi I, et al. Expression of p21WAF1/CIP1 in adenocarcinoma of the uterine cervix: a possible immunohistochemical marker of a favorable prognosis. Cancer. 1998;82:2409–17.
Kapranos N, Stathopoulos GP, Manolopoulos L, et al. p53, p21 and p27 protein expression in head and neck cancer and their prognostic value. Anticancer Res. 2001;21:521–8.
Ceccarelli C, Santini D, Chieco P, et al. Quantitative p21(waf-1)/p53 immunohistochemical analysis defines groups of primary invasive breast carcinomas with different prognostic indicators. Int J Cancer. 2001;95:128–34.
Sarbia M, Gabbert HE. Modern pathology: prognostic parameters in squamous cell carcinoma of the esophagus. Recent Results Cancer Res. 2000;155:15–27.
Cheung TH, Lo KW, Yu MM, et al. Aberrant expression of p21(WAF1/CIP1) and p27(KIP1) in cervical carcinoma. Cancer Lett. 2001;172:93–8.
Besson A, Assoian RK, Roberts JM. Regulation of the cytoskeleton: an oncogenic function for CDK inhibitors? Nat Rev Cancer. 2004;4:948–55.
Kumar R, Hung MC. Signaling intricacies take center stage in cancer cells. Cancer Res. 2005;65:2511–5.
Al-Moundhri MS, Nirmala V, Al-Hadabi I, et al. The prognostic significance of p53, p27 kip1, p21 waf1, HER-2/neu, and Ki67 proteins expression in gastric cancer: a clinicopathological and immunohistochemical study of 121 Arab patients. J Surg Oncol. 2005;91:243–52.
Sohn D, Essmann F, Schulze-Osthoff K, et al. p21 blocks irradiation-induced apoptosis downstream of mitochondria by inhibition of cyclin-dependent kinase-mediated caspase-9 activation. Cancer Res. 2006;66:11254–62.
Xia W, Chen JS, Zhou X, et al. Phosphorylation/cytoplasmic localization of p21Cip1/WAF1 is associated with HER2/neu overexpression and provides a novel combination predictor for poor prognosis in breast cancer patients. Clin Cancer Res. 2004;10:3815–24.
Koster R, di Pietro A, Timmer-Bosscha H, et al. Cytoplasmic p21 expression levels determine cisplatin resistance in human testicular cancer. J Clin Invest. 2010;120:3594–605.
Xia X, Ma Q, Li X, et al. Cytoplasmic p21 is a potential predictor for cisplatin sensitivity in ovarian cancer. BMC Cancer. 2011;11:399.
Gamboa-Dominguez A, Seidl S, Reyes-Gutierrez E, et al. Prognostic significance of p21WAF1/CIP1, p27Kip1, p53 and E-cadherin expression in gastric cancer. J Clin Pathol. 2007;60:756–61.
Wang S, Wu X, Chen Y, et al. Prognostic and predictive role of JWA and XRCC1 expressions in gastric cancer. Clin Cancer Res. 2012;18:2987–96.
Lauren P. The two histological main types of gastric carcinoma: diffuse and so-called intestinal-type carcinoma. An attempt at a histo-clinical classification. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand. 1965;64:31–49.
Japanese Gastric Cancer A. Japanese classification of gastric carcinoma, 2nd English edition. Gastric Cancer. 1998;1:10–24.
Mackintosh KA, Fairclough SJ, Stratton G, et al. A calibration protocol for population-specific accelerometer cut-points in children. PLoS One. 2012;7:e36919.
Rodriguez-Vilarrupla A, Diaz C, Canela N, et al. Identification of the nuclear localization signal of p21(cip1) and consequences of its mutation on cell proliferation. FEBS Lett. 2002;531:319–23.
Wang S, Wu X, Zhang J, et al. CHIP functions as a novel suppressor of tumour angiogenesis with prognostic significance in human gastric cancer. Gut. 2013;62:496–508.
Shen L, Xu W, Li A, et al. JWA enhances As(2)O(3)-induced tubulin polymerization and apoptosis via p38 in HeLa and MCF-7 cells. Apoptosis. 2011;16:1177–93.
Heagerty PJ, Lumley T, Pepe MS. Time-dependent ROC curves for censored survival data and a diagnostic marker. Biometrics. 2000;56:337–44.
Cheng X, Xia W, Yang JY, et al. Activation of p21(CIP1/WAF1) in mammary epithelium accelerates mammary tumorigenesis and promotes lung metastasis. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2010;403:103–7.
Bang YJ, Van Cutsem E, Feyereislova A, et al. Trastuzumab in combination with chemotherapy versus chemotherapy alone for treatment of HER2-positive advanced gastric or gastro-oesophageal junction cancer (ToGA): a phase 3, open-label, randomised controlled trial. Lancet. 2010;376:687–97.
Marrelli D, Roviello F, De Stefano A, et al. Risk factors for liver metastases after curative surgical procedures for gastric cancer: a prospective study of 208 patients treated with surgical resection. J Am Coll Surg. 2004;198:51–8.
Mattioli E, Vogiatzi P, Sun A, et al. Immunohistochemical analysis of pRb2/p130, VEGF, EZH2, p53, p16(INK4A), p27(KIP1), p21(WAF1), Ki-67 expression patterns in gastric cancer. J Cell Physiol. 2007;210:183–91.
Zhou BP, Liao Y, Xia W, et al. Cytoplasmic localization of p21Cip1/WAF1 by Akt-induced phosphorylation in HER-2/neu-overexpressing cells. Nat Cell Biol. 2001;3:245–52.
Ma L, Young J, Prabhala H, et al. miR-9, a MYC/MYCN-activated microRNA, regulates E-cadherin and cancer metastasis. Nat Cell Biol. 2010;12:247–56.
Murata-Kamiya N, Kurashima Y, Teishikata Y, et al. Helicobacter pylori CagA interacts with E-cadherin and deregulates the beta-catenin signal that promotes intestinal transdifferentiation in gastric epithelial cells. Oncogene. 2007;26:4617–26.
Lilien J, Balsamo J. The regulation of cadherin-mediated adhesion by tyrosine phosphorylation/dephosphorylation of beta-catenin. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 2005;17:459–65.
Jung IM, Chung JK, Kim YA, et al. Epstein-Barr virus, beta-catenin, and E-cadherin in gastric carcinomas. J Korean Med Sci. 2007;22:855–61.
Zhang Y, Yan W, Jung YS, et al. PUMA cooperates with p21 to regulate mammary epithelial morphogenesis and epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition. PLoS One. 2013;8:e66464.
Acknowledgments
This project is supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (#81370078, #81001231, #81161120537, and #30930080), the Natural Science Foundation of Jiangsu Province (#BK2012840), the Postdoctoral Science Foundation of China (#20100481165), and the Priority Academic Program Development of Jiangsu Higher Education Institutions (Public Health and Preventive Medicine).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Y. Huang, W. Wang and Y. Chen contributed equally to this work.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Huang, Y., Wang, W., Chen, Y. et al. The opposite prognostic significance of nuclear and cytoplasmic p21 expression in resectable gastric cancer patients. J Gastroenterol 49, 1441–1452 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00535-013-0900-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00535-013-0900-4