Abstract
Background
Renal dysfunction and Fanconi’s syndrome associated with hypophosphatemia caused by long-term administration of low-dose adefovir dipivoxil (ADV) has been reported in recent years. The aim of this retrospective study was to determine the incidence and factors associated with renal dysfunction and hypophosphatemia in patients with hepatitis B infection on long-term treatment with ADV and lamivudine (LAM).
Methods
The study subjects were 292 patients treated with 10 mg/day ADV and 100 mg/day LAM for more than 6 months. We evaluated estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR), serum creatinine and serum phosphate level at the start of ADV and every 6 months.
Result
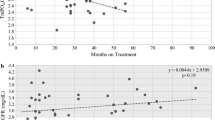
During a median treatment duration of 64 months, 28 (9.6 %) patients developed renal impairment (defined as eGFR < 50 ml/min/1.73 m2), and 73 (27.1 %) developed hypophosphatemia, including 14 with persistent hypophosphatemia. The cumulative incidences of renal impairment at 1, 3, and 5 years were 1.4, 7.5, 10.5 %, respectively, and those of hypophosphatemia were 6.8, 20.6, 26.7 %, respectively. Multivariate analysis identified old age, liver cirrhosis and hypertension as determinants of renal impairment, and male sex, HCC, low baseline serum phosphate as determinants of hypophosphatemia. Three of the 14 patients with persistent hypophosphatemia developed Fanconi’s syndrome; their serum creatinine level remained normal, but eGFR was lower than at baseline.
Conclusion
Long-term treatment of hepatitis B with low-dose (10 mg/day) ADV and LAM can potentially cause renal impairment and hypophosphatemia. We advocate regular monitoring of serum phosphate and evaluation of eGFR, in addition to serum creatinine, in such patients.




Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- ALT:
-
Alanine aminotransferase
- AST:
-
Aspartate aminotransferase
- BMI:
-
Body mass index
- CHB:
-
Chronic hepatitis B
- CHBI:
-
Chronic hepatitis B infection
- CI:
-
Confidence interval
- eGFR:
-
Estimated glomerular filtration rate
- HBeAg:
-
Hepatitis B e antigen
- HBsAg:
-
Hepatitis B surface antigen
- HBV:
-
Hepatitis B virus
- HCC:
-
Hepatocellular carcinoma
- IFN:
-
Interferon
- IP:
-
Inorganic phosphate
- LC:
-
Liver cirrhosis
References
Lee WM, Hepatitis B. Virus infection. N Engl J Med. 1997;337:1733–45.
Dienstag JL, Hepatitis B. Virus infection. N Engl J Med. 2008;359:1486–500.
Lai C-L, Chien R-N, Leung NWY, Chang TT, Guan R, Tai D-I, et al. A one-year trial of lamivudine for chronic hepatitis B. N Engl J Med. 1998;339:61–8.
Chen CH, Lee CM, Lu SN, Wang JH, Tung HD, Hung CH, et al. Comparison of clinical outcome between patients continuing and discontinuing lamivudine therapy after biochemical breakthrough of YMDD mutants. J Hepatol. 2004;41:454–61.
Suzuki F, Suzuki Y, Tsubota A, Akuta N, Someya T, Kobayashi M, et al. Mutations of polymerase, precore and core promoter gene in hepatitis B virus during 5-year lamivudine therapy. J Hepatol. 2002;37:824–30.
Suzuki F, Tsubota A, Arase Y, Suzuki Y, Akuta N, Hosaka T, et al. Efficacy of lamivudine therapy and factors associated with emergence ofresistance in chronic hepatitis B virus infection in Japan. Intervirology. 2003;46:182–9.
Hashimoto Y, Suzuki F, Hirakawa M, Kawamura Y, Yatsuji H, Sezaki H, et al. Clinical and virological effects of long-term (over 5 years) lamivudine therapy. J Med Virol. 2010;82:684–91.
