Abstract
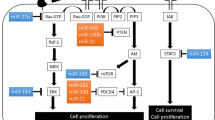
MicroRNAs (miRNAs) are small noncoding RNAs that function as endogenous silencers of numerous target genes. Hundreds of human miRNAs have been identified in the human genome, and they are expressed in a tissue-specific manner and play important roles in cell proliferation, apoptosis, and differentiation. Links between miRNAs and human diseases are increasingly apparent, and aberrant expression of miRNAs may contribute to the development and progression of human malignancies. Recent studies have shown that some miRNAs play roles as tumor suppressors or oncogenes in gastrointestinal cancers. miRNA expression is regulated by different mechanisms including transcription factor binding, epigenetic alterations, and chromosomal abnormalities. miRNA expression profiling may be a powerful clinical tool for cancer diagnosis, and regulation of miRNA expression could be a novel strategy for the chemoprevention of human gastrointestinal cancers. In this article, the biological importance of miRNAs in human gastrointestinal cancers is summarized.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
He L, Hannon GJ. MicroRNAs: small RNAs with a big role in gene regulation. Nat Rev Genet 2004;5:522–531.
Calin GA, Croce CM. MicroRNA signatures in human cancers. Nat Rev Cancer 2006;6:857–866.
Lewis BP, Shih IH, Jones-Rhoades MW, Bartel DP, Burge CB. Prediction of mammalian microRNA targets. Cell 2003;115:787–798.
John B, Enright AJ, Aravin A, Tuschl T, Sander C, Marks DS. Human MicroRNA targets. PLoS Biol 2004;2:e363.
Krek A, Grun D, Poy MN, Wolf R, Rosenberg L, Epstein EJ, et al. Combinatorial microRNA target predictions. Nat Genet 2005;37:495–500.
Griffiths-Jones S, Grocock RJ, van Dongen S, Bateman A, Enright AJ. miRBase: microRNA sequences, targets and gene nomenclature. Nucleic Acids Res 2006;34:D140–D144.
Xia L, Zhang D, Du R, Pan Y, Zhao L, Sun S, et al. miR-15b and miR-16 modulate multidrug resistance by targeting BCL2 in human gastric cancer cells. Int J Cancer 2008;123(2):372–379.
Tazawa H, Tsuchiya N, Izumiya M, Nakagama H. Tumor-suppressive miR-34a induces senescence-like growth arrest through modulation of the E2F pathway in human colon cancer cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2007;104:15472–15477.
Michael MZ, O’Connor SM, van Holst Pellekaan NG, Young GP, James RJ. Reduced accumulation of specific microRNAs in colorectal neoplasia. Mol Cancer Res 2003;1:882–891.
Akao Y, Nakagawa Y, Naoe T. MicroRNAs 143 and 145 are possible common onco-microRNAs in human cancers. Oncol Rep 2006;16:845–850.
Eis PS, Tam W, Sun L, Chadburn A, Li Z, Gomez MF, et al. Accumulation of miR-155 and BIC RNA in human B cell lymphomas. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2005;102:3627–3632.
Volinia S, Calin GA, Liu CG, Ambs S, Cimmino A, Petrocca F, et al. A microRNA expression signature of human solid tumors defines cancer gene targets. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2006;103:2257–2261.
Gironella M, Seux M, Xie MJ, Cano C, Tomasini R, Gommeaux J, et al. Tumor protein 53-induced nuclear protein 1 expression is repressed by miR-155, and its restoration inhibits pancreatic tumor development. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2007;104:16170–16175.
He L, Thomson JM, Hemann MT, Hernando-Monge E, Mu D, Goodson S, et al. A microRNA polycistron as a potential human oncogene. Nature (Lond) 2005;435:828–833.
O’Donnell KA, Wentzel EA, Zeller KI, Dang CV, Mendell JT. c-Myc-regulated microRNAs modulate E2F1 expression. Nature (Lond) 2005;435:839–843.
Meng F, Henson R, Wehbe-Janek H, Ghoshal K, Jacob ST, Patel T. MicroRNA-21 regulates expression of the PTEN tumor suppressor gene in human hepatocellular cancer. Gastroenterology 2007;133:647–658.
Petrocca F, Visone R, Onelli MR, Shah MH, Nicoloso MS, de Martino I, et al. E2F1-regulated microRNAs impair TGF-beta-dependent cell-cycle arrest and apoptosis in gastric cancer. Cancer Cell 2008;13:272–286.
Rodriguez A, Griffiths-Jones S, Ashurst JL, Bradley A. Identification of mammalian microRNA host genes and transcription units. Genome Res 2004;14:1902–1910.
