Abstract
Background
Gastric cancer is a worldwide cancer with poor prognosis. Identification of diagnostic biomarkers and effective therapeutic targets is important in the treatment and diagnosis of gastric cancer. Recently, researchers have found that microRNAs play several important roles in carcinogenesis. The purpose of this study was to investigate the relationships between miR-421 expression patterns in human gastric cancer tissues with clinicopathological features.
Methods
Sixty gastric carcinoma and 18 non-tumor tissues were collected from the Secondary Hospital of Ningbo, China. For quantitative detection of the expression level of miR-421, total RNA was extracted and then reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction was performed. The relationship between miR-421 expression in gastric cancer and clinicopathological features was analyzed. After miR-421 inhibitor was transfected into gastric cancer cells, cell growth was measured by MTT assay. Finally, the expression of its target genes was detected by Western blotting.
Results
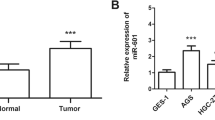
The miR-421 was over-expressed in 73.33% (44/60) of the gastric cancer samples examined. Over-expression of miR-421 in gastric cancer tissues was not found associated with clinicopathological features. The positive detection rate of miR-421 was higher than that of serum carcino-embryonic antigen (χ2 = 39.811, P < 0.001). Inhibition of miR-421 expression decreased the growth of both MGC-803 and SGC-7901 gastric cancer cells in vitro, with up-regulating the expression of its cancer-related target genes, CBX7 and RBMXL1.
Conclusions
miR-421 may involve in the early stage of stomach carcinogenesis and could be used as an efficient diagnostic biomarker.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bartel DP. MicroRNAs: genomics, biogenesis, mechanism, and function. Cell. 2004;116:281–97.
Brennecke J, Hipfner DR, Stark A, Russell RB, Cohen SM. Bantam encodes a developmentally regulated microRNA that controls cell proliferation and regulated the proapoptotic gene hid in Drosophila. Cell. 2003;113:25–36.
Chan JA, Krichevsky AM, Kosik KS. MicroRNA-21 is an antiapoptotic factor in human glioblastoma cells. Cancer Res. 2005;65:6029–33.
Xu P, Vernooy SY, Guo M, Hay BA. The Drosophila microRNA Mir-14 suppresses cell death and is required for normal fat metabolism. Curr Biol. 2003;13:790–5.
Lee RC, Feinbaum RL, Ambros V. The C. elegans heterochronic gene lin-4 encodes small RNAs with antisense complementarity to lin-14. Cell. 1993;75:843–54.
Wightman B, Ha I, Ruvkun G. Posttranscriptional regulation of the heterochronic gene lin-14 by lin-4 mediates temporal pattern formation in C. elegans. Cell. 1993;75:855–62.
Chen CZ, Li L, Lodish HF, Bartel DP. MicroRNAs modulate hematopoietic lineage differentiation. Science. 2004;303:83–6.
Calin GA, Croce CM. MicroRNA signatures in human cancers. Nat Rev Cancer. 2006;6:857–66.
Esquela-Kerscher A, Slack FJ. Oncomirs—microRNAs with a role in cancer. Nat Rev Cancer. 2006;6:259–69.
Calin GA, Dumitru CD, Shimizu M, Bichi R, Zupo S, Noch E, et al. Frequent deletions and down-regulation of micro- RNA genes miR15 and miR16 at 13q14 in chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2002;99:15524–9.
Guo JM, Miao Y, Xiao BX, Huan R, Jiang Z, Meng D, et al. Differential expression of microRNA species in human gastric cancer versus non-tumorous tissues. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2009;24:652–7.
Sobin LH, Wittekind CH. TNM classification of malignant tumors. 5th ed. New York: Wiley; 1997. p. 59–62.
Solcia E, Capella C. Endocrine tumours of the gastrointestinal tract. In: Solcia E, Klöppel G, Sobin LH, editors. Histological typing of endocrine tumours. 2nd ed. Berlin: Springer; 2000. p. 61–8.
Xiao B, Guo J, Miao Y, Jiang Z, Huan R, Zhang Y, et al. Detection of miR-106a in gastric carcinoma and its clinical significance. Clin Chim Acta. 2009;400:97–102.
Lawrie CH, Gal S, Dunlop HM, Pushkaran B, Liggins AP, Pulford K, et al. Detection of elevated levels of tumour-associated microRNAs in serum of patients with diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. Br J Haematol. 2008;141:672–5.
