Abstract.
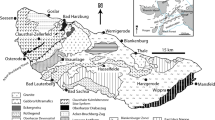
Accessory monazites from 35 granitoid samples from the Western Carpathian basement have been analysed with the electron microprobe in an attempt to broadly constrain their formation ages, on the basis of their Th, U and Pb contents. The sample set includes representative granite types from the Tatric, Veporic and Gemeric tectonic units. In most cases Lower Carboniferous (Variscan) ages have been obtained. However, a much younger mid-Permian age has been recorded for the specialised S-type granites of the Gemeric Unit, and several small A- and S-type granite bodies in the Veporic Unit and the southern Tatric Unit. This distinct Permian plutonic activity in the southern part of the Western Carpathians is an important, although previously little considered geological feature. It appears to be not related to the Variscan orogeny and is interpreted here to reflect the onset of the Alpine orogenic cycle, with magma generation in response to continental rifting. The voluminous Carboniferous granitoid bodies in the Tatric and Veporic units comprise S- and I-type variants which document crustal anatexis accompanying the collapse of a compressional Variscan orogen sector. The Variscan magmas were most likely produced through the remelting of a subducted Precambrian volcanic arc-type crust which included both igneous and sedimentary reworked volcanic-arc material. Although the 2σ errors of the applied dating method are quite large and typically ±10–20 Ma for single samples, it would appear from the data that the Variscan S-type granitoids (333–367 Ma) are systematically older than the Variscan I-type granitoids (308–345 Ma). This feature is interpreted in terms of a prograde temperature evolution in the deeper parts of the post-collisional Variscan crust. In accordance with recently published zircon ages, this study shows that the Western Carpathian basement must be viewed as a distinct "eastern" tectonomagmatic province in the Variscan collision zone, where the post-collisional crustal melting processes occurred ~20 Ma earlier than in the central sector (South Bohemian Batholith, Hohe Tauern Batholith).
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Electronic Publication
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Finger, .F., Broska, .I., Haunschmid, .B. et al. Electron-microprobe dating of monazites from Western Carpathian basement granitoids: plutonic evidence for an important Permian rifting event subsequent to Variscan crustal anatexis. Int J Earth Sci (Geol Rundsch) 92, 86–98 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00531-002-0300-0
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00531-002-0300-0