Abstract
Purpose
The study seeks to prospectively evaluate pulmonary function and quality of life (QOL) in medically inoperable early-stage lung cancer patients undergoing stereotactic body radiotherapy (SBRT).
Methods
QOL was assessed by Functional Assessment of Cancer Therapy-Lung (FACT-L) and the UCSD Medical Center Pulmonary Rehabilitation Program Shortness-of-Breath Questionnaire before and after SBRT at 6 weeks, and every 3 months until 12 months. Clinical investigations included pulmonary functions tests and blood profile and chemistries. SBRT was delivered on a Novalis/BrainLab system.
Results
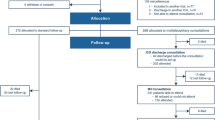
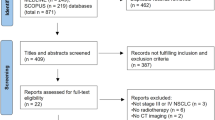
Twenty-one analyzable patients were enrolled between July 2008 to April 2009. There were 12 males (52.4 %), 14 patients (66.7 %) had Zubrod performance 1, the median age was 77 years (range 61–90), and 87 % was inoperable because of pulmonary impairment. Median tumor size was 3.0 cm (range 1–4.6). Median follow-up was 17.6 months. One-year local control was 100 %. There were no significant changes in the median total FACT-L scores: 109 at baseline compared to 112 at 1 year. Mean UCSD scores were not significant for the year. No significant changes in mean baseline compared to 1-year FEV1 and 6-min walks as % predicted were seen but a significant DLCO change (p = 0.012) was attributed to the decreased range in the standard deviations.
Conclusions
Following SBRT, QOL is not significantly degraded. Pulmonary function is likewise not significantly impaired overall. Along with favorable survival results, these findings confirm that SBRT is appropriate for this patient population.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Hansen HH (2009) Introduction. In: Hansen HH (ed) Lung Cancer Therapy Annual 6. Informa Health Care, New York, pp 1–6
Jemal A, Siegel R, Ward E, Hao Y, Xu J, Thun MJ (2009) Cancer statistics, 2009. CA Cancer J Clin 59:225–249
Hansen HH (2009) Histopathology. In: Hansen HH (ed) Lung cancer therapy annual 6. Informa Health Care, New York, pp 45–56
Juettner-Smolle FM, Lindenmann J, Matzi V, Neubock N (2010) Resection in stage I/II non-small cell lung cancer. In: Heide J et al (eds) Controversies in the treatment of lung cancer. Karger, Basel, pp 71–77
Little AG, Rusch VW, Bonner JA, Gaspar LE, Green MR, Webb WR, Stewart AK (2005) Patterns of surgical care of lung cancer patients. Ann Thorac Surg 80:2051–2056
Ginsberg RJ, Rubinstein LV (1995) Randomized trial of lobectomy versus limited resection for T1 N0 non-small cell lung cancer. Lung Cancer Study Group. Ann Thorac Surg 60:615–622
Nyman J, Johansson KA, Hultén U (2006) Stereotactic hypofractionated radiotherapy for stage I non-small cell lung cancer—mature results for medically inoperable patients. Lung Cancer 51:97–103
Lax I, Blomgren H, Näslund I, Svanström R (1994) Stereotactic radiotherapy of malignancies in the abdomen. Methodological aspects. Acta Oncol 33:677–683
Stephans KL, Djemil T, Reddy CA et al (2009) A comparison of two stereotactic body radiation fractionation schedules for medically inoperable stage I non-small cell lung cancer: the Cleveland Clinic experience. J Thorac Oncol 4:976–982
Haasbeek CJ, Lagerwaard FJ, de Jaeger K, Slotman BJ, Senan S (2009) Outcomes of stereotactic radiotherapy for a new clinical stage I lung cancer arising postpneumonectomy. Cancer 115:587–594
Haasbeek CJ, Lagerwaard FJ, Antonisse ME, Slotman BJ, Senan S (2010) Stage I nonsmall cell lung cancer in patients aged > or =75 years: outcomes after stereotactic radiotherapy. Cancer 116:406–414
Hoopes DJ, Tann M, Fletcher JW, Forquer JA, Lin PF, Lo SS, Timmerman RD, McGarry RC (2007) FDG-PET and stereotactic body radiotherapy (SBRT) for stage I non-small-cell lung cancer. Lung Cancer 56:229–234
Onishi H, Shirato H, Nagata Y et al (2007) Hypofractionated stereotactic radiotherapy (HypoFXSRT) for stage I non-small cell lung cancer: updated results of 257 patients in a Japanese multi-institutional study. J Thorac Oncol 2:S94–S100
Chang JY, Roth JA (2007) Stereotactic body radiation therapy for stage I non-small cell lung cancer. Thorac Surg Clin 17:251–259
Timmerman R, Papiez L, McGarry R et al (2003) Extracranial stereotactic radioablation: results of a phase I study in medically inoperable stage I non-small cell lung cancer. Chest 124:1946–1955
Timmerman R, McGarry R, Yiannoutsos C et al (2006) Excessive toxicity when treating central tumors in a phase II study of stereotactic body radiation therapy for medically inoperable early-stage lung cancer. J Clin Oncol 24:4833–4839
