Abstract
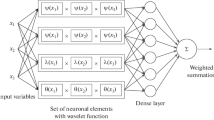
In this article, a wavelet neural network (WNN) model is proposed for approximating arbitrary nonlinear functions. Our WNN model structure comes from the idea of adaptive neuro-fuzzy inference system (ANFIS) which is used for obtaining fuzzy rule base from the input–output data of an unknown function. The WNN model which is called in this study as adaptive wavelet network (AWN) consists of wavelet scaling functions in its processing units whereas in an ANFIS, mostly Gaussian-type membership functions are used for a function approximation. We present to train an AWN by a hybrid-learning method containing least square estimation (LSE) with gradient-based optimization algorithm to obtain the optimal translation and dilation parameters of our AWN for model accuracy. Simulation examples are also given to illustrate the effectiveness of the method.













Similar content being viewed by others
References
Zhang Q (1997) Using wavelet networks in nonparametric estimation. IEEE Trans Neural Netw 8:227–336. doi:10.1109/72.557660
Zhang Q, Benveniste A (1992) Wavelet networks. IEEE Trans Neural Netw 3:889–898. doi:10.1109/72.165591
Zhang J, Walter GG, Lee WNW (1995) Wavelet neural networks for function learning. IEEE Trans Signal Process 43:1485–1497. doi:10.1109/78.388860
Ho Daniel WC, Zhang PA, Jinhua X (2001) Fuzzy wavelet networks for function learning. IEEE Trans Fuzzy Syst 9:200–211. doi:10.1109/91.917126
Kim J, Kasabov N (1999) HyFIS: adaptive neuro-fuzzy inference systems and their application to nonlinear dynamical systems. Neural Netw 12:1301–1319. doi:10.1016/S0893-6080(99)00067-2
Jang JSR (1993) ANFIS: adaptive-network-based fuzzy inference systems. IEEE Trans Syst Man Cybern 23(3):665–685. doi:10.1109/21.256541
Horikawa S, Furuhashi T, Uchikawa Y (1992) On fuzzy modeling using fuzzy neural networks with the back-propagation algorithm. IEEE Trans Neural Netw 3(5):801–806. doi:10.1109/72.159069
Leonard J, Kramer M (1991) Radial basis function networks for classifying process faults. IEEE Control Syst 11:31–38. doi:10.1109/37.75576
Tan Y, Dang X, Liang F, Su CY (2000) Dynamic wavelet neural network for nonlinear dynamic system identification. In: Proceedings of the 2000 IEEE, international conference on control applications
Mallat S (1989) A theory for multiresolution signal decomposition: the wavelet representation. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell 11(7):674–693. doi:10.1109/34.192463
Sanner R, Slotine J-JE (1992) Gaussian networks for direct adaptive control. IEEE Trans Neural Netw 13(6):837–863. doi:10.1109/72.165588
Ljung L (1987) System identification: theory for the user. Prentice-Hall, Englewood Cliffs
Strobach P (1990) Linear prediction theory: a mathematical basis for adaptive systems. Springer, New York
Gholizadeh S, Salajegheh E, Torkzadeh P (2008) Structural optimization with frequency constraints by genetic algorithm using wavelet radial basis function neural network. J Sound Vibrat 312:316–331. doi:10.1016/j.jsv.2007.10.050
Gill PE, Murray W, Wright MH (1993) Practical optimization. Academic Press Ltd, London
Chen J, Bruns DD (1995) WaveARX neural network development for system identification using a systematic design synthesis. Ind Eng Chem Res 34:4420–4435. doi:10.1021/ie00039a034
Box GEP (1970) Time series analysis, forecasting and control. Holden Day, San Francisco
Chen Y, Yang B, Dong J (2006) Time-series prediction using a local linear wavelet neural network. Neurocomputing 69:449–465. doi:10.1016/j.neucom.2005.02.006
Tong RM (1980) The evaluation of fuzzy models derived from experimental data. Fuzzy Sets Syst 4:1–12. doi:10.1016/0165-0114(80)90059-7
Pedrycz W (1984) An identification algorithm in fuzzy relational systems. Fuzzy Sets Syst 13:153–167. doi:10.1016/0165-0114(84)90015-0
Xu CW (1987) Fuzzy model identification and self-learning for dynamic systems. IEEE Trans Syst Man Cybern 17:683–689. doi:10.1109/TSMC.1987.289361
Sugeno M et al (1991) Linguistic modeling based on numerical data. Proc IFSA 91:234–247
Surmann H et al (1993) Self-organizing and genetic algorithm for an automatic design of fuzzy control and decision systems. Proc FUFIT’s 93:1079–1104
Jang JSR et al (1997) Neuro-fuzzy and Soft computing: a computational approach to learning and machine intelligence. Prentice-Hall, Upper Saddle river
Kasabov NK et al (1997) FuNN/2-A fuzzy neural network architecture for adaptive learning and knowledge acquisition. Inf Sci 101:155–175. doi:10.1016/S0020-0255(97)00007-8
Chen YH et al (2004) Nonlinear system modeling via optimal design of neural trees. Int J Neural Syst 14(2):125–137. doi:10.1142/S0129065704001905
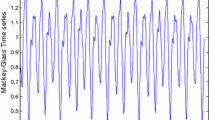
Mackey M, Glass L (1977) Oscillation and chaos in physiological control systems. Science 197:287–289. doi:10.1126/science.267326
Wang LX et al (1992) Generating fuzzy rules by learning from examples. IEEE Trans Fuzzy Syst Man Cybern 22:1414–1427. doi:10.1109/21.199466
Cho KB et al (1995) Radial basis function based adaptive fuzzy systems their application to system identification and prediction. Fuzzy Sets Syst 83:325–339. doi:10.1016/0165-0114(95)00322-3
Rojas I et al (2002) Time series analysis using normalized PG-RBF network with regression weights. Neurocomputing 42:167–285. doi:10.1016/S0925-2312(01)00338-1
Kim D et al (1997) Forecasting time series with genetic fuzzy predictor ensembles. IEEE Trans Fuzzy Syst 5(2):523–535
Narendra KS, Parthasarathy K (1990) Identification and control dynamical systems using neural networks. IEEE Trans Neural Netw 1(1):4–27. doi:10.1109/72.80202
Abiyev RH, Kaynak O (2008) Fuzzy wavelet neural network for identification and control of dynamic plants—a novel structure and comparative study. IEEE Trans Ind Electron 55(8):3133–3140. doi:10.1109/TIE.2008.924018
Elman JL (1990) Finding structure in time. Cogn Sci 14(2):179–211
Juang CF, Lin CT (1999) A recurrent self-organizing neural fuzzy inference network. IEEE Trans Neural Netw 10(4):828–845. doi:10.1109/72.774232
Juang C-F (2002) A TSK-type recurrent fuzzy network for dynamic systems processing by neural network and genetic algorithms. IEEE Trans Fuzzy Syst 10(2):155–170. doi:10.1109/91.995118
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Oysal, Y., Yilmaz, S. An adaptive wavelet network for function learning. Neural Comput & Applic 19, 383–392 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00521-009-0297-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00521-009-0297-4