Abstract
Background
MicroRNAs can promote or suppress the evolution of malignant behaviors by regulating multiple targets. We aimed to determine the expression of miR-301a recently screened in gastric cancer, to investigate the biological effects of miR-301a and to identify the specific miR-301a target gene.
Methods
Quantitative real-time RT-PCR was used to test miR-301a expression. Functional effects were explored by a water-soluble tetrazolium salt assay, a colony formation assay in soft agar, a migration assay, an invasion assay and cytometry used to determine apoptosis and cell cycle. Nude mice were inoculated subcutaneously by retrovirus-mediated stably expressed SGC-7901 cells. The target gene was determined by bioinformatic algorithms, dual luciferase reporter assay and Western blot.
Results
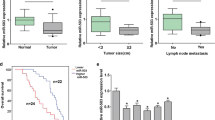
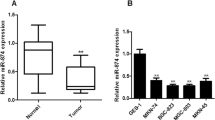
Firstly, we found that miR-301a was significantly upregulated both in cells and tissues of gastric cancer. The expression level of miR-301a was inversely correlated with tumor differentiation of gastric cancer tissues. Secondly, miR-301a promoted cell growth, soft agar clonogenicity, migration, invasion, and decreased cell apoptosis induced by cisplatin in vitro, while blockage of miR-301a reduced the percentage of G2/M phase cells via flow cytometry in gastric cancer cells. Ectopic expression of miR-301a enhanced the subcutaneous tumorigenesis in vivo. Finally, miR-301a directly downregulated RUNX3 expression post-transcriptionally in gastric cancer.
Conclusion
Our results demonstrate that miR-301a plays important roles in the development of gastric cancer.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Jemal A, Bray F, Center MM, Ferlay J, Ward E, Forman D. Global cancer statistics. CA Cancer J Clin. 2011;61:69–90.
Stock M, Otto F. Gene deregulation in gastric cancer. Gene. 2005;360:1–19.
Yasui W, Yokozaki H, Fujimoto J, Naka K, Kuniyasu H, Tahara E. Genetic and epigenetic alterations in multistep carcinogenesis of the stomach. J Gastroenterol. 2000;35(Suppl 12):111–5.
Ambros V. The functions of animal microRNAs. Nature. 2004;431:350–5.
Bartel DP. MicroRNAs: genomics, biogenesis, mechanism, and function. Cell. 2004;116:281–97.
Pasquinelli AE, Hunter S, Bracht J. MicroRNAs: a developing story. Curr Opin Genet Dev. 2005;15:200–5.
Ahmed FE. Role of miRNA in carcinogenesis and biomarker selection: a methodological view. Expert Rev Mol Diagn. 2007;7:569–603.
Michael MZ, O’Connor SM, van Holst Pellekaan NG, Young GP, James RJ. Reduced accumulation of specific microRNAs in colorectal neoplasia. Mol Cancer Res. 2003;1:882–91.
Cummins JM, He Y, Leary RJ, Pagliarini R, Diaz LA Jr, Sjoblom T, et al. The colorectal microRNAome. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2006;103:3687–92.
Calin GA, Liu CG, Sevignani C, Ferracin M, Felli N, Dumitru CD, et al. MicroRNA profiling reveals distinct signatures in B cell chronic lymphocytic leukemias. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2004;101:11755–60.
Iorio MV, Ferracin M, Liu CG, Veronese A, Spizzo R, Sabbioni S, et al. MicroRNA gene expression deregulation in human breast cancer. Cancer Res. 2005;65:7065–70.
Yanaihara N, Caplen N, Bowman E, Seike M, Kumamoto K, Yi M, et al. Unique microRNA molecular profiles in lung cancer diagnosis and prognosis. Cancer Cell. 2006;9:189–98.
Pallante P, Visone R, Ferracin M, Ferraro A, Berlingieri MT, Troncone G, et al. MicroRNA deregulation in human thyroid papillary carcinomas. Endocr Relat Cancer. 2006;13:497–508.
Murakami Y, Yasuda T, Saigo K, Urashima T, Toyoda H, Okanoue T, et al. Comprehensive analysis of microRNA expression patterns in hepatocellular carcinoma and non-tumorous tissues. Oncogene. 2006;25:2537–45.
Jiang J, Gusev Y, Aderca I, Mettler TA, Nagorney DM, Brackett DJ, et al. Association of MicroRNA expression in hepatocellular carcinomas with hepatitis infection, cirrhosis, and patient survival. Clin Cancer Res. 2008;14:419–27.
Lee EJ, Gusev Y, Jiang J, Nuovo GJ, Lerner MR, Frankel WL, et al. Expression profiling identifies microRNA signature in pancreatic cancer. Int J Cancer. 2007;120:1046–54.
Miko E, Czimmerer Z, Csanky E, Boros G, Buslig J, Dezso B, et al. Differentially expressed microRNAs in small cell lung cancer. Exp Lung Res. 2009;35:646–64.