Calin GA, Sevignani C, Dumitru CD, Hyslop T, Noch E, Yendamuri S, et al. Human microRNA genes are frequently located at fragile sites and genomic regions involved in cancers. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2004;101:2999–3004.
Saito Y, Liang G, Egger G, Friedman JM, Chuang JC, Coetzee GA, Jones PA. Specific activation of microRNA-127 with down-regulation of the proto-oncogene BCL6 by chromatin-modifying drugs in human cancer cells. Cancer Cell 2006;9:435–443.
Lu J, Getz G, Miska EA, Alvarez-Saavedra E, Lamb J, Peck D, et al. MicroRNA expression profiles classify human cancers. Nature (Lond) 2005;435:834–838.
Calin GA, Ferracin M, Cimmino A, Di Leva G, Shimizu M, Wojcik SE, et al. A microRNA signature associated with prognosis and progression in chronic lymphocytic leukemia. N Engl J Med 2005;353:1793–1801.
Yanaihara N, Caplen N, Bowman E, Seike M, Kumamoto K, Yi M, et al. Unique microRNA molecular profiles in lung cancer diagnosis and prognosis. Cancer Cell 2006;9:189–198.
Schetter AJ, Leung SY, Sohn JJ, Zanetti KA, Bowman ED, Yanaihara N, et al. MicroRNA expression profiles associated with prognosis and therapeutic outcome in colon adenocarcinoma. JAMA 2008;299:425–436.
Arber N, Eagle CJ, Spicak J, Racz I, Dite P, Hajer J, et al. Celecoxib for the prevention of colorectal adenomatous polyps. N Engl J Med 2006;355:885–895.
Bertagnolli MM, Eagle CJ, Zauber AG, Redston M, Solomon SD, Kim K, et al. Celecoxib for the prevention of sporadic colorectal adenomas. N Engl J Med 2006;355:873–884.
Mott JL, Kobayashi S, Bronk SF, Gores GJ. mir-29 regulates Mcl-1 protein expression and apoptosis. Oncogene 2007;26:6133–6140.
Yoo CB, Jones PA. Epigenetic therapy of cancer: past, present and future. Nat Rev Drug Disc 2006;5:37–50.
Saito Y, Jones PA. Epigenetic activation of tumor suppressor microRNAs in human cancer cells. Cell Cycle 2006;5:2220–2222.
Parkin DM. Global cancer statistics in the year 2000. Lancet Oncol 2001;2:533–543.
Suzuki H, Hibi T, Marshall BJ. Helicobacter pylori: present status and future prospects in Japan. J Gastroenterol 2007;42:1–15.
Kuipers EJ, Nelis GF, Klinkenberg-Knol EC, Snel P, Goldfain D, Kolkman JJ, et al. Cure of Helicobacter pylori infection in patients with reflux oesophagitis treated with long term omeprazole reverses gastritis without exacerbation of reflux disease: results of a randomised controlled trial. Gut 2004;53:12–20.
Leung WK, Lin SR, Ching JY, To KF, Ng EK, Chan FK, et al. Factors predicting progression of gastric intestinal metaplasia: results of a randomised trial on Helicobacter pylori eradication. Gut 2004;53:1244–1249.
Ley C, Mohar A, Guarner J, Herrera-Goepfert R, Figueroa LS, Halperin D, et al. Helicobacter pylori eradication and gastric pre-neoplastic conditions: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev 2004;13:4–10.
Mera R, Fontham ET, Bravo LE, Bravo JC, Piazuelo MB, Camargo MC, Correa P. Long term follow up of patients treated for Helicobacter pylori infection. Gut 2005;54:1536–1540.
Schenk BE, Kuipers EJ, Nelis GF, Bloemena E, Thijs JC, Snel P, et al. Effect of Helicobacter pylori eradication on chronic gastritis during omeprazole therapy. Gut 2000;46:615–621.
Wong BC, Lam SK, Wong WM, Chen JS, Zheng TT, Feng RE, et al. Helicobacter pylori eradication to prevent gastric cancer in a high-risk region of China: a randomized controlled trial. JAMA 2004;291:187–194.
Maekita T, Nakazawa K, Mihara M, Nakajima T, Yanaoka K, Iguchi M, et al. High levels of aberrant DNA methylation in Helicobacter pylori-infected gastric mucosae and its possible association with gastric cancer risk. Clin Cancer Res 2006;12:989–995.
Ushijima T, Nakajima T, Maekita T. DNA methylation as a marker for the past and future. J Gastroenterol 2006;41:401–407.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Saito, Y., Suzuki, H. & Hibi, T. The role of microRNAs in gastrointestinal cancers. J Gastroenterol 44 (Suppl 19), 18–22 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00535-008-2285-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00535-008-2285-3