Abstract
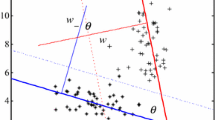
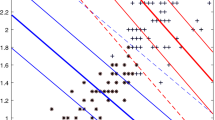
In this paper, we propose a novel nonparallel hyperplane classifier, named ν-nonparallel support vector machine (ν-NPSVM), for binary classification. Based on our recently proposed method, i.e., nonparallel support vector machine (NPSVM), which has been proved superior to the twin support vector machines, ν-NPSVM is parameterized by the quantity ν to let ones effectively control the number of support vectors. By combining the ν-support vector classification and the ν-support vector regression together to construct the primal problems, ν-NPSVM inherits the advantages of ν-support vector machine so that enables us to eliminate one of the other free parameters of the NPSVM: the accuracy parameter ε and the regularization constant C. We describe the algorithm, give some theoretical results concerning the meaning and the choice of ν, and also report the experimental results on lots of data sets to show the effectiveness of our method.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Cortes C, Vapnik VN (1995) Support-vector networks. Mach Learn 20(3):273–297
Vapnik VN (1996) The nature of statistical learning theory. Springer, New York
Vapnik VN (1998) Statistical learning theory. Wiley, New York
Burges C (1998) A tutorial on support vector machines for pattern recognition. Data Min Knowl Disc 2:121–167
Deng NY, Tian YJ, Zhang CH (2012) Support vector machines: optimization based theory, algorithms, and extensions. Chapman and Hall/CRC, London
Trafalis TB, Ince H (2000) Support vector machine for regression and applications to financial forecasting. In: Proceedings of IEEE-INNSENNS international joint conference neural networks, vol 6, pp 348–353
Li S, Kwok JT, Zhu H, Wang Y (2003) Texture classification using the support vector machines. Pattern Recogn 36(12):2883–2893
Wu YC, Lee YS, Yang JC (2008) Robust and efficient multiclass SVM models for phrase pattern recognition. Pattern Recogn 41(9):2874–2889
Isa D, Lee LH, Kallimani VP, RajKumar R (2008) Text document preprocessing with the Bayes formula for classification using the support vector machine. IEEE Trans Knowl Data Eng 20(9):1264–1272
Karsten MB (2011) Kernel methods in bioinformatics. Handb Stat Bioinform Part 3:317–334
Wang XY, Wang T, Bu J (2011) Color image segmentation using pixel wise support vector machine classification. Pattern Recogn 44(4):777–787
Khan N, Ksantini R, Ahmad I, Boufama B (2012) A novel SVM+ NDA model for classification with an application to face recognition. Pattern Recogn 45(1):66–79
Mangasarian OL, Wild EW (2006) Multisurface proximal support vector classification via generalized eigenvalues. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell 28(1):69–74
Jayadeva RK, Khemchandani R, Chandra S (2007) Twin support vector machines for pattern classification. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell 29(5):905–910
Kumar MA, Gopal M (2008) Application of smoothing technique on twin support vector machines. Pattern Recogn Lett 29(13):1842–1848
Khemchandani R, Jayadeva RK, Chandra S (2009) Optimal kernel selection in twin support vector machines. Optim Lett 3(1):77–88
Kumar MA, Gopal M (2009) Least squares twin support vector machines for pattern classification. Expert Syst Appl 36(4):7535–7543
Shao YH, Zhang CH, Wang XB, Deng NY (2011) Improvements on twin support vector machines. IEEE Trans Neural Netw 22(6):962–968
Shao YH, Deng NY (2013) A novel margin-based twin support vector machine with unity norm hyperplanes. Neural Comput Appl 22:1627–1635
Shao Y-H, Deng N-Y (2012) A coordinate descent margin based-twin support vector machine for classification. Neural Netw 25:114–121
Peng XJ (2010) Tsvr: An efficient twin support vector machine for regression. Neural Netw 23(3):365–372
Chen X, Yang J, Ye Q, Liang J (2011) Recursive projection twin support vector machine via within-class variance minimization. Pattern Recogn. doi:10.1016/j.patcog.2011.03.001
Qi ZQ, Tian YJ, Shi Y (2012) Laplacian twin support vector machine for semi-supervised classification. Neural Netw 35:46–53
Qi ZQ, Tian YJ, Shi Y (2012) Twin support vector machine with universum data. Neural Netw 36:112–119
Qi ZQ, Tian YJ, Shi Y (2013) Robust twin support vector machine for pattern classification. Pattern Recogn 46:305–316
Qi ZQ, Tian YJ, Shi Y (2013) Structural twin support vector machine for classification. Knowl-Based Syst 43:74–81
Tian YJ, Shi Y, Liu XH (2012) Recent advances on support vector machines research. Technol Econ Dev Econ 18:5–33
Tian YJ, Ju XC, Qi ZQ (2013) Efficient sparse nonparallel support vector machines for classification. Neural Comput Appl. doi:10.1007/s00521-012-1331-5
Tian YJ, Qi ZQ, Ju XC, Shi Y, Liu XH (2013) Nonparallel support vector machines for pattern classification. IEEE Trans Cybern. doi:10.1109/TCYB.2013.2279167
Tian YJ, Ju XC, Qi ZQ, Shi Y (2013) Improved twin support vector machine. Sci China Math. doi:10.1007/s11425-013-4718-6
Platt J (2000) Fast training of support vector machines using sequential minimal optimization. In: Schölkopf B, Burges CJC, Smola AJ (eds) Advances in kernel methods—support vector learning. MIT Press, Cambridge
Williamson RC, Scholkopf B, Smola A, Bartlett PL (2000) New support vector algorithms. Neural Comput 12:1207–1245
Blake CL, Merz CJ (1998) UCI repository for machine learning databases. Department of Information and Computer Science, University of California, Irvine (Online). http://www.ics.uci.edu/~mlearn/MLRepository.html
Acknowledgments
This work has been partially supported by grants from National Natural Science Foundation of China (Nos. 11271361, 71331005), the CAS/SAFEA International Partnership Program for Creative Research Teams, Major International (Regional) Joint Research Project (No. 71110107026), and the Ministry of water resources’ special funds for scientific research on public causes (No. 201301094).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tian, Y., Zhang, Q. & Liu, D. ν-Nonparallel support vector machine for pattern classification. Neural Comput & Applic 25, 1007–1020 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00521-014-1575-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00521-014-1575-3