Peters MG, Hann HH, Martin P, Heathcote EJ, Buggisch P, Rubin R, et al. Adefovir dipivoxil alone or in combination with lamivudine in patients with lamivudine-resistant chronic hepatitis B. Gastroenterology. 2004;126:91–101.
Hosaka T, Suzuki F, Suzuki Y, Saitoh S, Kobayashi M, Someya T, Sezaki H, Akuta N, Arase Y, Ikeda K, Kumada H. Factors associated with the virological response of lamivudine-resistant hepatitis B virus during combination therapy with adefovir dipivoxil plus lamivudine. J Gastroenterol. 2007;42:368–74.
Rapti I, Dimou E, Mitsoula P, Hadziyannis SJ. Adding-on versus switching-to adefovir therapy in lamivudine-resistant HBeAg-negative chronic hepatitis B. Hepatology. 2007;45:307–13.
Kumada H, Okanoue T, Onji M, Moriwaki H, Izumi N, Tanaka E, et al. Guidelines for the treatment of chronic hepatitis and cirrhosis due to hepatitis B virus infection for the fiscal year 2008 in Japan. Hepatol Res. 2010;40:1–7.
Izzedine H, Hulot JS, Launay-Vacher V, Marcellini P, Hadziyannis SJ, Currie G, et al. Renal safety of adefovir dipivoxil in patients with chronic hepatitis B: two double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled studies. Kidney Int. 2004;66:1153–8.
Ha NB, Ha NB, Garcia RT, Trinh HN, Vu AA, Nguyen HA, et al. Renal dysfunction in chronic hepatitis B patients treated with adefovir dipivoxil. Hepatology. 2009;50:727–34.
Tamori A, Enomoto M, Kobayashi S, Iwai S, Morikawa H, Sakaguchi H, et al. Add-on combination therapy with adefovir dipivoxil induces renal impairment in patients with lamivudine-refractory hepatitis B virus. J Viral Hepat. 2010;17:123–9.
Kim YJ, Cho HC, Sinn DH, Gwak GY, Choi MS, Koh KC, et al. Frequency and risk factors of renal impairment during long-term adefovir dipivoxil treatment in chronic hepatitis B patients. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2012;27:306–12.
Jung YK, Yeon JE, Choi JH, Kim CH, Jung ES, Kim JH, et al. Fanconi’s syndrome associated with prolonged adefovir dipivoxil therapy in a hepatitis B virus patient. Gut Liver. 2010;4:389–93.
Law ST, Li KK, Ho YY. Nephrotoxicity, including acquired Fanconi’s syndrome, caused by adefovir dipivoxil—is there a safe dose? J Clin Pharm Ther. 2012;37:128–31.
Izzedine H, Launay-Vacher V, Isnard-Bagnis C, Deray G. Drug-induced Fanconi’s syndrome. Am J Kidney Dis. 2003;41:292–309.
Cihlar T, Ho ES, Lin DC, Mulato AS. Human renal organic anion transporter 1 (hOAT1) and its role in the nephrotoxicity of antiviral nucleotide analogs. Nucleosides, Nucleotides Nucleic Acids. 2001;20:641–8.
Marcellin P, Chang TT, Lim SG, Tong MJ, Sievert W, Shiffman ML, et al. Adefovir dipivoxil for the treatment of hepatitis B e antigen-positive chronic hepatitis B. N Engl J Med. 2003;348:808–16.
Davies DF, Shock NW. Age changes in glomerular filtration rate, effective renal plasma flow, and tubular excretory capacity in adult males. J Clin Invest. 1950;29:496–507.
Lewis WH, Alvey AS. Changes with age in the renal function in adult men. I. Clearance of urea. Am J Physiol. 1938;123:500–15.
Wollom GL, Gifford RW. The kidney as a target organ in hypertension. Geriatrics. 1976;31:71–9.
Lindeman RD, Tobin JD, Shock NW. Association between blood pressure and the rate of decline in renal function with age. Kidney Int. 1984;26:861–8.
