Abstract
Background
The aim of this study was to investigate the efficacy of rikkunshito (RKT), a traditional Japanese medicine, combined with proton pump inhibitor (PPI) in patients with PPI-refractory non-erosive reflux disease (NERD).
Methods
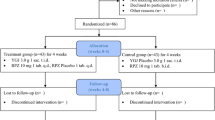
Patients with PPI-refractory NERD (n = 242) were randomly assigned to the RKT group [rabeprazole (10 mg/day) + RKT (7.5 g/t.i.d.) for 8 weeks] or the placebo group (rabeprazole + placebo). After the 4- and 8-week treatments, we assessed symptoms and quality of life (QOL) using the Frequency Scale for the Symptoms of Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease (FSSG), Gastrointestinal Symptom Rating Scale (GSRS), and Short-Form Health Survey-8 (SF-8).
Results
There were no significant differences in FSSG and GSRS score improvement between these groups after the 4- and 8-week treatments. The mental component summary (MCS) scores of the SF-8 improved more in the RKT group (from 45.8 ± 8.1 to 48.5 ± 7.4) than in the placebo group (from 47.7 ± 7.1 to 48.4 ± 7.5) after the 4-week treatment (P < 0.05). The 8-week treatment with RKT was more effective for improvement of the degree of MCS score in patients with a low body mass index (<22) (P < 0.05) and significantly improved the acid-related dysmotility symptoms of FSSG in female and elderly patients (≥65 years).
Conclusion
There were no significant differences in improvement of GERD symptoms in patients with PPI-refractory NERD between these groups. However, RKT may be useful for improving mental QOL in non-obese patients and acid-related dyspeptic symptoms, especially in women and the elderly.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Fujimoto K. Review article: prevalence and epidemiology of gastro-oesophageal reflux disease in Japan. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2004;20(Suppl 8):5–8.
Hiyama T, Yoshihara M, Tanaka S, Haruma K, Chayama K. Strategy for treatment of nonerosive reflux disease in Asia. World J Gastroenterol. 2008;14:3123–8.
Furukawa N, Iwakiri R, Koyama T, Okamoto K, Yoshida T, Kashiwagi Y, et al. Proportion of reflux esophagitis in 6,010 Japanese adults: prospective evaluation by endoscopy. J Gastroenterol. 1999;34:441–4.
Shimazu T, Matsui T, Furukawa K, Oshige K, Mitsuyasu T, Kiyomizu A, et al. A prospective study of the prevalence of gastroesophageal reflux disease and confounding factors. J Gastroenterol. 2005;40:866–72.
Mishima I, Adachi K, Arima N, Amano K, Takashima T, Moritani M, et al. Prevalence of endoscopically negative and positive gastroesophageal reflux disease in the Japanese. Scand J Gastroenterol. 2005;40:1005–9.
Fujiwara Y, Arakawa T. Epidemiology and clinical characteristics of GERD in the Japanese population. J Gastroenterol. 2009;44:518–34.
Vakil N, van Zanten SV, Kahrilas P, Dent J, Jones R, Global Consensus Group. The Montreal definition and classification of gastroesophageal reflux disease: a global evidence-based consensus. Am J Gastroenterol. 2006;101:1900–20.
Coté GA, Howden CW. Potential adverse effects of proton pump inhibitors. Curr Gastroenterol Rep. 2008;10:208–14.
Fass R. Proton-pump inhibitor therapy in patients with gastro-oesophageal reflux disease: putative mechanisms of failure. Drugs. 2007;67:1521–30.
Fass R, Shapiro M, Dekel R, Sewell J. Systematic review: proton pump inhibitor failure in gastro-oesophageal reflux disease. Where next? Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2005;22:79–94.
Hershcovici T, Fass R. Nonerosive reflux disease (NERD)—an update. J Neurogastroenterol Motil. 2010;16:8–21.
Holloway RH, Dent J, Narielval F, Mackinnon AM. Relation between oesophageal acid exposure and healing of oesophagitis with omeprazole in patients with severe reflux oesophagitis. Gut. 1996;38:649–54.