Peng JJ, Cai SJ, Lu HF, Cai GX, Lian P, Guan ZQ, et al. Predicting prognosis of rectal cancer patients with total mesorectal excision using molecular markers. World J Gastroenterol. 2007;13:3009–15.
Cummins JM, He Y, Leary RJ, Pushkaran B, Liggins AP, Pulford Kl, et al. The colorectal microRNAome. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2006;103:3687–92.
Landgraf P, Rusu M, Sheridan R, Sewer A, Iovino N, Aravin A, et al. A mammalian microRNA expression atlas based on small RNA library sequencing. Cell. 2007;129:1401–14.
Cui XY, Guo YJ, Yao HR. Analysis of microRNA in drug-resistant breast cancer cell line MCF-7/ADR. Nan Fang Yi Ke Da Xue Xue Bao. 2008;28:1813–5.
Takahashi Y, Takeuchi T, Sakamoto J, Touge T, Mai M, Ohkura H, et al. The usefulness of CEA and/or CA19-9 in monitoring for recurrence in gastric cancer patients: a prospective clinical study. Gastric Cancer. 2003;6:142–5.
Scott CL, Gil J, Hernando E, ewer A, Iovino N, Aravin A, et al. Role of the chromobox protein CBX7 in lymphomagenesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2007;104:5389–94.
Bernard D, Martinez-Leal JF, Rizzo S, Martinez D, Hudson D, Visakorpi T, et al. CBX7 controls the growth of normal and tumor-derived prostate cells by repressing the Ink4a/Arf locus. Oncogene. 2005;24:5543–51.
Chao TF, Zhang Y, Yan XQ, Yin B, Gong Y-H, Yuan J-G, et al. MiR-9 regulates the expression of CBX7 in human glioma. Zhongguo Yi Xue Ke Xue Yuan Xue Bao. 2008;30:268–74.
Hinz S, Kempkensteffen C, Christoph F, Yin B, Gong Y-H, Yuan J-G, et al. Expression parameters of the polycomb group proteins BMI1, SUZ12, RING1 and CBX7 in urothelial carcinoma of the bladder and their prognostic relevance. Tumour Biol. 2008;29:323–9.
Allante P, Federico A, Berlingieri MT, Bianco M, Ferraro A, Forzati F, et al. Loss of the CBX7 gene expression correlates with a highly malignant phenotype in thyroid cancer. Cancer Res. 2008;68:6770–8.
Martínez-Arribas F, Agudo D, Pollán M, Gómez-Esquer F, Díaz-Gil G, Lucas R, et al. Positive correlation between the expression of X-chromosome RBM genes (RBMX, RBM3, RBM10) and the proapoptotic Bax gene in human breast cancer. J Cell Biochem. 2006;97:1275–82.
Su JL, Yang CY, Shih JY, Wei LH, Hsieh CY, Jeng YN, et al. Knockdown of contactin-1 expression suppresses invasion and metastasis of lung adenocarcinoma. Cancer Res. 2006;66:2553–61.
Eckerich C, Zapf S, Ulbricht U, Muller S, Fillbrandt R, Westphal M, et al. Contactin is expressed in human astrocytic gliomas and mediates repulsive effects. Glia. 2006;53:1–12.
Uemura N, Okamoto S, Yamamoto S, Matsumura N, Yamaguchi S, Yamakido M, et al. Helicobacter pylori infection and the development of gastric cancer. N Engl J Med. 2001;345:784–9.
Petrocca F, Visone R, Onelli MR, Shah MH, Nicoloso MS, de Martino I, et al. E2F1-regulated microRNAs impair TGFbeta-dependent cell-cycle arrest and apoptosis in gastric cancer. Cancer Cell. 2008;13:272–86.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by Ningbo Natural Science Foundation (No. 200901A6010024), Zhejiang Provincial Research Project (Nos. 2008C33020 and 2008F70052), Zhejiang Natural Sciences Foundation (Nos. Y207240 and Y207244), Scientific Research Fund of Zhejiang Provincial Education Department (No. 20070965), National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 30872420), Post-graduate Innovative Research Project in Zhejiang Province (No. YK2008046), and K.C. Wong Magna Fund in Ningbo University.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jiang, Z., Guo, J., Xiao, B. et al. Increased expression of miR-421 in human gastric carcinoma and its clinical association. J Gastroenterol 45, 17–23 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00535-009-0135-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00535-009-0135-6