Abstract
Purpose
Advances in the understanding of the mechanisms involved in oncogenesis have led to the development of so-called targeted therapies such as epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) inhibitors, which take on an increasingly important role in the management of cancer. These treatments have the advantage not to trigger the adverse effects traditionally encountered with chemotherapy, such as nausea, vomiting or haematological toxicity. However, they do cause new forms of toxicity: the most common one is skin toxicity. It is important to be aware of it because it can be debilitating, adversely impacting patients’ quality of life and altering treatment compliance, although it appears to be correlated with treatment response in certain series. Non-specialists can have difficulty in recognising this unusual skin toxicity.
Methods
The dermatologic side effects most frequently triggered by EGFR inhibitors are discussed in this article.
Results
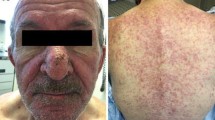
They are divided into three categories depending on their target: inflammation of the pilo-sebaceous follicle, represented by EGFR inhibitor-associated folliculitis, which occurs at an early stage and is frequent; alteration in the skin barrier, primarily responsible for xerosis, fissures and pruritus, which are frequent and delayed; and lesions of the skin appendages (paronychia, pyogenic granuloma, hair changes), which are delayed and less frequent.
Conclusion
It is essential for all practitioners concerned to know about these dermatologic side effects in order to ensure better global management of patients, particularly in terms of quality of life.
















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Perez-Soler R, Saltz L (2005) Cutaneous adverse effects with HER1/EGFR-targeted agents: is there a silver lining? J Clin Oncol 23(22):5235–5246
Joshi SS, Ortiz S, Witherspoon JN, Rademaker A, West DP, Anderson R, Rosenbaum SE, Lacouture ME (2010) Effects of epidermal growth factor receptor inhibitor-induced dermatologic toxicities on quality of life. Cancer 116(16):3916–3923
Boone SL, Rademaker A, Liu D, Pfeiffer C, Mauro DJ, Lacouture ME (2007) Impact and management of skin toxicity associated with anti-epidermal growth factor receptor therapy: survey results. Oncology 72(3–4):152–159
Segaert S, Van Cutsem E (2005) Clinical signs, pathophysiology and management of skin toxicity during therapy with epidermal growth factor receptor inhibitors. Ann Oncol 16(9):1425–1433
Segaert S, Chiritescu G, Lemmens L, Dumon K, Van Cutsem E, Tejpar S (2009) Skin toxicities of targeted therapies. Eur J Cancer 45(Suppl 1):295–308
Perez-Soler R, Delord JP, Halpern A, Kelly K, Krueger J, Sureda BM, von Pawel J, Temel J, Siena S, Soulieres D, Saltz L, Leyden J (2005) HER1/EGFR inhibitor-associated rash: future directions for management and investigation outcomes from the HER1/EGFR inhibitor rash management forum. Oncologist 10(5):345–356
Robert C, Soria JC, Spatz A, Le Cesne A, Malka D, Pautier P, Wechsler J, Lhomme C, Escudier B, Boige V, Armand JP, Le Chevalier T (2005) Cutaneous side-effects of kinase inhibitors and blocking antibodies. Lancet Oncol 6(7):491–500
Van Cutsem E, Peeters M, Siena S, Humblet Y, Hendlisz A, Neyns B, Canon JL, Van Laethem JL, Maurel J, Richardson G, Wolf M, Amado RG (2007) Open-label phase III trial of panitumumab plus best supportive care compared with best supportive care alone in patients with chemotherapy-refractory metastatic colorectal cancer. J Clin Oncol 25(13):1658–1664
Galimont-Collen AF, Vos LE, Lavrijsen AP, Ouwerkerk J, Gelderblom H (2007) Classification and management of skin, hair, nail and mucosal side-effects of epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) inhibitors. Eur J Cancer 43(5):845–851
Agero AL, Dusza SW, Benvenuto-Andrade C, Busam KJ, Myskowski P, Halpern AC (2006) Dermatologic side effects associated with the epidermal growth factor receptor inhibitors. J Am Acad Dermatol 55(4):657–670