Futagami S, Iwakiri K, Shindo T, Kawagoe T, Horie A, Shimpuku M, et al. The prokinetic effect of mosapride citrate combined with omeprazole therapy improves clinical symptoms and gastric emptying in PPI-resistant NERD patients with delayed gastric emptying. J Gastroenterol. 2010;45:413–21.
Tominaga K, Arakawa T. Kampo medicines for gastrointestinal tract disorders: a review of basic science and clinical evidence and their future application. J Gastroenterol. 2013;48:452–62.
Hattori T, Fujitsuka N, Asakawa A, Inui A. A strategy using rikkunshito (Liu-Jun-Zi-Tang), a Japanese traditional medicine, to treat gastrointestinal disease. In: Satoh H, editor. Basics of evidences-based herbal medicine. Kerala: Research Signpost; 2010. p. 149–60.
Hayakawa T, Arakawa T, Kase Y, Akiyama S, Ishige A, Takeda S, et al. Liu-Jun-Zi-Tang, a kampo medicine, promotes adaptive relaxation in isolated guinea pig stomachs. Drugs Exp Clin Res. 1999;25:211–8.
Kido T, Nakai Y, Kase Y, Sakakibara I, Nomura M, Takeda S, et al. Effects of rikkunshi-to, a traditional Japanese medicine, on the delay of gastric emptying induced by N(G)-nitro-l-arginine. J Pharmacol Sci. 2005;98:161–7.
Tominaga K, Kido T, Ochi M, Sadakane C, Mase A, Okazaki H, et al. The traditional Japanese medicine rikkunshito promotes gastric emptying via the antagonistic action of the 5-HT3 receptor pathway in rats. eCAM. 2009:1–8. doi:10.1093/ecam/nep173.
Kawahara H, Kubota A, Hasegawa T, Okuyama H, Ueno T, Ida S, et al. Effects of rikkunshito on the clinical symptoms and esophageal acid exposure in children with symptomatic gastroesophageal reflux. Pediatr Surg Int. 2007;23:1001–5.
Tominaga K, Iwakiri R, Fujimoto K, Fujiwara Y, Tanaka M, Shimoyama Y, et al. Rikkunshito improves symptoms in PPI-refractory GERD patients: a prospective, randomized, multicenter trial in Japan. J Gastroenterol. 2012;47:284–92.
Kusano M, Shimoyama Y, Sugimoto S, Kawamura O, Maeda M, Minashi K, et al. Development and evaluation of FSSG; frequency scale for the symptoms of GERD. J Gastroenterol. 2004;39:888–91.
Muro Y, Sugiura K, Nitta Y, Mitsuma T, Hoshino K, Usuda T, et al. Scoring of reflux symptoms associated with scleroderma and the usefulness of rabeprazole. Clin Exp Rheumatol. 2009;27:15–21.
Fass R. Symptom assessment tools for gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) treatment. J Clin Gastroemterol. 2007;41:437–44.
Fujikawa Y, Tominaga K, Fujii H, Machida H, Okazaki H, Yamagami H, et al. High prevalence of gastroesophageal reflux symptoms in patients with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease associated with serum levels of triglyceride and cholesterol but not simple visceral obesity. Digestion. 2012;86:228–37.
Tominaga K, Higuchi K, Iketani T, Ochi M, Kadouchi K, Tanigawa T, et al. Comparison of gastrointestinal symptoms and psychological factors of functional dyspepsia to peptic ulcer or panic disorder patients. Inflammopharmacology. 2007;15:84–9.
Miwa H, Nagahara A, Tominaga K, Yokoyama T, Sawada Y, Inoue K, et al. Efficacy of the 5-HT1A agonist tandospirone citrate in improving symptoms of patients with functional dyspepsia: a randomized controlled trial. Am J Gastroenterol. 2009;104:2779–87.
Hill LD, Kozarek RA, Kraemer SJ, Aye RW, Mercer CD, Low DE, et al. The gastroesophageal flap valve: in vitro and in vivo observations. Gastrointest Endosc. 1996;44(5):541–7.