Hanisch A, Sillje HH, Nigg EA. Timely anaphase onset requires a novel spindle and kinetochore complex comprising Ska1 and Ska2. EMBO J. 2006;25:5504–15.
Yano T, Ito K, Fukamachi H, Chi XZ, Wee H. The RUNX3 tumor suppressor upregulates Bim in gastric epithelial cells undergoing transforming growth factor beta-induced apoptosis. Mol Cell Biol. 2006;26:4474–88.
Chen Y, Wei X, Guo C, Jin H, Han Z, Han Y, et al. Runx3 suppresses gastric cancer metastasis through inactivation of MMP9 by upregulation of TIMP-1. Int J Cancer. 2011;129:1586–98.
Cao G, Huang B, Liu Z, Zhang J, Xu H, Xia W, et al. Intronic miR-301 feedback regulates its host gene, ska2, in A549 cells by targeting MEOX2 to affect ERK/CREB pathways. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2010;396:978–82.
Calin GA, Dumitru CD, Shimizu M, Bichi R, Zupo S, Noch E, et al. Frequent deletions and down-regulation of micro- RNA genes miR15 and miR16 at 13q14 in chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2002;99:15524–9.
Metzler M, Wilda M, Busch K, Viehmann S, Borkhardt A. High expression of precursor microRNA-155/BIC RNA in children with Burkitt lymphoma. Genes Chromosom Cancer. 2004;39:167–9.
Eis PS, Tam W, Sun L, Chadburn A, Li Z, Gomez MF, et al. Accumulation of miR-155 and BIC RNA in human B cell lymphomas. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2005;102:3627–32.
Lu J, Getz G, Miska EA, Alvarez-Saavedra E, Lamb J, Peck D, et al. MicroRNA expression profiles classify human cancers. Nature. 2005;435:834–8.
Volinia S, Calin GA, Liu CG, Ambs S, Cimmino A, Petrocca F, et al. A microRNA expression signature of human solid tumors defines cancer gene targets. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2006;103:2257–61.
Shi W, Gerster K, Alajez NM, Tsang J, Waldron L, Pintilie M, et al. MicroRNA-301 mediates proliferation and invasion in human breast cancer. Cancer Res. 2011;71:2926–37.
Lu Z, Li Y, Takwi A, Li B, Zhang J, Conklin DJ, et al. miR-301a as an NF-kappaB activator in pancreatic cancer cells. EMBO J. 2011;30:57–67.
Fukamachi H, Mimata A, Tanaka I, Ito K, Ito Y, Yuasa Y. In vitro differentiation of Runx3−/− p53−/− gastric epithelial cells into intestinal type cells. Cancer Sci. 2008;99:671–6.
Lai KW, Koh KX, Loh M, Tada K, Subramaniam MM, Lim XY, et al. MicroRNA-130b regulates the tumour suppressor RUNX3 in gastric cancer. Eur J Cancer. 2010;46:1456–63.
Wei D, Gong W, Oh SC, Li Q, Kim WD, Wang L, et al. Loss of RUNX3 expression significantly affects the clinical outcome of gastric cancer patients and its restoration causes drastic suppression of tumor growth and metastasis. Cancer Res. 2005;65:4809–16.
Li QL, Ito K, Sakakura C, Fukamachi H, Inoue K, Chi XZ, et al. Causal relationship between the loss of RUNX3 expression and gastric cancer. Cell. 2002;109:113–24.
Fukamachi H, Ito K, Ito Y. Runx3−/− gastric epithelial cells differentiate into intestinal type cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2004;321:58–64.
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by grants from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 30872476, No. 30900670, No. 81101585, No. 91229106 and No. 81172324), and Science and Technology Commission of Shanghai Municipality (No. 12XD1403700, and No. 12PJ1406300).
Conflict of interest
None declared.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
535_2012_733_MOESM2_ESM.tif
S2 The miR-301a expression in SGC-7901 cells was effectively altered by transient transfection of miR-301a (miR-301a mimics) as detected by RT-PCR. U6 snRNA was used for normalization. (TIFF 429 kb)
535_2012_733_MOESM3_ESM.tif
S3 The miR-301a expression in SGC-7901 cells was effectively altered by transient transfection of anti-miR-301a (miR-301a inhibitors) as detected by RT-PCR. (TIFF 434 kb)
535_2012_733_MOESM6_ESM.tif
S6 RUNX3 mRNA expression in SGC-7901 cells was analyzed by qRT-PCR 48 h post-transfection with miR-301a precursor and control precursor (100 nM). The results was shown as fold change relative to the control precursor-transfected SGC-7901 cells. (TIFF 541 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, M., Li, C., Yu, B. et al. Overexpressed miR-301a promotes cell proliferation and invasion by targeting RUNX3 in gastric cancer. J Gastroenterol 48, 1023–1033 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00535-012-0733-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00535-012-0733-6