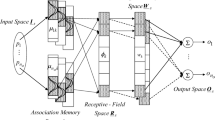
Abstract
In this study, a novel indirect adaptive controller is introduced for a class of unknown nonlinear systems. The proposed method provides a simple control architecture that merges from the cerebellar model articulation controller (CMAC) network and hierarchical fuzzy logic; therefore, the complicated CMAC structure can be simplified. The overall adaptive scheme guarantees the uniform stability of the closed-loop system. A simulation is presented to demonstrate the performance of the proposed methodology.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aguilar-Ibañez CF (2009) The Lyapunov direct method for the stabilization of the ball on the actuated beam. Int J Control 82(12):2169–2178
Aguilar-Ibañez CF, Garrido Moctezuma R, Davila J (2012) Output feedback trajectory stabilization of the uncertainty DC servomechanism system. ISA Trans 51(6):801–807
Angelov P, Kordon A (2010) Adaptive inferential sensors based on evolving fuzzy models. IEEE Trans Syst Man Cybern B Cybern 40(2):529–539
Angelov P (2011) Fuzzily connected multimodel systems evolving autonomously from data streams. IEEE Trans Syst Man Cybern B Cybern 41(4):898–910
Albus JS (1975) A New approach to manipulator control: the cerebellar model articulation controller (CMAC). J Dyn Syst Meas Control Trans ASME 97:220–227
Chen C-T (1998) Linear system theory and design, 3rd edn. Oxford University Press, Oxford, ISBN 0-19-511777-8
Chen C-H (2012) Wavelet-based adaptive robust control for a class of MIMO uncertain nonlinear systems. Neural Comput Appl 21:747–762
Chen C-S (2011) Supervisory adaptive tracking control of robot manipulators using interval type-2 TSK fuzzy logic system. IET Control Theory Appl 5(15):1796–1807
Fan X, Zhang N, Teng S (2003) Trajectory planning and tracking of ball and plate system using hierarchical fuzzy control scheme. Fuzzy Sets Syst 144:297–312
Fan L-L, Song Y-D (2012) Neuro-adaptive model-reference fault-tolerant control with application to wind turbines. IET Control Theory Appl 6(4):475–486
Han SI, Lee JM (2011) Friction and uncertainty compensation of robot manipulator using optimal recurrent cerebellar model articulation controller and elasto-plastic friction observer. IET Control Theory Appl 5(18):2120–2141
Hojati M, Gazor S (2002) Hybrid adaptive fuzzy identification and control of nonlinear systems. IEEE Trans Fuzzy Syst 10(2):198–210
Isidori A (1999) Nonlinear control systems II. Springer, Berlin, ISBN 1-85233-188-7
Jimenez-Lizarraga M, Basin M, Rodriguez-Ramirez P (2012) Robust mini–max regulator for uncertain non-linear polynomial systems. IET Control Theory Appl 6(7):963–970
Jimenez-Lizarraga M, Basin M, Rodriguez-Ramirez P, Rubio JJ (2012) Robust control of a nonlinear electrical oscillator modeled by buffing equation. Int J Innov Comput Inf Control 8(5(A)):2941–2952
Jiménez-Lizárraga M, Poznyak A (2012) Necessary conditions for Robust Stackelberg equilibrium in a multi-model differential game. Optim Control Appl Methods 33(5):595–613
Knuplez A, Chowdhury A, Svecko R (2003) Modeling and control design for the ball and plate system. IEEE Int Conf Indus Technol 2:1064–1067
Leite D, Ballini R, Costa P, Gomide F (2012) Evolving fuzzy granular modeling from nonstationary fuzzy data streams. Evol Syst 3(2):65–79
Lemos A, Caminhas W, Gomide F (2011) Multivariable Gaussian evolving fuzzy modeling system. IEEE Trans Fuzzy Syst 19(1):91–104
Lin C-M, Lin M-H, Yeh R-G (2012) Synchronization of unified chaotic system via adaptive wavelet cerebellar model articulation controller. Neural Comput Appl. doi:10.1007/s00521-012-1021-3
Lughofer E, Angelov P (2011) Handling drifts and shifts in online data streams with evolving fuzzy systems. Appl Soft Comput 11(2):2057–2068
Lughofer E (2012) Single pass active learning with conflict and ignorance. Evol Syst 3:251–271
