Abstract
Object
The interferon-induced Jak-STAT signal alone is not sufficient to explain all the biological effects of IFN. The PI3-K pathways have emerged as a critical additional component of IFN-induced signaling. This study attempted to clarify that relationship between IFN-induced PI3-K-Akt-mTOR activity and anti-viral action.
Result
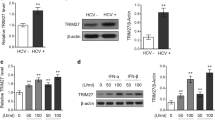
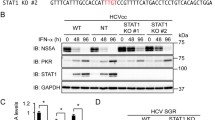
When the human normal hepatocyte derived cell line was treated with rapamycin (rapa) before accretion of IFN-α, tyrosine phosphorylation of STAT-1 was diminished. Pretreatment of rapa had an inhibitory effect on the IFN-α-induced expression of PKR and p48 in a dose dependent manner. Rapa inhibited the IFN-α inducible IFN-stimulated regulatory element luciferase activity in a dose-dependent manner. However, wortmannin, LY294002 and Akt inhibitor did not influence IFN-α inducible luciferase activity. To examine the effect of PI3-K-Akt-mTOR on the anti-HCV action of IFN-α, the full-length HCV replication system, OR6 cells were used. The pretreatment of rapa attenuated its anti-HCV replication effect in comparison to IFN-α alone, whereas the pretreatment with PI3-K inhibitors, wortmannin and LY294002 and Akt inhibitor did not influence IFN-induced anti-HCV replication.
Conclusion
IFN-induced mTOR activity, independent of PI3K and Akt, is the critical factor for its anti-HCV activity. Jak independent mTOR activity involved STAT-1 phosphorylation and nuclear location, and then PKR is expressed in hepatocytes.






Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- IFN:
-
Interferon
- HCV:
-
Hepatitis C virus
- STAT:
-
Signal transducers and activators of transcription
- ISGF-3:
-
IFN-stimulated gene factor 3
- ISRE:
-
IFN-stimulated regulatory element
- PKR:
-
Double-stranded RNA-dependent protein kinase
- Rapa:
-
Rapamycin
- PI3-K:
-
Phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase
- mTOR:
-
Mammalian target of rapamycin
- siRNA:
-
Small interfering RNA
References
Fattovich G, Stroffolini T, Zagni I, Donato F. Hepatocellular carcinoma in cirrhosis: incidence and risk factors. Gastroenterology. 2004;127:S35–50.
Pawlotsky JM, Chevaliez S, McHutchison JG. The hepatitis C virus life cycle as a target for new antiviral therapies. Gastroenterology. 2007;132:1979–98.
Persico M, Capasso M, Persico E, Svelto M, Russo R, Spano D, et al. Suppressor of cytokine signaling 3 (SOCS3) expression and hepatitis C virus-related chronic hepatitis: insulin resistance and response to antiviral therapy. Hepatology. 2007;46:1009–15.
Walsh MJ, Jonsson JR, Richardson MM, Lipka GM, Purdie DM, Clouston AD, et al. Non-response to antiviral therapy is associated with obesity and increased hepatic expression of suppressor of cytokine signaling 3 (SOCS-3) in patients with chronic hepatitis C, viral genotype 1. Gut. 2006;55:529–35.
Huang Y, Feld JJ, Sapp RK, Nanda S, Lin JH, Blatt LM, et al. Defective hepatic response to interferon and activation of suppressor of cytokine signaling 3 in chronic hepatitis C. Gastroenterology. 2007;132:733–44.
Taylor MW, Tsukahara T, Brodsky L, Schaley J, Sanda C, Stephens MJ, et al. Changes in gene expression during pegylated interferon and ribavirin therapy of chronic hepatitis C virus distinguish responders from nonresponders to antiviral therapy. J Virol. 2007;81:3391–401.
Lan KH, Lan KL, Lee WP, Sheu ML, Chen MY, Lee YL, et al. HCV NS5A inhibits interferon-alpha signaling through suppression of STAT1 phosphorylation in hepatocyte-derived cell lines. J Hepatol. 2007;46:759–67.
van Boxel-Dezaire AH, Rani MR, Stark GR. Complex modulation of cell type-specific signaling in response to type I interferons. Immunity. 2006;25:361–72.
Ichikawa T, Nakao K, Nakata K, Yamashita M, Hamasaki K, Shigeno M, et al. Involvement of IL-1beta and IL-10 in IFN-alpha-mediated antiviral gene induction in human hepatoma cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2002;294:414–22.
Kaur S, Uddin S, Platanias LC. The PI3’ kinase pathway in interferon signaling. J Interferon Cytokine Res. 2005;25:780–7.
Kaur S, Lal L, Sassano A, Majchrzak-Kita B, Srikanth M, Baker DP, et al. Regulatory effects of mammalian target of rapamycin-activated pathways in type I and II interferon signaling. J Biol Chem. 2007;282:1757–68.
Kudchodkar SB, Del Prete GQ, Maguire TG, Alwine JC. AMPK-mediated inhibition of mTOR kinase is circumvented during immediate-early times of human cytomegalovirus infection. J Virol. 2007;81:3649–51.