Burtness B, Anadkat M, Basti S, Hughes M, Lacouture ME, McClure JS, Myskowski PL, Paul J, Perlis CS, Saltz L, Spencer S (2009) NCCN Task Force Report: Management of dermatologic and other toxicities associated with EGFR inhibition in patients with cancer. J Natl Compr Canc Netw 7(Suppl 1):S5–S21, quiz S22-24
Jacot W, Bessis D, Jorda E, Ychou M, Fabbro M, Pujol JL, Guillot B (2004) Acneiform eruption induced by epidermal growth factor receptor inhibitors in patients with solid tumours. Br J Dermatol 151(1):238–241
Roe E, Garcia Muret MP, Marcuello E, Capdevila J, Pallares C, Alomar A (2006) Description and management of cutaneous side effects during cetuximab or erlotinib treatments: a prospective study of 30 patients. J Am Acad Dermatol 55(3):429–437
Wacker B, Nagrani T, Weinberg J, Witt K, Clark G, Cagnoni PJ (2007) Correlation between development of rash and efficacy in patients treated with the epidermal growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitor erlotinib in two large phase III studies. Clin Cancer Res 13(13):3913–3921
Fernandez-Torres R, Martinez Gomez W, Cuevas Santos J, Paradela S, Fonseca Capdevila E (2010) Rosaceiform eruption induced by cetuximab. Eur J Dermatol 20(3):392–393
Nardone B, Nicholson K, Newman M, Guitart J, Gerami P, Talarico N, Yang XJ, Rademaker A, West DP, Lacouture ME (2010) Histopathologic and immunohistochemical characterization of rash to human epidermal growth factor receptor 1 (HER1) and HER1/2 inhibitors in cancer patients. Clin Cancer Res 16(17):4452–4460
Krueger JG, McCarthy SP, Conlan MG, Iwata KK (2008) Characterization of skin pathology in non-small cell lung cancer patients treated with the EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitor erlotinib. J Am Acad Dermatol 58(2 S2):AB33
Lacouture ME (2006) Mechanisms of cutaneous toxicities to EGFR inhibitors. Nature reviews 6(10):803–812
Wolf M, Swaisland H, Averbuch S (2004) Development of the novel biologically targeted anticancer agent gefitinib: determining the optimum dose for clinical efficacy. Clin Cancer Res 10(14):4607–4613
Peeters M, Siena S, Van Cutsem E, Sobrero A, Hendlisz A, Cascinu S, Kalofonos H, Devercelli G, Wolf M, Amado RG (2009) Association of progression-free survival, overall survival, and patient-reported outcomes by skin toxicity and KRAS status in patients receiving panitumumab monotherapy. Cancer 115(7):1544–1554
Van Cutsem E, Peeters M, Gelderblom H (2007) Cetuximab dose-escalation in mCRC patients with no or slight skin reactions on standard treatment (EVEREST). Ann Oncol 18S(suppl vii)(22), Abstract O-0034
Senderowicz AM, Johnson JR, Sridhara R, Zimmerman P, Justice R, Pazdur R (2007) Erlotinib/gemcitabine for first-line treatment of locally advanced or metastatic adenocarcinoma of the pancreas. Oncology (Williston Park, NY) 21(14):1696–1706, discussion 1706-1699, 1712, 1715
Shepherd FA, Rodrigues Pereira J, Ciuleanu T, Tan EH, Hirsh V, Thongprasert S, Campos D, Maoleekoonpiroj S, Smylie M, Martins R, van Kooten M, Dediu M, Findlay B, Tu D, Johnston D, Bezjak A, Clark G, Santabarbara P, Seymour L (2005) Erlotinib in previously treated non-small-cell lung cancer. N Engl J Med 353(2):123–132
Perez-Soler R, Chachoua A, Hammond LA, Rowinsky EK, Huberman M, Karp D, Rigas J, Clark GM, Santabarbara P, Bonomi P (2004) Determinants of tumor response and survival with erlotinib in patients with non-small-cell lung cancer. J Clin Oncol 22(16):3238–3247
Ouwerkerk J, Boers-Doets C (2010) Best practices in the management of toxicities related to anti-EGFR agents for metastatic colorectal cancer. Eur J Oncol Nurs 14(4):337–349
Jatoi A, Nguyen PL (2008) Do patients die from rashes from epidermal growth factor receptor inhibitors? A systematic review to help counsel patients about holding therapy. Oncologist 13(11):1201–1204
Bernier J, Bonner J, Vermorken JB, Bensadoun RJ, Dummer R, Giralt J, Kornek G, Hartley A, Mesia R, Robert C, Segaert S, Ang KK (2008) Consensus guidelines for the management of radiation dermatitis and coexisting acne-like rash in patients receiving radiotherapy plus EGFR inhibitors for the treatment of squamous cell carcinoma of the head and neck. Ann Oncol 19(1):142–149
