Abstract
Purpose
Steatosis is a histological finding associated with the progression of chronic hepatitis C. The aims of this study were to elucidate risk factors associated with steatosis and to evaluate the association between steatosis and hepatic expression of genes regulating lipid metabolism.
Methods
We analyzed 297 Japanese patients infected with hepatitis C virus and a subgroup of 100 patients who lack metabolic factors for steatosis. We determined intrahepatic mRNA levels of 18 genes regulating lipid metabolism in these 100 patients using real-time reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction. Levels of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor α and sterol regulatory element-binding protein 1 proteins were assessed by immunohistochemistry.
Results
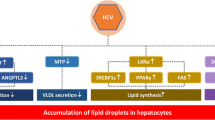
Steatosis was present in 171 (57%) of 297 patients. The presence of steatosis was independently associated with a higher body mass index, higher levels of γ-glutamyl transpeptidase and triglyceride, and a higher fibrosis stage. Steatosis was present in 43 (43%) of 100 patients lacking metabolic factors. Levels of mRNA and protein of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor α, which regulates β-oxidation of fatty acid, were lower in patients with steatosis than in patients without steatosis.
Conclusions
These findings indicate that impaired degradation of lipid may contribute to the development of hepatitis C virus-related steatosis.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Asselah T, Bieche I, Narguet S, Sabbagh A, Laurendeau I, Ripault MP, et al. Liver gene expression signature to predict response to pegylated interferon plus ribavirin combination therapy in patients with chronic hepatitis C. Gut. 2008;57:516–24.
Clark JM, Brancati FL, Diehl AM. Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Gastroenterology. 2002;122:1649–57.
Negro F. Mechanisms and significance of liver steatosis in hepatitis C virus infection. World J Gastroenterol. 2006;12:6756–65.
Poynard T, McHutchison J, Manns M, Myers RP, Albrecht J. Biochemical surrogate markers of liver fibrosis and activity in a randomized trial of peginterferon alfa-2b and ribavirin. Hepatology. 2003;38:481–92.
Leandro G, Mangia A, Hui J, Fabris P, Rubbia-Brandt L, Colloredo G, et al. Relationship between steatosis, inflammation, and fibrosis in chronic hepatitis C: a meta-analysis of individual patient data. Gastroenterology. 2006;130:1636–42.
Mihm S, Fayyazi A, Hartmann H, Ramadori G. Analysis of histopathological manifestations of chronic hepatitis C virus infection with respect to virus genotype. Hepatology. 1997;25:735–9.
Rubbia-Brandt L, Quadri R, Abid K, Giostra E, Malé PJ, Mentha G, et al. Hepatocyte steatosis is a cytopathic effect of hepatitis C virus genotype 3. J Hepatol. 2000;33:106–15.
Kumar D, Farrell GC, Fung C, George J. Hepatitis C virus genotype 3 is cytopathic to hepatocytes: reversal of hepatic steatosis after sustained therapeutic response. Hepatology. 2002;36:1266–72.
Monto A, Alonzo J, Watson JJ, Grunfeld C, Wright TL. Steatosis in chronic hepatitis C: relative contributions of obesity, diabetes mellitus, and alcohol. Hepatology. 2002;36:729–36.
Barba G, Harper F, Harada T, Kohara M, Goulinet S, Matsuura Y, et al. Hepatitis C virus core protein shows a cytoplasmic localization and associates to cellular lipid storage droplets. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 1997;94:1200–5.
Moriya K, Yotsuyanagi H, Shintani Y, Fujie H, Ishibashi K, Matsuura Y, et al. Hepatitis C virus core protein induces hepatic steatosis in transgenic mice. J Gen Virol. 1997;78:1527–31.
Perlemuter G, Sabile A, Letteron P, Vona G, Topilco A, Chrétien Y, et al. Hepatitis C virus core protein inhibits microsomal triglyceride transfer protein activity and very low density lipoprotein secretion: a model of viral-related steatosis. FASEB J. 2002;16:185–94.
