Abstract.
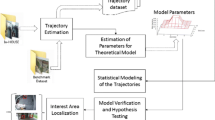
We present a framework for multicamera video surveillance. The framework consists of three phases: detection, representation, and recognition. The detection phase handles multisource spatiotemporal data fusion for efficiently and reliably extracting motion trajectories from video. The representation phase summarizes raw trajectory data to construct hierarchical, invariant, and content-rich descriptions of the motion events. Finally, the recognition phase deals with event classification and identification on the data descriptors. Through empirical study in a parking-lot-surveillance setting, we show that our spatiotemporal fusion scheme and biased sequence-data learning method are highly effective in identifying suspicious events.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Amari S, Wu S (1999) Improving support vector machine classifiers by modifying kernel functions. Neural Netw 12(6):783-789
Azuma R (1995) Predicative tracking for augmented reality. University of North Carolina-Chapel Hill, Department of Computer Science, TR-95-007
Bengio Y (1998) Markovian models for sequential data. Neural Comput Surv 2:129-162
Boyd JE, Hunter E, Kelly PH, Tai LC, Phillips CB, Jain RC (1998) Mpi-video infrastructure for dynamic environments. In: IEEE international conference on multimedia systems ‘98, June 1998
Bozkaya T, Ozsoyoglu M (1997) Distanced-based indexing for high-dimensional metric spaces. In: Proc. ACM SIGMOD, pp 357-368
Brown RG (1983) Introduction to random signal analysis and Kalman filtering. Wiley, New York
Burden RL, Faires JD (eds) (1993) Numerical analysis, 5th edn. PWS, New York
Burges CJC (1999) Geometry and invariance in kernel based methods. In: Schlkopf B, Burges CJC, Smola AJ (eds) Advances in kernel methods: support vector learning. MIT Press, Cambridge, MA
Christin L, Eskin E, Cohen A, Westo J, Noble WS (2002) Mismatch string kernels for svm protein classification. Neural Inf Process Syst 15:1441-1448
Chudova D, Smyth P (2002) Pattern discovery in sequences under a markov assumption, ACM SIGKDD
Church E (1945) Revised geometry of the aerial photograph. Bull Aerial Photogrammetry 15
Cohn H (1980) Conformal mapping on Riemann surfaces. Dover, Mineola, NY
Collins RT, Lipton AJ (2000) A system for video surveillance and monitoring (vsam project final report). CMU Technical Report CMU-RI-TR-00-12
DeMenthon DF, Davis LS (1995) Model-based object pose in 25 lines of code. Int J Comput Vision 15:123-141
Duda RO, Hart RE, Stork DG (2001) Pattern classification, 2nd edn. Wiley, New York
Farin G (1997) Curves and surfaces for computer aided geometric design, 4th edn. Academic, San Diego
Faugeras O (1993) Three-dimensional computer vision. MIT Press, Cambridge, MA
Foley JD, van Dam A, Feiner SK, Hughes JF (1990) Computer graphics: principles and practice, 2nd edn. Addison-Wesley, Reading, MA
Fukunaga K (1990) Introduction to statistical pattern recognition, 2nd edn. Academic, Boston
Haralick R, Joo H, Lee C, Zhuang X, Vaidya V, Kim M (1989) Pose estimation from corresponding point data. IEEE Trans Syst Man Cybern 19:1426-46
Haykin S (1999) Neural networks, 2nd edn. Prentice Hall, Englewood Cliffs, NJ
Horaud R, Dornaika F, Lamiroy B, Christy S (1997) Object pose: the link between weak perspective, paraperspective and full perspective. Int J Comput Vision 22:173-189
Isard M, Blake A (1998) Condensation - conditional density propagation for visual tracking. Int J Comput Vision 29:5-28
Isard M, Blake A (1998) ICONDENSATION: Unifying low-level and high-level tracking in a stochastic framework. Lecture notes in computer science vol 1406. Springer, Berlin Heidelberg New York, pp 893-908. Int J Comput Vis 29(1):5-28
Jaakkola TS, Diekhans M, Haussler D (1999) Using the fisher kernel method to detect remote protein homologies. In: Proc. 7th international conference on intelligent system for molecular biology