Dronavalli S, Duka I, Bakris GL. The pathogenesis of diabetic nephropathy. Nat Clin Pract Endocrinol Metab. 2008;4:444–52.
Ginès P, Schrier RW. Renal failure in cirrhosis. N Engl J Med. 2009;361:1279–90.
Kahn J, Lagakos S, Wulfsohn M, Cherng D, Miller M, Cherrington J, et al. Efficacy and safety of adefovir dipivoxil with antiretroviral therapy: a randomized controlled trial. JAMA. 1999;282:2305–12.
Hadziyannis SJ, Tassopoulos NC, Heathcote EJ, Chang TT, Kitis G, Rizzetto M, et al. Long-term therapy with adefovir dipivoxil for HBeAg-negative chronic hepatitis B. N Engl J Med. 2005;352:2673–81.
Gara N, Zhao X, Collins MT, Chong WH, Kleiner DE, Jake Liang T, et al. Renal tubular dysfunction during long-term adefovir or tenofovir therapy in chronic hepatitis B. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2012;35:1317–25.
Amanzadeh J, Jr. Reilly RF. Hypophosphatemia: an evidence-based approach to its clinical consequences and management. Nat Clin Pract Nephrol. 2006;2:136–48.
Bushinsky DA, Monk RD. Electrolyte quintet: calcium. Lancet. 1998;352:306–11.
Weisinger JR, Bellorín-Font E. Magnesium and phosphorus. Lancet. 1998;352:391–6.
Cirillo M, Ciacci C, De Santo NG. Age, renal tubular phosphate reabsorption, and serum phosphate levels in adults. N Engl J Med. 2008;359:864–6.
Izzedine H, Launay-Vacher V, Isnard-Bagnis C, Deray G. Drug-induced Fanconi’s syndrome. Am J Kidney Dis. 2003;41:292–309.
Kim DH, Sung DH, Min YK. Hypophosphatemic osteomalacia induced by low-dose adefovir therapy: focus on manifestations in the skeletal system and literature review. J Bone Miner Metab. 2012;14.
Carpenter TO. The expanding family of hypophosphatemic syndromes. J Bone Miner Metab. 2012;30:1–9.
Laing CM, Toye AM, Capasso G, Unwin RJ. Renal tubular acidosis: developments in our understanding of the molecular basis. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2005;37:1151–61.
Clarke BL, Wynne AG, Wilson DM, Fitzpatrick LA. Osteomalacia associated with adult Fanconi’s syndrome: clinical and diagnostic features. Clin Endocrinol. 1995;43:479–90.
Wong T, Girgis CM, Ngu MC, Chen RC, Emmett L, Archer KA, et al. Hypophosphatemic osteomalacia after low-dose adefovir dipivoxil therapy for hepatitis B. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2010;95:479–80.
Girgis CM, Wong T, Ngu MC, Emmett L, Archer KA, Chen RC, Seibel MJ. Hypophosphataemic osteomalacia in patients on adefovir dipivoxil. J Clin Gastroenterol. 2011;45:468–73.
Kim DH, Sung DH, Min YK. Hypophosphatemic osteomalacia induced by low-dose adefovir therapy: focus on manifestations in the skeletal system and literature review. J Bone Miner Metab. 2012; Epub ahead of print.
Ozeki I, Karino Y, Akaike J, Kimura R, Arakawa T, Nakashima T, et al. Renal dysfunction in chronic hepatitis B patients treated with adefovir dipivoxil. Kanzo. 2011;52:102–11.
Acknowledgments
This study was supported in part by a Grant-in-aid from the Ministry of Health, Labor and Welfare of Japan.
Conflict of interest
None.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tanaka, M., Suzuki, F., Seko, Y. et al. Renal dysfunction and hypophosphatemia during long-term lamivudine plus adefovir dipivoxil therapy in patients with chronic hepatitis B. J Gastroenterol 49, 470–480 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00535-013-0779-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00535-013-0779-0