Bonner JA, Ang K (2007) More on severe cutaneous reaction with radiotherapy and cetuximab. N Engl J Med 357(18):1872–1873, author reply 1873
Tejwani A, Wu S, Jia Y, Agulnik M, Millender L, Lacouture ME (2009) Increased risk of high-grade dermatologic toxicities with radiation plus epidermal growth factor receptor inhibitor therapy. Cancer 115(6):1286–1299
Jatoi A, Green EM, Rowland KM Jr, Sargent DJ, Alberts SR (2009) Clinical predictors of severe cetuximab-induced rash: observations from 933 patients enrolled in north central cancer treatment group study N0147. Oncology 77(2):120–123
Cunningham D, Humblet Y, Siena S, Khayat D, Bleiberg H, Santoro A, Bets D, Mueser M, Harstrick A, Verslype C, Chau I, Van Cutsem E (2004) Cetuximab monotherapy and cetuximab plus irinotecan in irinotecan-refractory metastatic colorectal cancer. N Engl J Med 351(4):337–345
Togashi Y, Masago K, Fujita S, Hatachi Y, Fukuhara A, Nagai H, Sakamori Y, Kim YH, Mio T, Mishima M (2011) Differences in adverse events between 250 mg daily gefitinib and 150 mg daily erlotinib in Japanese patients with non-small cell lung cancer. Lung Cancer (Amsterdam, Netherlands) 74(1):98–102
Rukazenkov Y, Speake G, Marshall G, Anderton J, Davies BR, Wilkinson RW, Mark Hickinson D, Swaisland A (2009) Epidermal growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitors: similar but different? Anti-cancer Drugs 20(10):856–866
Van Erp NP, Gelderblom H, Guchelaar HJ (2009) Clinical pharmacokinetics of tyrosine kinase inhibitors. Cancer Treatment Reviews 35(8):692–706
Grenader T, Gipps M, Goldberg A (2008) Staphylococcus aureus bacteremia secondary to severe erlotinib skin toxicity. Clinical Lung Cancer 9(1):59–60
Saurat JH (2009) Dermatologie et infections sexuellement transmissibles, 5eth edn. Masson, Issy-les-Moulineaux
Karthaus M, Hofheinz R, Mineur L, Letocha H, Greil R, Thaler J et al (2009) Epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) inhibitor-related skin toxicity: review of interim data from a phase II study (2260314) of panitumumab with FOLFIRI in the first-line treatment of metastatic colorectal cancer. J Clin Oncol 27(15S):e20364
Ocvirk J, Cencelj S (2010) Management of cutaneous side-effects of cetuximab therapy in patients with metastatic colorectal cancer. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol 24(4):453–459
Osio A, Mateus C, Soria JC, Massard C, Malka D, Boige V, Besse B, Robert C (2009) Cutaneous side-effects in patients on long-term treatment with epidermal growth factor receptor inhibitors. Br J Dermatol 161(3):515–521
Muro K, Yoshino T, Doi T, Shirao K, Takiuchi H, Hamamoto Y, Watanabe H, Yang BB, Asahi D (2009) A phase 2 clinical trial of panitumumab monotherapy in Japanese patients with metastatic colorectal cancer. Jpn J Clin Oncol 39(5):321–326. doi:5
Miettinen PJ, Berger JE, Meneses J, Phung Y, Pedersen RA, Werb Z, Derynck R (1995) Epithelial immaturity and multiorgan failure in mice lacking epidermal growth factor receptor. Nature 376(6538):337–341
Gerber PA, Buhren BA, Cevikbas F, Bolke E, Steinhoff M, Homey B (2010) Preliminary evidence for a role of mast cells in epidermal growth factor receptor inhibitor-induced pruritus. J Am Acad Dermatol 63(1):163–165
Hu JC, Sadeghi P, Pinter-Brown LC, Yashar S, Chiu MW (2007) Cutaneous side effects of epidermal growth factor receptor inhibitors: clinical presentation, pathogenesis, and management. J Am Acad Dermatol 56(2):317–326
Rigopoulos D, Larios G, Gregoriou S, Alevizos A (2008) Acute and chronic paronychia. Am Fam Physician 77(3):339–346
Lacouture ME, Lai SE (2006) The PRIDE (Papulopustules and/or paronychia, Regulatory abnormalities of hair growth, Itching, and Dryness due to Epidermal growth factor receptor inhibitors) syndrome. Br J Dermatol 155(4):852–854
Piraccini BM, Bellavista S, Misciali C, Tosti A, de Berker D, Richert B (2010) Periungual and subungual pyogenic granuloma. Br J Dermatol 163(5):941–953
Melichar B, Nemcova I (2007) Eye complications of cetuximab therapy. Eur J Cancer Care 16(5):439–443
