Abstract
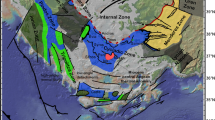
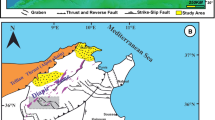
The Rides Prerifaines (RP) of Morocco constitute the leading edge of the Rif chain. They involve a Triassic–Palaeocene succession deposited on a peneplained Palaeozoic fold belt and accumulated in basins delimited by NE–SW-trending normal fault systems. A significant hiatus separates an overlying Middle Miocene–Upper Miocene foredeep sequence. The reconstruction of the complex structural evolution of the RP during the later compressive phases that affected the Rif chain since Middle Miocene time has been the aim of this paper. We integrated field structural analyses, seismic line interpretation, and analogue modelling in order to evaluate the control exerted by the Late Triassic–Jurassic normal fault systems onto the later compressive tectonics. The maximum compression direction associated with the first compressive phase is roughly NE–SW to ENE–WSW oriented. During this phase the Mesozoic basin fill was scooped-out from the graben and the main décollement level were the Triassic evaporites. Since Pliocene times the maximum compression direction was oriented roughly N–S. During this phase the RP assumed their present structural setting. The earlier normal faults delimiting the Mesozoic graben were reactivated in a strike–slip mode also involving the Palaeozoic basement. The analogue modelling experiments demonstrated that the basement reactivation promoted salt tectonics and favoured fluid circulation.
















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aït Brahim L, Chotin P (1984) Mise en évidence d’un changement de direction de compression dans l’avant-pays rifain (Maroc) au cours du Tertiaire et du Quaternaire. Bull Soc Géol Fr Ser 7(26):681–691
Aït Brahim L, Chotin P (1989) Genèse et déformation des bassins néogènes du Rif central (Maroc) au cours du rapprochement Europe-Afrique. Geodinamica Acta 3:295–304
Aït Brahim L, Chotin P, Hinaj S, Abdelouafi A, El Adraoui A, Nakcha C, Dhont D, Charroud M, Sossey Alaoui F, Amrhar M, Bouaza A, Tabyaoui H, Chaouni A (2002) Paleostress evolution in the Moroccan African margin from Triassic to Present. Tectonophysics 357:187–205
Bargach K, Ruano P, Chabli A, Galindo-Zaldivar J, Chalouan A, Jabaloy A, Akil M, Ahmamou M, Sanz de Galdeano C, Benmakhlouf M (2004) Recent tectonic deformations and stresses in the frontal part of the Rif Cordillera and the Saïss Basin (Fes and Rabat regions, Morocco). Pure Appl Geophys 161:521–540
Bendkik A (2004) Carte Géologique du Maroc, Feuille Sidi Kacem, echelle 1:50.000. Notes Mém Serv Géol Maroc 431
Bernini M, Boccaletti M, Moratti G, Papani G (2000) Structural development of the Taza-Guercif Basin as a constraint for the Middle Atlas Shear Zone tectonic evolution. Mar Pet Geol 17:391–408
Bettelli G, Vannucchi P (2003) Structural style of the offscraped Ligurian oceanic sequences of the Northern Apennines: new hypothesis concerning the development of mélange block-in-matrix fabric. J Struct Geol 25:371–388
Bourcart J (1932) La Ride Prérifaine d’El Kansera (Maroc). Boll Doc Géol Fr Ser 5(2):221–236
Boutakiout M (1990) Les foraminifères du Jurassique des Rides Sud-Rifaines et des régions voisines (Maroc). Doc des Lab Géol Lyon 112:1–247