Jaakkola TS, Haussler D (1998) Exploiting generative models in discriminative classifiers. In: Proceedings of the conference on advances in neural information processing systems II, pp 487-493
Jaakola TS, Haussler D (1999) Probabilistic kernel regression models. In: Conference on AI and statistics
Julier SJ, Uhlmann JK, Durrant-Whyte HF (1995) A new approach for filtering nonlinear systems. In: Proc. American Control Conference, Seattle
Kanatani K (1998) Optimal homography computation with a reliability measure. In: Proc. IAPR workshop on machine vision applications, November 1998
Kettnaker V, Zabih R (1999) Bayesian multi-camera surveillance. In: CVPR
Kitagawa G (1996) Monte Carlo filter and smoother for non-Gaussian nonlinear state space models. J Comput Graph Stat 5:1-25
Lee L, Romano R, Stein G (2000) Monitoring activities from multiple video streams: establishing a common coordinate system. IEEE Trans PAMI 22(8):758-767
Leslie C, Eskin E, Noble WS (2002) The spectrum kernel: a string kernel for svm protein classification. In: Proc. Pacific symposium on biocomputing. World Scientific, Singapore
Lou J, Yang H, Hu W, Tan T (2002) Visual vehicle tracking using an improved ekf. In: ACCV
Maybank SJ, Worrall AD, Sullivan GD (1996) Filter for car tracking based on acceleration and steering angle. In: Proc. British Machine Vision Conference
Maybeck PS (1979) Stochastic models, estimation, and control, vol 1. Academic, New York
Pavlidis I, Morellas V (2001) Two examples of indoor and outdoor surveillance systems: motivation, design, and testing. In: Proc. 2nd European workshop on advanced video-based surveillance
Pavlidis I, Morellas V, Tsiamyrtzis P, Harp S (2001) Urban surveillance systems: from the laboratory to the commercial world. Proc IEEE 89(10):1478-1497
Pitt MK, Shephard N (1999) Filtering via simulation: Auxiliary particle filters. J Am Stat Assoc 94:590-599
Regazzoni C, Varshney PK (2002) Multisensor surveillance systems based on image and video data. In: Proc. IEEE conference on image processing
Sears FW (1958) Optics, 3rd edn. Addison-Wesley, Reading, MA
Starner T, Pentland A (1994) Visual recognition of American sign language using hidden Markov models. Technical Report Master’s thesis, MIT, February 1995, Program in Media Arts & Sciences, MIT Media Laboratory. Also Media Lab VISMOD TR 316. http://www-white.media.mit.edu vismod people publications publications.html [860 Kb]
Struik DJ (1961) Differential geometry, 2nd edn. Addison-Wesley, Reading, MA
Vapnik V (1995) The Nature of statistical learning theory. Springer, Berlin Heidelberg New York
Watkins C (1999) Dynamic alignment kernels. Technical Report, Department of Computer Science, University of London
Welch G, Bishop G (2002) http://www.cs.unc.edu/welch/kalman
Welch G, Bishop G (2002) An introduction to the Kalman filter. University of North Carolina-Chapel Hill, TR 95-041
Wu G, Chang E Adaptive feature-space conformal transformation for learning imbalanced data. In: International conference on machine learning (ICML), August 2003
Xu G, Zhang Z (1996) Epipolar geometry in stereo, motion and object recognition. Kluwer, Dordrecht
Wu Y, Jiao L, Wu G, Wang YF, Chang E (2003) Invaraint feature extraction and biased statistical inference for video surveillance. In: Proc. IEEE conference on advanced video and signal-based surveillance, Miami, FL
Zhang Z (2000) A flexible new technique for camera calibration. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell 22:1330-4
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Published online: 11 October 2004
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jiao, L., Wu, Y., Wu, G. et al. Anatomy of a multicamera video surveillance system. Multimedia Systems 10, 144–163 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00530-004-0147-2
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00530-004-0147-2