Mirandola S, Realdon S, Iqbal J, Gerotto M, Dal Pero F, Bortoletto G, et al. Liver microsomal triglyceride transfer protein is involved in hepatitis C liver steatosis. Gastroenterology. 2006;130:1661–9.
Su AI, Pezacki JP, Wodicka L, Brideau AD, Supekova L, Thimme R, et al. Genomic analysis of the host response to hepatitis C virus infection. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2002;99:15669–74.
Kim KH, Hong SP, Kim K, Park MJ, Kim KJ, Cheong J. HCV core protein induces hepatic lipid accumulation by activating SREBP1 and PPARgamma. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2007;355:883–8.
Tsutsumi T, Suzuki T, Shimoike T, Suzuki R, Moriya K, Shintani Y, et al. Interaction of hepatitis C virus core protein with retinoid X receptor alpha modulates its transcriptional activity. Hepatology. 2002;35:937–46.
Yamaguchi A, Tazuma S, Nishioka T, Ohishi W, Hyogo H, Nomura S, et al. Hepatitis C virus core protein modulates fatty acid metabolism and thereby causes lipid accumulation in the liver. Dig Dis Sci. 2005;50:1361–71.
Cheng Y, Dharancy S, Malapel M, Desreumaux P. Hepatitis C virus infection down-regulates the expression of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor alpha and carnitine palmitoyl acyl-CoA transferase 1A. World J Gastroenterol. 2005;11:7591–6.
Dharancy S, Malapel M, Perlemuter G, Roskams T, Cheng Y, Dubuquoy L, et al. Impaired expression of the peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor alpha during hepatitis C virus infection. Gastroenterology. 2005;128:334–42.
Japan Society for the Study of Obesity. New criteria of obesity (in Japanese). J Jpn Soc Study Obes. 2000;6:18–28.
Simmonds P, Alberti A, Alter HJ, Bonino F, Bradley DW, Brechot C, et al. A proposed system for the nomenclature of hepatitis C viral genotypes. Hepatology. 1994;19:1321–4.
Desmet VJ, Gerber M, Hoofnagle JH, Manns M, Scheuer PJ. Classification of chronic hepatitis: diagnosis, grading and staging. Hepatology. 1994;19:1513–20.
Brunt EM, Janney CG, Di Bisceglie AM, Neuschwander-Tetri BA, Bacon BR. Nonalcoholic steatohepatitis: a proposal for grading and staging the histological lesions. Am J Gastroenterol. 1999;94:2467–74.
Lefkowitch JH, Schiff ER, Davis GL, Perrillo RP, Lindsay K, Bodenheimer HC Jr, et al. Pathological diagnosis of chronic hepatitis C: a multicenter comparative study with chronic hepatitis B. The Hepatitis Interventional Therapy Group. Gastroenterology. 1993;104:595–603.
Lonardo A, Loria P, Adinolfi LE, Carulli N, Ruggiero G. Hepatitis C and steatosis: a reappraisal. J Viral Hepat. 2006;13:73–80.
Akuta N, Suzuki F, Tsubota A, Suzuki Y, Someya T, Kobayashi M, et al. Efficacy of interferon monotherapy to 394 consecutive naive cases infected with hepatitis C virus genotype 2a in Japan: therapy efficacy as consequence of tripartite interaction of viral, host and interferon treatment-related factors. J Hepatol. 2002;37:831–6.
Ohata K, Hamasaki K, Toriyama K, Matsumoto K, Saeki A, Yanagi K, et al. Hepatic steatosis is a risk factor for hepatocellular carcinoma in patients with chronic hepatitis C virus infection. Cancer. 2003;97:3036–43.
Fujie H, Yotsuyanagi H, Moriya K, Shintani Y, Tsutsumi T, Takayama T, et al. Steatosis and intrahepatic hepatitis C virus in chronic hepatitis. J Med Virol. 1999;59:141–5.