Bruderer W, Levy RG (1954) Considerations sur la “Nappe Prerifaine” d’apres les travaux de la Societè Cherifienne des petroles Congres Geologique International Alger XIX session, Association des Services Geologiques Africains. Deuxieme partie—Questions Diverses et annexes-Fascicule XX:277–294
Bruderer W, Delga G,Gouskov N, Gubler J, Lardenois E, Levy RG, Marquis Ch, Mourou C, Naif R, Nouet G, Ramette C, Tenaille M (1950a) Carte géologique régulière du Maroc au 1:100.000éme. Feuille Petitjean. Notes Mem Serv Géol Maroc 108
Bruderer W, Gouskov N, Gubler J, Jacquemont P, Levy RG, Tilloy R (1950b) Carte géologique régulière du Maroc au 1:100.000éme. Feuille Fés-ouest. Notes Mem Serv Géol Maroc 109
Brun JP (1999) Narrow rifts versus wide rifts: inferences for the mechanics of rifting from laboratory experiments. Philos Trans R Soc Lond A 357:695–712
Burger J-J, Housse B, Levy R (1962) Contribution des travaux d’exploration de la Société Chérifienne des Pétroles a la connaissance de la Nappe Prérifaine. Livre Mém Fallot Mém Geol Fr 1:423–430
Carey E (1979) Recherche des directions principales des contraintes associees au jeu d’une population de failles. Rev Geol Dyn Geogr Phis 21:57–66
Carte Géologique du Maroc (1985) Royaume du Maroc, Ministère de l’Energie et des Mines, Direction de la Géologie. Publ. 260 du Service Géologique du Maroc (scale 1:1,000,000)
Chenakeb M (2004) Carte Géologique du Maroc, Feuille Beni Ammar, echelle 1:50.000. Notes Mem Serv Géol Maroc 428
Choubert G, Faure-Muret A (1962) Evolution du domaine atlasique marocain depuis les temps paléozoiques. Livre Mém Fallot Mém Geol Fr 1:447–527
Costagliola A, El Alji M, Jabour H, Degnati A (1997) Middle Atlas and High Atlas Geotraverse. Field trip guidebook, Peri-Tethys Program-Onarep, Rabat, 13–15 June 1997, pp 1–88
Daguin F (1927) Contribution à l’étude géologique de la région Prérifaine (Maroc septentrional). Notes Mém Serv Géol Maroc 1:1–413
Del Ventisette C, Montanari D, Bonini M, Sani F (2005) Positive fault inversion triggering ‘intrusive diapirism’: an analogue modelling perspective. Terra Nova, vol 17. DOI 10.1111/j.1365–3121.2005.00637.x
Del Ventisette C, Montanari D, Bonini M, Sani F (2006) Basin inversion and fault reactivation in laboratory experiments. J Struct Geol (in press)
Faugères J-C (1978) Les rides sud-rifaines. Evolution sedimentaire et structurale d’un bassin atlantico-mésogéen de la marge africaine. These Doct. Etat. Univ. Bordeaux, pp 1–480
Faugères J-C (1981) Évolution structurale d’un bassin atlantico-mésogéen de la marge africaine: les rides sud-rifaines (Maroc). Bull Soc Géol Fr 23:229–244
Faure Muret A, Morel JL (1992) Carte Néotectonique du Maroc 1: 100.000. Feuille 1: Provinces du Nord. Notes Mem Serv Géol Maroc 368
Feinberg H (1986) Les series tertiaires des zones externes du Rif (Maroc). Notes Mém Serv Géol Maroc 315:1–192
Flinch JF (1993) Tectonic evolution of the Gibraltar Arc. Ph.D. Thesis, Rice University, Houston, pp 1–381
Flinch JF (1996) Accretion and extensional collapse of the external Western Rif (Northern Morocco). In: Ziegler PA, Horvath F (eds) Peri-Tethys Memoir 2: Structure and prospects of Alpine basins and forelands. Mém Mus Natn Hist Nat 170:61–85
Frizon de Lamotte D, Crespo-Blanc A, Saint-Bézar B, Comas M, Fernàndez M, Zeyen H, Ayarza P, Robert-Charrue C, Chalouan A, Zizi M, Teixell A, Arboleya M-L, Alvarez-Lobato F, Julivert M, Michard A (2004) TRANSMED Transect I. In: Cavzza W, Roure F, Spakman W, Stampfli GM, Ziegler PA (eds) The TRANSMED Atlas—the Mediterranean Region from crust to mantle. Springer, Berlin Heidelberg New York