Dean BB, Gano AD Jr, Knight K, Ofman JJ, Fass R. Effectiveness of proton pump inhibitors in nonerosive reflux disease. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2004;2:656–64.
Hershcovici T, Fass R. Step-by-step management of refractory gastroesophageal reflux disease. Dis Esophagus. 2013;26:27–36.
Kaji M, Fujiwara Y, Shiba M, Kohata Y, Yamagami H, Tanigawa T, et al. Prevalence of overlaps between GERD, FD and IBS and impact on health-related quality of life. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2010;25:1151–6.
Kulig M, Leodolter A, Vieth M, Schulte E, Jaspersen D, Labenz J, et al. Quality of life in relation to symptoms in patients with gastro-oesophageal reflux disease—an analysis based on the ProGERD initiative. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2003;18:767–76.
Oh JH, Kim TS, Choi MG, Lee H, Jeon EJ, Choi SW, et al. Relationship between psychological factors and quality of life in subtypes of gastroesophageal reflux disease. Gut Liver. 2009;3:259–65.
Naito T, Itoh H, Takeyama M. Some gastrointestinal function regulatory Kampo medicines have modulatory effects on human plasma adrenocorticotropic hormone and cortisol levels with continual stress exposure. Biol Pharm Bull. 2003;26:101–4.
Sato Y, Katagiri F, Itoh H, Takeyama M. Effects of some kampo medicines on plasma levels of neuropeptide Y under venipuncture stress. Biol Pharm Bull. 2005;28:1757–61.
Fujitsuka N, Asakawa A, Uezono Y, Minami K, Yamaguchi T, Niijima A, et al. Potentiation of ghrelin signaling attenuates cancer anorexia-cachexia and prolongs survival. Transl Psychiatry. 2011;26:e23.
Shiratori M, Shoji T, Kanazawa M, Hongo M, Fukudo S. Effect of rikkunshito on gastric sensorimotor function under distention. Neurogastroenterol Motil. 2011;23:323–9.
Cremonini F, Ziogas DC, Chang HY, Kokkotou E, Kelley JM, Conboy L, et al. Meta-analysis: the effects of placebo treatment on gastrooesophageal reflux disease. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2010;32:29–42.
Hongo M. Epidemiology of FGID symptoms in Japanese general population with reference to life style. J Gastroenterol Hepatol Suppl. 2011;26:19–22.
Pehlivanov N, Liu J, Mittal R. Sustained esophageal contraction: a motor correlate of heartburn symptom. Am J Gastroenterol. 2001;281:743–51.
Xenos ES. The role of esophageal motility and hiatal hernia in esophageal exposure to acid. Surg Endosc. 2002;16:914–20.
Vela MF, Tutuian R, Katz PO, Castell DO. Baclofen decreases acid and non-acid post-prandial gastro-oesophageal reflux measured by combined multichannel intraluminal impedance and pH. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2003;17:243–51.
Fass R, Naliboff B, Higa L, Johnson C, Kodner A, Munakata J, et al. Differential effect of long-term esophageal acid exposure on mechanosensitivity and chemosensitivity in humans. Gastroenterology. 1998;115:1363–73.
Sifrim D, Mittal R, Fass R, Smout A, Castell D, Tack J, et al. Acidity and volume of the refluxate in the genesis of gastrooesophageal reflux disease symptoms. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2007;25:1003–15.
Miwa H, Minoo T, Hojo M, Yaginuma R, Nagahara A, Kawabe M, et al. Oesophageal hypersensitivity in Japanese patients with non-erosive gastro-oesophageal reflux diseases. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2004;20:112–7.
Sifrim D, Zerbib F. Diagnosis and management of patients with reflux symptoms refractory to proton pump inhibitors. Gut. 2012;61:1340–54.
Kusunoki H, Haruma K, Hata J, Ishii M, Kamada T, Yamashita N, et al. Efficacy of rikkunshito, a traditional Japanese medicine (Kampo), in treating functional dyspepsia. Intern Med. 2010;49:2195–202.