Timmerman R, Paulus R, Galvin J, Michalski J, Straube W, Bradley J, Fakiris A, Bezjak A, Videtic G, Johnstone D, Fowler J, Gore E, Choy H (2010) Stereotactic body radiation therapy for inoperable early stage lung cancer. JAMA 303:1070–1076
Langendijk JA, Aaronson NK, de Jong JM, ten Velde GP, Muller MJ, Slotman BJ, Wouters EF (2002) Quality of life after curative radiotherapy in Stage I non-small-cell lung cancer. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 53:847–853
van der Voort van Zyp NC, Prévost JB, van der Holt B, Braat C, van Klaveren RJ, Pattynama PM, Levendag PC, Nuyttens JJ (2010) Quality of life after stereotactic radiotherapy for stage I non-small-cell lung cancer. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 77:31–37
Lung (2002) In: Greene FL et al. (eds) AJCC cancer staging handbook, 6th edn. Springer, New York, pp 191–204
Videtic GM, Stephans K, Reddy C, Gajdos S, Kolar M, Clouser E, Djemil T (2010) Intensity-modulated radiotherapy-based stereotactic body radiotherapy for medically inoperable early-stage lung cancer: excellent local control. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 77:344–349
Stephans KL, Djemil T, Reddy CA et al (2009) Comprehensive analysis of pulmonary function test (PFT) changes after stereotactic body radiotherapy (SBRT) for stage I lung cancer in medically inoperable patients. J Thorac Oncol 4:838–844
Lagerwaard FJ, Haasbeek CJ, Smit EF, Slotman BJ, Senan S (2008) Outcomes of risk-adapted fractionated stereotactic radiotherapy for stage I non-small-cell lung cancer. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 70:685–692
Cella DF, Bonomi AE, Lloyd SR, Tulsky DS, Kaplan E, Bonomi P (1995) Reliability and validity of the Functional Assessment of Cancer Therapy-Lung (FACT-L) quality of life instrument. Lung Cancer 12:199–220
Henoch I, Bergman B, Gustafsson M, Gaston-Johansson F, Danielson E (2007) The impact of symptoms, coping capacity, and social support on quality of life experience over time in patients with lung cancer. J Pain Symptom Manag 34:370–379
Eakin EG, Resnikoff PM, Prewitt LM, Ries AL, Kaplan RM (1998) Validation of a new dyspnea measure: the UCSD Shortness of Breath Questionnaire. University of California, San Diego. Chest 113:619–624
http://ctep.cancer.gov/protocolDevelopment/electronic_applications/docs/ctcaev3.pdf, accessed January 2, 2011
Mohan A, Mohan C, Pathak AK, Pandey RM, Guleria R (2007) Impact of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease on respiratory status and quality of life in newly diagnosed patients with lung cancer. Respirology 12:240–247
Lima LN, da Silva RA, Gross JL, Deheinzelin D, Negri EM (2009) Assessment of pulmonary function and quality of life in patients submitted to pulmonary resection for cancer. J Bras Pneumol 35:521–528
Osoba D, Rodrigues G, Myles J, Zee B, Pater J (1998) Interpreting the significance of changes in health-related quality-of-life scores. J Clin Oncol 16:139–144
Sorenson LM, Reddy C, Videtic G (2010) Lessons learned from a prospective study of quality of life in lung cancer patients undergoing stereotactic body radiotherapy: the earlier, the better! Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 78(suppl):S608–S609
Conflict of interest statement
With respect to submitting this original manuscript titled:
A prospective study of quality of life including fatigue and pulmonary function after stereotactic body radiotherapy for medically inoperable early-stage lung cancer.
I declare formally and on behalf of Chandana A. Reddy, MS, Lisa Sorenson, MSN, CNP and myself that we have no conflicts of interest to report in conducting or reporting on the research for this study. No funding was received by any of the authors from any source to carry out this research, and there are no conflicting financial relationships for any of the authors with respect to the research conducted, the data analyzed or the results of this research. As the lead and corresponding author for this manuscript, I have full control of all primary data and I agree to allow the journal to review the data for this study if requested.
Funding
None
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Videtic, G.M.M., Reddy, C.A. & Sorenson, L. A prospective study of quality of life including fatigue and pulmonary function after stereotactic body radiotherapy for medically inoperable early-stage lung cancer. Support Care Cancer 21, 211–218 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00520-012-1513-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00520-012-1513-9