Gentil L (1918) Notes d’un voyage géologique a Taza (Maroc septentrional) (Contribution a l’étude du Detroit Sudrifain). Bull Soc Geol Fr Ser 4(18):129–177
Hubbert MK (1937) Theory of scale models as applied to the study of geologic structures. Geol Soc Am Bull 48:1459–1520
Jabour H, Morabet Al M., Bouchta R (2000) Hydrocarbon systems of Morocco. In: Crasquin-Soleau S, Barrier E’ (eds) Peri-Tethys Memoir 5: New data on Peri-Tethyan sedimentary basins. Mém Mus Natn Hist Nat 182:143–158
Jacobshagen VH, Gorler K, Giese P (1988) Geodynamic evolution of the Atlas system. In: Jacobshagen H (eds) The Atlas system of Morocco. Springer, Berlin Heidelberg New York, pp 481–499
Laville E, Piqué A (1991) La distension crustale atlantique et atlasique au Maroc au début du Mésozoïque: le rejeu des structures hercyniennes. Bull Soc Géol Fr 162:1161–1171
Laville E, Piqué A, Amrhar M, Charroud M (2004) A restatement of the Mesozoic Atlasic Rifting (Morocco). J Afr Earth Sci 38:145–153
Levy RG, Tilloy R (1952) Maroc Septentrional (Chaine du Rif), partie B. Livret-Guide des escursions A31 et C31. Congres Geologique International, XIX session. Alger 1952, série: Maroc 8:65
Michard A (1976) Elements de Géologie Marocaine. Notes Mém Serv Géol Maroc 252:408
Moratti G, Piccardi L, Vannucci G, Belardinew ME, Dahmani M, Bendkik A, Chenakeb M (2003) The 1755 “Meknes” Earthquake (Morocco): field data and geodynamic implications. J Geodyn 36:305–322
Morel JL (1988) Evolution recente de l’orogene rifain et de son avant pays depuis la fin de la mise en place des nappes (Rif- Maroc). Mem Geodiffusion 4:584
Morel JL (1989) Etats de contrainte et cinématique de la chaine rifaine (Maroc) du Tortonien à l’actuel. Geodinamica Acta 3:238–294
Morel JL, Zouine EM, Poisson A (1993) Relations entre la subsidence des bassins moulouyens et la création des relief atlasiques (Maroc): un example d’inversion tectonique depuis le Néogène. Bull Soc Geol Fr 164:79–91
Morley CK (1986) A classification of thrust fronts. Am Ass Pet Geol 70:12–25
Morley CK, Woganan N, Sankumarn N, Hoon TB, Alief A, Simmons M (2001) Late Oligocene—recent stress evolution in rift basins of northern and central Thailand: implications for escape tectonics. Tectonophysics 334:115–150
Morley CK, Back S, Rensbergen P, Crevello P, Lambiase JJ (2003) Characteristics of repeated, detached, Miocene–Pliocene tectonic inversion events, in a large delta province on an active margin, Brunei Darussalam, Borneo. J Struct Geol 25:1147–1169
Olsen PE (1997) Stratigraphic record of the early Mesozoic breakup of Pangea in the Laurasia–Gondwana rift system. Annu Rev Earth Planet Sci 25:337–401
Ramberg H (1981) Gravity, deformation and the Earth’s crust in theory, experiments and geologic application, 2nd edn. Academic, London, pp 1–452
Suter G (1980a) Carte géologique de la Chaine Rifaine, échelle 1:500.000. Ministère de l’Energie et des Mines du Maroc, Direction de la Géologie, Rabat, Notes Mem Serv Geol Maroc 245a
Suter G (1980b) Carte structurale du Maroc, échelle 1:500.000. Ministère de l’Energie et des Mines du Maroc, Direction de la Géologie, Rabat. Notes Mem Serv Geol Maroc 245b
Taltasse P (1953) Recherches géologiques et hydrogéologiques dans le Bassin lacustre de Fès-Meknès. Notes Mem Serv Géol Maroc 115:1–300
