Abstract
Background
T follicular helper (TFH) cells are a subpopulation of T-helper cells which regulate humoral immune responses. The role of TFH cells in viral infection is unclear. This study examined the possible involvement of CD4+CXCR5+ TFH cells in chronic hepatitis C (HCV) infection.
Methods
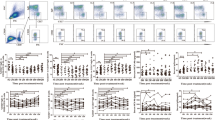
The percentages of peripheral blood CD4+CXCR5+ TFH cells, inducible T-cell costimulator cells, and/or programmed death 1-positive CD4+CXCR5+ TFH cells in 39 HCV-infected patients, 12 patients with spontaneously resolved HCV infection (SR-HCV), and 12 healthy controls were characterized by flow cytometry analysis. The subjects’ serum HCV RNA loads and alanine aminotransferase and aspartate aminotransferase levels were measured. The potential association of the percentage of peripheral CD4+CXCR5+ TFH cells with clinical data was analyzed.
Results
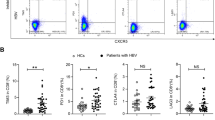
Higher percentages of peripheral blood CD4+CXCR5+ TFH cells were found in SR-HCV and HCV-infected patients as compared with healthy controls. Interestingly, a statistically significant negative correlation was found between the percentage of CD4+CXCR5+ TFH cells and the HCV RNA load.
Conclusions
These data suggest that CD4+CXCR5+ TFH cells may participate in HCV-related immune responses. Increased TFH cells in peripheral blood may help to control HCV infection.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ashfaq UA, Javed T, Rehman S, Nawaz Z, Riazuddin S. An overview of HCV molecular biology, replication and immune responses. Virol J. 2011;8:161.
Raja NS, Janjua KA. Epidemiology of hepatitis C virus infection in Pakistan. J Microbiol Immunol Infect. 2008;41:4–8.
Berenguer M, Lopez-Labrador FX, Wright TL. Hepatitis C and liver transplantation. J Hepatol. 2001;35:666–78.
Ciborowski P, Gendelman HE. Human immunodeficiency virus-mononuclear phagocyte interactions: emerging avenues of biomarker discovery, modes of viral persistence and disease pathogenesis. Curr HIV Res. 2006;4:279–91.
Rehermann B. Chronic infections with hepatotropic viruses: mechanisms of impairment of cellular immune responses. Semin Liver Dis. 2007;27:152–60.
Pawlotsky JM. Diagnostic tests for hepatitis C. J Hepatol. 1999;31:71–9.
Cramp ME, Carucci P, Rossol S, Chokshi S, Maertens G, Williams R, et al. Hepatitis C virus (HCV) specific immune responses in anti-HCV positive patients without hepatitis C viraemia. Gut. 1999;44:424–9.
Koziel MJ, Wong DK, Dudley D, Houghton M, Walker BD. Hepatitis C virus-specific cytolytic T lymphocyte and T helper cell responses in seronegative persons. J Infect Dis. 1997;176:859–66.
Pelletier N, McHeyzer-Williams LJ, Wong KA, Urich E, Fazilleau N, McHeyzer-Williams MG. Plasma cells negatively regulate the follicular helper T cell program. Nat Immunol. 2010;11:1110–8.
Laurent C, Fazilleau N, Brousset P. A novel subset of T-helper cells: follicular T-helper cells and their markers. Haematologica. 2010;95:356–8.
Linterman MA, Vinuesa CG. Signals that influence T follicular helper cell differentiation and function. Semin Immunopathol. 2010;32:183–96.
Zhang CM, Zhang B, Zhang Y, Xu ZW, Yang K, Yang AG, et al. Identification of human follicular helper T cells in peripheral blood by flow cytometry. Chin J Cell Mol Immunol. 2009;25:1063–4.
Rodríguez Pinilla SM, Roncador G, Rodríguez-Peralto JL, Mollejo M, García JF, Montes-Moreno S, et al. Primary cutaneous CD4+ small/medium-sized pleomorphic t-cell lymphoma expresses follicular T-cell markers. Am J Surg Pathol. 2009;33:81–90.
