Abstract
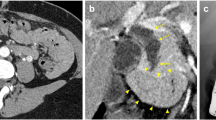
In pancreatic lithiasis in elderly autopsy cases, the stones are small and the pancreatic duct is changed very slightly when viewed by simple X-ray film, pancreatic ductography and gross appearance. Histologically, a slight fibrous increase is seen very locally, but findings consistent with chronic pancreatitis are not found throughout the whole pancreas. However, marked, diffuse and irregular dilatation of the pancreatic duct is frequently found in operative cases with chronic pancreatitis and pancreatic stones. These findings show that the changes seen with aging and with chronic pancreatitis can be distinguished based on the findings of pancreatic ductography. Mucin production in epithelia in intraductal papillary-mucinous neoplasm (IPMN) may not be strongly associated with the pathogenesis of pancreatic lithiasis. Pancreatic lithiasis may be related to squamous cell metaplasia. IPMN and dilatation of the pancreatic duct are closely associated with mucin production. An increase in intraductal pressure of the pancreatic duct may be somewhat related to the mechanism of stone formation. The incidental co-existence of pancreatic epithelia with pancreatic lithiasis in patients with chronic pancreatitis and the development of IPMN may also be possible. IPMN and pancreatic lithiasis may be related through the mechanism(s) of their pathogenesis, their synergism and the pathogenesis of stone formation. The relation between mucinous metaplasia and stone formation is slight and, therefore, there may be only a weak correlation between IPMN and pancreatic stones. This may explain why there are few reports of the co-existence of IPMN and pancreatic stones (Kimura in Kan Tan Sui 58:485–492, 2009).






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kimura W, Nagai H, Kuroda A, Muto T, Esaki Y. Analysis of small cystic lesions of the pancreas. Int J Pancreatol. 1995;18:197–206.
Kimura W. Histological study on pathogenesis of sites of isolated islets of Langerhans and their course to the terminal state. Am J Gastroenterol. 1989;84:517–22.
Nagai H, Ohtsubo K. Pancreatic lithiasis in the aged: Its clinicopathology and pathogenesis. Gastroenterology. 1984;86:331–8.
Japanese Committee of Investigation of Diagnostic Criteria for Chronic Pancreatitis. Diagnostic criteria for chronic pancreatitis. Jpn J Panc Soc. 1995;10:22–5.
Ohhashi Murakami Y, Maruyama M, et al. Four cases of mucin producing cancer of the pancreas—with special reference to special findings of the papilla of Vater. Prog Dig Endosc. 1982;20:348–51.
Kimura W, Muto T, Makuuchi M. Pancreatic lithiasis and dilatation of the pancreatic ducts in the aged. Shokakika. 1997;24:549–53.
Kimura W, Kubota K, Yasuhara Y, et al. Acute pancreatitis, pancreatic lithiasis and dilatation of the pancreatic ducts. Ronen Shokakibyo. 1998;10:61–7.
Kimura W, Sasahira N, Yoshikawa T, Muto T, Makuuchi M. Duct-ectatic type of mucin producing tumor of the pancreas—new concept of pancreatic neoplasia. Hepatogastroenterology. 1996;43:692–709.
Kimura W, Kuroda A, Makuuchi M. Problems in the diagnosis and treatment of a so-called mucin-producing tumor of the pancreas. Pancreas. 1998;16:363–9.
Kimura W. Intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasm (IPMN) and mucinous cystic neoplasm (MCN) of the pancreas. Clin Dig Organs. 2009;12:5–21.
Origuchi N, Kimura W, Muto T, Esaki Y. Pancreatic mucin-producing adenocarcinoma associated with a pancreatic stone: report of a case. Surg Today. 1998;28:1261–5.
Hara T, Takanashi S. Intra-ductal papillary mucinous tumor (IPMT) with pancreato lithiasis. Case Report. Jpn J Panc Soc. 2003;18:501–6.
Imai A, Arai M, Kuroda M, et al. Invasive carcinoma derived from intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasm (IPMN) of the pancreas with pancreatic stones and pancreatitis. Kyoto Med J. 2007;54:143–8.
Zapiach M, Yadav D, Smyrk TC, Fletcher JG, Pearson RK, Clain JE, et al. Calcifying obstructive pancreatitis: a study of intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasm associated with pancreatic calcification. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2004;2(1):57–63.
Kimura W. Pancreatic lithiasis and intraductal papillary-mucinous neoplasm with special reference to the pathogenesis of lithiasis. Kan Tan Sui. 2009;58:485–92.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
About this article
Cite this article
Kimura, W. Pancreatic lithiasis and intraductal papillary-mucinous neoplasm with special reference to the pathogenesis of lithiasis. J Hepatobiliary Pancreat Sci 17, 776–781 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00534-009-0180-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00534-009-0180-9