Tilloy R (1955) Notice explicative de Feuille Fes-ouest de la Carte Geologique du maroc au 1:100.000. Notes Mem Serv Géol Maroc 109:1–62
Vannucchi P, Bettelli G (2002) Mechanics of subduction accretion as implied from the broken formations in the Apennines, Italy. Geology 30:835–838
Vially R, Letouzey J, Bénard F, Haddadi N, Desforges G, Asri H, Boudjema A (1994) Basin inversion along the North African Margin: The Saharan Atlas (Algeria). In: Roure F (ed) Peri-Tethyan Platform. Éditions Technip Paris, pp 79–118
Weijermars R, Schmeling H (1986) Scaling of Newtonian and non-Newtonian fluid dynamics without inertia for quantitative modelling of rock flow due to gravity (including the concept of rheological similarity). Phys Earth Planet Inter 43:316–330
Weijermars R, Jackson MPA, Vendeville B (1993) Rheological and tectonic modelling of salt provinces. Tectonophysics 217:143–174
Wernli R (1988) Micropaléontologie du Néogène post-nappes du Maroc septentrional et description systématique des foraminifères planctoniques. Notes Mem Serv Géol Maroc 331:1–270
Yovanovitch B (1922) La géologie du pétrole au Maroc. Bull Soc Géol Fr Ser 4(22):234–245
Zizi M (1996a) Triassic–Jurassic extensional systems and their Neogene reactivation in Northern Morocco (the Rides Prerifaines and Guercif basin), Ph.D. Thesis, Rice University, pp 1–230
Zizi M (1996b) Triassic–Jurassic extension and Alpine inversion in the northern Morocco. In: Ziegler PA, Horvath F (eds) Peri-Tethys Memoir 2: Structure and prospects of the Alpine basins and forelands. Mem Mus Natn Hist Nat 170:87–101
Zizi M (2002) Triassic-Jurassic extensional systems and their Neogene reactivation in Northern Morocco (the Rides Prerifaines and Guercif basin). Notes Mem Serv Géol Maroc 416:1–138
Zouhri M, Lamouroux C, Buret C (2001) La Mamora, charnière entre la Meseta et le Rif: son importance dans l’évolution géodynamique post-paléozoïque du Maroc. Geodinamica Acta 14:361–372
Acknowledgments
This work strongly benefited from the discussion with Prof. A. W. Bally, who is warmly thanked also for making available a lot of material about the area. ONAREP (now ONHYM) is also thanked for providing seismic sections and well logs studied and illustrated in this work. Dr. M. Dahmani, past Director of the Geological Survey of Morocco, is warmly acknowledged for his help during fieldwork years and for useful suggestions. Useful discussion in the field with M. Boccaletti, R. Gelati, G. Moratti and G. Papani greatly improved the paper. Anonymous referees and Prof. R. Greiling are also thanked for their help in improving the manuscript. Field work was funded by Italian Consiglio Nazionale delle Ricerche (CNR), Ministero dell’Università e della Ricerca (MIUR) and by the bilateral project between CNR (Italy) and CNRST (Morocco) “Structural analysis, active tectonics and fluids geochemistry in the Rif-Middle Atlas-High Atlas System of Morocco” (Italian responsible Dr. G. Moratti)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sani, F., Del Ventisette, C., Montanari, D. et al. Structural evolution of the Rides Prerifaines (Morocco): structural and seismic interpretation and analogue modelling experiments. Int J Earth Sci (Geol Rundsch) 96, 685–706 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00531-006-0118-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00531-006-0118-2