Miwa H, Koseki J, Oshima T, Kondo T, Tomita T, Watari J, et al. Rikkunshito, a traditional Japanese medicine, may relieve abdominal symptoms in rats with experimental esophagitis by improving the barrier function of epithelial cells in esophageal mucosa. J Gastroenterol. 2010;45:478–87.
Araki Y, Mukaisho KI, Fujiyama Y, Hattori T, Sugihara H. The herbal medicine rikkunshito exhibits strong and differential adsorption properties for bile salts. Exp Ther Med. 2012;3:645–9.
Takeda H, Sadakane C, Hattori T, Katsurada T, Ohkawara T, Nagai K, et al. Rikkunshito, an herbal medicine, suppresses cisplatin-induced anorexia in rats via 5-HT2 receptor antagonism. Gastroenterology. 2008;134:2004–13.
Nahata M, Muto S, Oridate N, Ohnishi S, Nakagawa K, Sadakane C, et al. Impaired ghrelin signaling is associated with gastrointestinal dysmotility in rats with gastroesophageal reflux disease. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2012;303:G42–53.
Takeda H, Muto S, Hattori T, Sadakane C, Tsuchiya K, Katsurada T, et al. Rikkunshito ameliorates the aging-associated decrease in ghrelin receptor reactivity via phosphodiesterase III inhibition. Endocrinology. 2010;151:244–52.
Acknowledgments
We thank the site investigators and Sogo Rinsho Holdings Co., Ltd, Tokyo, Japan for their participation in the present study. We are grateful to the G-PRIDE study group as described below for their contribution to this study. The G-PRIDE study group: Katsuhiro Mabe, Hokkaido University Hospital; Mineo Kudo, Sapporo Hokuyu Hospital; Hiroko Oizumi, Hokuyukai Kaisei Hospital; Kazunori Eto, Shuichi Muto, Tomakomai City Hospital; Shinya Serikawa, Jyun Sakamoto, Sapporo Higashi Tokushukai Hospital; Kaku Hokari, Keiyukai Sapporo Hospital; Hiroaki Nema, Nikko Memorial Hospital; Satoru Kakizaki, Gunma University Hospital; Tomohiro Kudo, Takasaki General Medical Center, Hideyuki Suzuki, Kazuhiro Takahashi, Haramachi Red Cross Hospital; Daisuke Asaoka, Mariko Hojyo, Jyuntendo University School of Medicine; Kenji Nakamura, Kengo Tokunaga, Kyorin University School of Medicine; Tomoaki Matsumura, Chiba University Graduate School of Medicine; Kenichi Nakajima, Tako Central Hospital; Mitsushige Sugimoto, Takanori Yamada, Hamamatsu University School of Medicine; Yasuhiko Maruyama, Masanobu Kageoka, Fujieda Municipal General Hospital; Naohito Shirai, Enshu Hospital; Makoto Kodaira, Yaizu City General Hospital; Testuya Tanigawa, Osaka City University Guraduate School of Medicine; Natsuhiko Kameda, Hironori Uno, Ohno Memorial Hospital; Koichiro Nakagawa, Higashisumiyoshi Morimoto Hospital; Masahiro Ochi, Meijibashi Hospital; Kenjiro Otani, Ryuta Oiso, Nagayoshi General Hospital; Kiyoshi Ashida, Hirosi Yamashita, Osaka Saiseikai Nakatsu Hospital; Masahiro Sakaguchi, Moriguchi Keijinkai Hospital; Sanomura Makoto, Shinya Kaseda, Hokusetsu General Hopital, Seikeikai Hospital; Masahiro Shiraki, Shinsei Hospital; Osamu Saito, Rapport Aoyama Second Hospital; Takashi Kondo, Toshihiko Tomita, Jiro Watari, Hirokazu Fukui; Takashi Abe, Jyunsuke Oku, Takarazuka City Hospital; Mitsuhiko Kawaguchi, Kawaguchi Medical Clinic; Kyoichi Adachi, Shimane University Faculty of Medicine; Yoshinori Komazawa, Mika Yuki, Izumo City General Medical Center; Tomoo Fujisawa, Yoshinori Kushiyama, Erina Kakuta, Matsue Red Cross Hospital; Youichi Miyaoka, Yoshiya Morito, Shimane Prefectural Central Hospital; Koichiro Furuta, Masuda Medical Association Hospital; Yuichiro Eguchi, Shigetaka Kuroki, Eguchi Hospital; Seiji Tsunada, Ureshino Medical Center; Shinichi Ogata, Saga Prefectural Hospital Koseikan; Kohei Yamanouchi, Imari Arita Kyoritsu Hospital; Takahiro Noda, Nanae Tsuruoka, Karatsu Red Cross Hospital; Kiwamu Hasuda, Hattori Gastrointestinal Clinic; Yasushi Oda, Oda Gastrointestinal Clinic; Testuya Murao, Kumamoto Medical Center; Seiji Shiota, Oita University Faculty of Medicine; Hisanori Abe, Arita Gastrointestinal Hospital; Shigeaki Yasaka, Health Insurance Nankai Hospital; Fuminao Takeshima, Nagasaki University Graduate School of Biomedical Sciences.