Lughofer E (2012) A dynamic split-and-merge approach for evolving cluster models. Evol Syst 3:135–151
Maciel L, Lemos A, Gomide F, Ballini R (2012) Evolving fuzzy systems for pricing fixed income options. Evol Syst 3:5–18
Macnab CJB (2011) Neural-adaptive control using alternate weights. Neural Comput Appl 20:211–221
Pérez-Cruz JH, Poznyak A (2010) Control of nuclear research reactors based on a generalized hopfield neural network. Intell Autom Soft Comput 16(1):39–60
Pérez Cruz JH, Ruiz Velázquez E, Rubio JJ, de Alba Padilla CA (2012) Robust adaptive neurocontrol of SISO nonlinear systems preceded by unknown deadzone. Math Probl Eng 2012:1–23
Pérez-Cruz JH, Rubio JJ, Ruiz-VelPázquez E, Solís-Perales G. (2012) Tracking control based on recurrent neural networks for nonlinear systems with multiple inputs and unknown deadzone. Abstr Appl Anal 2012:1–18
Pérez-Cruz JH, Alanis AY, Rubio JJ, Pacheco J (2012) System identification using multilayer differential neural networks: a new result. J Appl Math 2012:1–20
Pérez-Olvera CA (2009) Control visual difuso de un sistema no-lineal, CIC-IPN, Master thesis
Pérez-Olvera CA, Moreno-Armendáriz MA, Rubio-Espino E, Zaragoza-Díaz JO (2008) Modulo de visión por computadora en tiempo real para el control de un sistema plano-esfera. Res Comput Sci 38:283–293
Rubio JJ, Yu W (2006) A new discrete-time sliding-mode control with time-varying gain and neural identification. Int J Control 79(4):338–348
Rubio JJ, Yu W (2007) Stability analysis of nonlinear system identification via delayed neural networks. IEEE Trans Circuits Syst II 54(2):161–165
Rubio JJ, Angelov P, Pacheco J (2011) An uniformly stable backpropagation algorithm to train a feedforward neural network. IEEE Trans Neural Netw 22(3):356–366
Rubio JJ, Torres C, Aguilar C (2011) Optimal control based in a mathematical model applied to robotic arms. Int J Innov Comput Info Control 7(8):5045–5062
Rubio JJ (2012) Modified optimal control with a backpropagation network for robotic arms. IET Control Theory Appl 6(14):2216–2225
Rubio JJ, Figueroa M, Pérez-Cruz JH, Bejarano FJ (2012) Geometric approach and structure at infinite controls for the disturbance rejection. IET Control Theory Appl 6(16):2528–2537
Rubio JJ, Figueroa M, Pérez Cruz JH, Rumbo J (2012) Control to stabilize and mitigate disturbances in a rotatory inverted pendulum. Mexican J Phys E 58(2):107–112
Wang LX (1994) Adaptive fuzzy systems and control. Prentice-Hall, Englewood Cliffs
Wang C, Lin Y (2012) Decentralised adaptive dynamic surface control for a class of interconnected non-linear systems. IET Control Theory Appl 6(9):1172–1181
Yoo SJ (2012) Adaptive neural output-feedback control for a class of non-linear systems with unknown time-varying delays. IET Control Theory Appl 6(1):130–140
Yen M-C, Hsu C-F, Chung I-H (2012) Design of a CMAC-based smooth adaptive neural controller with a saturation compensator. Neural Comput Appl 21:35–44
Yu W, Panuncio F, Li X (2011) Two-stage neural sliding-mode control of magnetic levitation in minimal invasive surgery. Neural Comput Appl 20:1141–1147
Acknowledgments
The authors are grateful to the editors and reviewers for their valuable comments and insightful suggestions, which helped to improve this research significantly. The authors thank the Secretaría de Investigación y Posgrado, Comisión de Operación y Fomento de Actividades Académicas del IPN, and Consejo Nacional de Ciencia y Tecnología for their help in this research. The first author thanks the Secretaría de Investigación y Posgrado of the IPN under Research Grand No. 20113187.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rodríguez, F.O., de Jesús Rubio, J., Gaspar, C.R.M. et al. Hierarchical fuzzy CMAC control for nonlinear systems. Neural Comput & Applic 23 (Suppl 1), 323–331 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00521-013-1423-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00521-013-1423-x