Springer K, Brown M, Stulberg DL (2003) Common hair loss disorders. Am Fam Physician 68(1):93–102
Donovan JC, Ghazarian DM, Shaw JC (2008) Scarring alopecia associated with use of the epidermal growth factor receptor inhibitor gefitinib. Archives of Dermatology 144(11):1524–1525
Hepper DM, Wu P, Anadkat MJ (2011) Scarring alopecia associated with the epidermal growth factor receptor inhibitor erlotinib. J Am Acad Dermatol 64(5):996–998
Bonner JA, Harari PM, Giralt J, Azarnia N, Shin DM, Cohen RB, Jones CU, Sur R, Raben D, Jassem J, Ove R, Kies MS, Baselga J, Youssoufian H, Amellal N, Rowinsky EK, Ang KK (2006) Radiotherapy plus cetuximab for squamous-cell carcinoma of the head and neck. N Engl J Med 354(6):567–578
Lynch TJ Jr, Kim ES, Eaby B, Garey J, West DP, Lacouture ME (2007) Epidermal growth factor receptor inhibitor-associated cutaneous toxicities: an evolving paradigm in clinical management. Oncologist 12(5):610–621
Bossi P, Liberatoscioli C, Bergamini C, Locati LD, Fava S, Rinaldi G, Orlandi E, Olmi P, Tagliabue E, Menard S, Licitra L (2007) Previously irradiated areas spared from skin toxicity induced by cetuximab in six patients: implications for the administration of EGFR inhibitors in previously irradiated patients. Ann Oncol 18(3):601–602
Mitra SS, Simcock R (2006) Erlotinib induced skin rash spares skin in previous radiotherapy field. J Clin Oncol 24(16):e28–29
Gerber PA, Enderlein E, Homey B, Muller A, Boelke E, Budach W (2007) Radiation-induced prevention of erlotinib-induced skin rash is transient: a new aspect toward the understanding of epidermal growth factor receptor inhibitor associated cutaneous adverse effects. J Clin Oncol 25(29):4697–4698, author reply 4698-4699
(2006) CTCAE v3.0. http://ctep.cancer.gov/protocolDevelopment/electronic_applications/ctc.htm. Accessed 17 June 2011
(2009) CTCAE v4.0. http://ctep.cancer.gov/protocolDevelopment/electronic_applications/ctc.htm. Accessed 17 June 2011
Lacouture ME, Maitland ML, Segaert S, Setser A, Baran R, Fox LP, Epstein JB, Barasch A, Einhorn L, Wagner L, West DP, Rapoport BL, Kris MG, Basch E, Eaby B, Kurtin S, Olsen EA, Chen A, Dancey JE, Trotti A (2010) A proposed EGFR inhibitor dermatologic adverse event-specific grading scale from the MASCC skin toxicity study group. Support Care Cancer 18(4):509–522
Chan A, Tan EH (2010) How well does the MESTT correlate with CTCAE scale for the grading of dermatological toxicities associated with oral tyrosine kinase inhibitors? Support Care Cancer 19(10):1667–1774
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Appendix
Appendix
Glossary: dermatological semiology [36]
Macula: a flat, non-infiltrated lesion, characterised by a change in skin colour
Erythema: a red or pinkish lesion, disappearing on vitropressure corresponding to vasodilatation
Purpura: a dark red lesion that does not disappear on vitropressure corresponding to extravasation of the red blood cells
Papula: a solid raised lesion, less than one centimetre in diameter
Nodule: a solid raised lesion, greater than 1 cm in diameter
Plaque: a solid raised flat-topped lesion, greater than 1 cm in diameter
Vesicle: a raised lesion, filled with clear liquid, less than 1 cm in diameter
Bulla: a raised lesion, filled with liquid, more than 1 cm in diameter
Pustule: a raised lesion, filled with pus
Telangiectasia: permanent dilatations of superficial blood vessels in the skin
Scale: flakes or plates that represent compacted desquamated layers of stratum cornea that become detached from the epidermis
Crust: exudates coagulation on the surface of inflamed skin
Lichenification: a thickening of the epidermis, which appears with exaggeration of normal skin lines, usually due to chronic scratching
Fissure: linear cleavage of the skin
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Peuvrel, L., Bachmeyer, C., Reguiai, Z. et al. Semiology of skin toxicity associated with epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) inhibitors. Support Care Cancer 20, 909–921 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00520-012-1404-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00520-012-1404-0