Minami K, Tambe Y, Watanabe R, Isono T, Haneda M, Isobe K, et al. Suppression of viral replication by stress-inducible GADD34 protein via the mammalian serine/threonine protein kinase mTOR pathway. J Virol. 2007;81:11106–15.
Ishida H, Li K, Yi M, Lemon SM. p21-activated kinase 1 is activated through the mammalian target of rapamycin/p70 S6 kinase pathway and regulates the replication of hepatitis C virus in human hepatoma cells. J Biol Chem. 2007;282:11836–48.
Guo H, Zhou T, Jiang D, Cuconati A, Xiao GH, Block TM, et al. Regulation of hepatitis B virus replication by the phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase-Akt signal transduction pathway. J Virol. 2007;81:10072–80.
Mannova P, Beretta L. Activation of the N-Ras-PI3K-Akt-mTOR pathway by hepatitis C virus: control of cell survival and viral replication. J Virol. 2005;79:8742–9.
Nishimura D, Ishikawa H, Matsumoto K, Shibata H, Motoyoshi Y, Fukuta M, et al. DHMEQ, a novel NF-kappaB inhibitor, induces apoptosis and cell-cycle arrest in human hepatoma cells. Int J Oncol. 2006;29:713–9.
Ikeda M, Abe K, Dansako H, Nakamura T, Naka K, Kato N. Efficient replication of a full-length hepatitis C virus genome, strain O, in cell culture, and development of a luciferase reporter system. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2005;329:1350–9.
Obora A, Shiratori Y, Okuno M, Adachi S, Takano Y, Matsushima-Nishiwaki R, et al. Synergistic induction of apoptosis by acyclic retinoid and interferon-beta in human hepatocellular carcinoma cells. Hepatology. 2002;36:1115–24.
Wang C, Pflugheber J, Sumpter R Jr, Sodora DL, Hui D, Sen GC, et al. Alpha interferon induces distinct translational control programs to suppress hepatitis C virus RNA replication. J Virol. 2003;77:3898–912.
Liu WL, Su WC, Cheng CW, Hwang LH, Wang CC, Chen HL, et al. Ribavirin up-regulates the activity of double-stranded RNA-activated protein kinase and enhances the action of interferon-alpha against hepatitis C virus. J Infect Dis. 2007;196:425–34.
Tamada Y, Nakao K, Nagayama Y, Nakata K, Ichikawa T, Kawamata Y, et al. p48 Overexpression enhances interferon-mediated expression and activity of double-stranded RNA-dependent protein kinase in human hepatoma cells. J Hepatol. 2002;37:493–9.
Dowling RJ, Zakikhani M, Fantus IG, Pollak M, Sonenberg N. Metformin inhibits mammalian target of rapamycin-dependent translation initiation in breast cancer cells. Cancer Res. 2007;67:10804–12.
Mamane Y, Petroulakis E, LeBacquer O, Sonenberg N. mTOR, translation initiation and cancer. Oncogene. 2006;25:6416–22.
Hanada M, Feng J, Hemmings BA. Structure, regulation and function of PKB/AKT–a major therapeutic target. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2004;1697:3–16.
Hresko RC, Mueckler M. mTOR.RICTOR is the Ser473 kinase for Akt/protein kinase B in 3T3–L1 adipocytes. J Biol Chem. 2005;280:40406–16.
Engelman JA, Luo J, Cantley LC. The evolution of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinases as regulators of growth and metabolism. Nat Rev Genet. 2006;7:606–19.
Molnarfi N, Hyka-Nouspikel N, Gruaz L, Dayer JM, Burger D. The production of IL-1 receptor antagonist in IFN-beta-stimulated human monocytes depends on the activation of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase but not of STAT1. J Immunol. 2005;174:2974–80.
Parmar S, Smith J, Sassano A, Uddin S, Katsoulidis E, Majchrzak B, et al. Differential regulation of the p70 S6 kinase pathway by interferon alpha (IFNalpha) and imatinib mesylate (STI571) in chronic myelogenous leukemia cells. Blood. 2005;106:2436–43.
Nguyen H, Ramana CV, Bayes J, Stark GR. Roles of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase in interferon-gamma-dependent phosphorylation of STAT1 on serine 727 and activation of gene expression. J Biol Chem. 2001;276:33361–8.
Fang P, Hwa V, Rosenfeld RG. Interferon-gamma-induced dephosphorylation of STAT3 and apoptosis are dependent on the mTOR pathway. Exp Cell Res. 2006;312:1229–39.
El-Hashemite N, Zhang H, Walker V, Hoffmeister KM, Kwiatkowski DJ. Perturbed IFN-gamma-Jak-signal transducers and activators of transcription signaling in tuberous sclerosis mouse models: synergistic effects of rapamycin-IFN-gamma treatment. Cancer Res. 2004;64:3436–43.
Matsumoto K, Okano J, Murawaki Y. Differential effects of interferon alpha-2b and beta on the signaling pathways in human liver cancer cells. J Gastroenterol. 2005;40:722–32.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Matsumoto, A., Ichikawa, T., Nakao, K. et al. Interferon-α-induced mTOR activation is an anti-hepatitis C virus signal via the phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase-Akt-independent pathway. J Gastroenterol 44, 856–863 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00535-009-0075-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00535-009-0075-1