Castera L, Chouteau P, Hezode C, Zafrani ES, Dhumeaux D, Pawlotsky JM. Hepatitis C virus-induced hepatocellular steatosis. Am J Gastroenterol. 2005;100:711–5.
Westin J, Nordlinder H, Lagging M, Norkrans G, Wejstål R. Steatosis accelerates fibrosis development over time in hepatitis C virus genotype 3 infected patients. J Hepatol. 2002;37:837–42.
Patton HM, Patel K, Behling C, Bylund D, Blatt LM, Vallée M, et al. The impact of steatosis on disease progression and early and sustained treatment response in chronic hepatitis C patients. J Hepatol. 2004;40:484–90.
Fartoux L, Chazouillères O, Wendum D, Poupon R, Serfaty L. Impact of steatosis on progression of fibrosis in patients with mild hepatitis C. Hepatology. 2005;41:82–7.
Adinolfi LE, Gambardella M, Andreana A, Tripodi MF, Utili R, Ruggiero G. Steatosis accelerates the progression of liver damage of chronic hepatitis C patients and correlates with specific HCV genotype and visceral obesity. Hepatology. 2001;33:1358–64.
Ikai E, Honda R, Yamada Y. Serum gamma-glutamyl transpeptidase level and blood pressure in nondrinkers: a possible pathogenetic role of fatty liver in obesity-related hypertension. J Hum Hypertens. 1994;8:95–100.
Lee DS, Evans JC, Robins SJ, Wilson PW, Albano I, Fox CS, et al. Gamma glutamyl transferase and metabolic syndrome, cardiovascular disease, and mortality risk: the Framingham Heart Study. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2007;27:127–33.
Perry IJ, Wannamethee SG, Shaper AG. Prospective study of serum gamma-glutamyltransferase and risk of NIDDM. Diabetes Care. 1998;21:732–7.
de Gottardi A, Pazienza V, Pugnale P, Bruttin F, Rubbia-Brandt L, Juge-Aubry CE, et al. Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-alpha and -gamma mRNA levels are reduced in chronic hepatitis C with steatosis and genotype 3 infection. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2006;23:107–14.
Desvergne B, Wahli W. Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptors: nuclear control of metabolism. Endocr Rev. 1999;20:649–88.
Moriya K, Nakagawa K, Santa T, Shintani Y, Fujie H, Miyoshi H, et al. Oxidative stress in the absence of inflammation in a mouse model for hepatitis C virus-associated hepatocarcinogenesis. Cancer Res. 2001;61:4365–70.
Okuda M, Li K, Beard MR, Showalter LA, Scholle F, Lemon SM, et al. Mitochondrial injury, oxidative stress, and antioxidant gene expression are induced by hepatitis C virus core protein. Gastroenterology. 2002;122:366–75.
Lerat H, Honda M, Beard MR, Loesch K, Sun J, Yang Y, et al. Steatosis and liver cancer in transgenic mice expressing the structural and nonstructural proteins of hepatitis C virus. Gastroenterology. 2002;122:352–65.
Lai MM. Hepatitis C virus proteins: direct link to hepatic oxidative stress, steatosis, carcinogenesis and more. Gastroenterology. 2002;122:568–71.
Asselah T, Rubbia-Brandt L, Marcellin P, Negro F. Steatosis in chronic hepatitis C: why does it really matter? Gut. 2006;55:123–30.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by a Grant-in-Aid for Scientific Research from the Japan Society for the Program of Science (20590408) and by a grant from Ministry of Health, Labor and Welfare of Japan (H20-hepatitis-008; to K. Yasui).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yasui, K., Harano, Y., Mitsuyoshi, H. et al. Steatosis and hepatic expression of genes regulating lipid metabolism in Japanese patients infected with hepatitis C virus. J Gastroenterol 45, 95–104 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00535-009-0133-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00535-009-0133-8