Simpson N, Gatenby PA, Wilson A, Malik S, Fulcher DA, Tangye SG, et al. Expansion of circulating T cells resembling follicular helper T cells is a fixed phenotype that identifies a subset of severe systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheum. 2010;62:234–44.
Rodríguez-Pinilla SM, Atienza L, Murillo C, Pérez-Rodríguez A, Montes-Moreno S, Roncador G, et al. Peripheral T-cell lymphoma with follicular T-cell markers. Am J Surg Pathol. 2008;32:1787–99.
Feng JY, Lu L, Hua C, Qin L, Zhao PW, Wang J, et al. High frequency of CD4+CXCR5+TFH cells in patients with immune-active chronic hepatitis B. PLoS ONE. 2011;6(7):e21698.
Sarasin-Filipowicz M. Interferon therapy of hepatitis C: molecular insights into success and failure. Swiss Med Wkly. 2010;140:3–11.
Sherman M, Shafran S, Burak K, Doucette K, Wong W, Girgrah N, et al. Management of chronic hepatitis C: consensus guidelines. Can J Gastroenterol. 2007;21:25C–34C.
Jiang Y, Ma Z, Xin G, Yan H, Li W, Xu H, et al. Th1 and Th2 immune response in chronic hepatitis B patients during a long-term treatment with adefovir dipivoxil. Mediat Inflamm. 2010:143026.
Oliviero B, Cerino A, Varchetta S, Paudice E, Pai S, Ludovisi S, et al. Enhanced B-cell differentiation and reduced proliferative capacity in chronic hepatitis C and chronic hepatitis B virus infections. J Hepatol. 2011;55:53–60.
Shepard CW, Finelli L, Alter MJ. Global epidemiology of hepatitis C virus infection. Lancet Infect Dis. 2005;190:558–67.
Sallusto F, Geginat J, Lanzavecchia A. Central memory and effector memory T cell subsets: function, generation, and maintenance. Annu Rev Immunol. 2004;22:745–63.
Kim CH, Rott LS, Clark-Lewis I, Campbell DJ, Wu L, Butcher EC. Subspecialization of CXCR5+ T Cells: B helper activity is focused in a germinal center–localized subset of CXCR5+ T Cells. J Exp Med. 2001;193:1373–81.
Bustin LB, Rice CM. Flying under the radar: the immunobiology of hepatitis C. Annu Rev Immunol. 2007;25:71–99.
Dong C, Juedes AE, Temann UA, Shresta S, Allison JP, Ruddle NH, et al. ICOS co-stimulatory receptor is essential for T cell activation and function. Nature. 2001;409:97–101.
Nurieva RI, Chung Y, Hwang D, Yang XO, Kang HS, Ma L, et al. Generation of T follicular helper cells is mediated by interleukin 21 but independent of T helper 1, 2, or 17 cell lineages. Immunity. 2008;29:138–49.
Ye P, Weng ZH, Zhang SL, Zhang JA, Zhao L, Dong JH, et al. Programmed death-1 expression is associated with the disease status in hepatitis B virus infection. World J Gastroenterol. 2008;14:4551–7.
Acknowledgments
This work is supported by grants from the National Natural Science Foundation of China. (No. 30972610), Jilin Province Science and Technology Agency (No. 200705128 and 20110716), the Chinese Medical Science and Technology Projects of Jilin Province (08sys-086), The Health Department Research Projects in Jilin Province (2009Z054), and Cutting-edge Science and Interdisciplinary Innovation Projects of Jilin University.
Conflict of interest
The authors state that they have no conflicts of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
J. Feng and X. Hu made equal contributions to this study.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Feng, J., Hu, X., Guo, H. et al. Patients with chronic hepatitis C express a high percentage of CD4+CXCR5+ T follicular helper cells. J Gastroenterol 47, 1048–1056 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00535-012-0568-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00535-012-0568-1