Financial support for this study was provided by the Waksman Foundation of Japan INC., which has no commercial interest in RKT.
Conflict of interest
Some authors have received research grants, respectively: Mototsugu Kato from Otsuka Pharmaceutical Co. Ltd., Takeda Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd., AstraZeneca KK., Ltd., Astellas Pharma Inc., and Daiichi-Sankyo Co., Ltd.; Hiroshi Takeda from Tsumura & Co. Ltd., Eiji Umegaki from Takeda Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd.; Akihito Nagahara from Daiichi-Sankyo Co., Ltd.; Katsuhiko Iwakiri from Takeda Pharmaceutical Co.; Yoshikazu Kinoshita has served in speaking and teaching commitments for AstraZeneca KK, Takeda Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd., Astellas Pharma Inc., Eisai Co., Ltd., Taiho Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd., Daiichi-Sankyo, and MSD; ST from Eisai Co., Ltd.; Sumio Watanabe from AstraZeneca Inc., Eisai Co., Ltd., and Takeda Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd.; Kazuhide Higuchi from AstraZeneca KK, Otsuka Pharmaceutical Co. Ltd., Eisai Co., Ltd., Daiichi-Sankyo Co. Ltd., and Nippon-Shinyaku Co. Ltd.; Motoyasu Kusano from Eisai Co., Ltd.; Kazuma Fujimoto from Eisai Co., Ltd., AstraZeneca KK., and Daiichi-Sankyo Co. Ltd.; Tetsuo Arakawa from Eisai Co., Ltd., Daiichi-Sankyo Co. Ltd., and Otsuka Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd. The Center for Clinical Research at Hamamatsu University School of Medicine has received grants from Takeda Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd., AstraZeneca KK, Eisai Co., Ltd., and Daiichi-Sankyo Co. Ltd., and Takahisa Furuta has received lecture fees from those companies. The Division of Upper Gastroenterology, Department of Internal Medicine at Hyogo College of Medicine has received grants from AstraZeneca KK, Astellas Pharma Inc., Otsuka Pharmaceutical Co. Ltd., Eisai Co., Ltd., Tsumura & Co. Ltd., Dainippon Sumitomo Pharma Co. Ltd., Yakult Co. Ltd., and Takeda Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd. The following people have nothing to declare: Kazunari Tominaga, Yasuyuki Shimoyama, Ryuichi Iwakiri, Kenji Furuta, Koichi Sakurai, Takeo Odaka, Hiroaki Kusunoki, Kazunari Murakami, and Ken Haruma.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Consortia
Corresponding author
Additional information
K. Tominaga, M. Kato, H. Takeda, Y. Shimoyama, E. Umegaki, and R. Iwakiri contributed equally to this work.
ClinicalTrials.gov, Number UMIN000005880.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tominaga, K., Kato, M., Takeda, H. et al. A randomized, placebo-controlled, double-blind clinical trial of rikkunshito for patients with non-erosive reflux disease refractory to proton-pump inhibitor: the G-PRIDE study. J Gastroenterol 49, 1392–1405 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00535-013-0896-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00535-013-0896-9