Summary
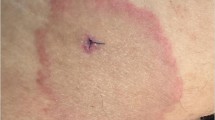
Nearly 100 years ago, Afzelius described a patient with an expanding skin lesion, called erythema migrans [1], which is now known to be the initial skin manifestation of Lyme borreliosis. Approximately 70 years later, in 1976, epidemiologic evaluation of a cluster of children with arthritis in Lyme, Connecticut [2] led to a complete description of the infection [3]. During the subsequent years, investigators in a number of countries have made remarkable strides in the elucidation of this tick-borne spirochetal infection. The purpose of this review is to discuss the current status of Lyme borreliosis, including areas in which knowledge of the infection is still incomplete.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Afzelius A (1921) Erythema chronicum migrans. Acta Derm Venereol 2: 120–125
Steere AC, Malawista SE, Snydman DR, Shope RE, Andiman WA, Ross MR, et al (1977) Lyme arthritis: an epidemic of oligoarticular arthritis in children and adults in three Connecticut communities. Arthritis Rheum 20: 7–17
Steere AC (1989) Lyme disease. N Engl J Med 321: 586–596
Sigal LH, Hassett AL (2002) Contributions of societal and geographical environments to "chronic Lyme disease": the psychopathogenesis and aporology of a new "medically unexplained symptoms" syndrome. Environ Health Perspect 110 [Suppl 4]: 607–611
Baranton G, Postic D, Saint-Girons I, Boerlin P, Piffaretti JC, Assous M, et al (1992) Delineation of Borrelia burgdorferi sensu stricto, Borrelia garinii sp. nov., and group VS461 associated with Lyme borreliosis. Int J Sys Bacteriol 42: 378–383
Steere AC, Coburn J, Glickstein L (2004) The emergence of Lyme disease. J Clin Invest 113: 1093–1101
Richter D, Schlee DB, Allgower R, Matuschka FR (2004) Relationships of a novel Lyme disease spirochete, Borrelia spielmani sp. nov., with its hosts in Central Europe. Appl Environ Microbiol 70: 6414–6419
Xu G, Fang QQ, Keirans JE, Durden LA (2003) Molecular phylogenetic analyses indicate that the Ixodes ricinus complex is a paraphyletic group. J Parasitol 89: 452–457
Kurtenbach K, Sewell HS, Ogden NH, Randolph SE, Nutall PA (1998) Serum complement sensitivity as a key factor in Lyme disease ecology. Infect Immun 66: 1248–1251
LoGiudice K, Ostfeld RS, Schmidt KA, Keesing F (2003) The ecology of infectious disease: effects of host diversity and community composition on Lyme disease risk. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 100: 567–571
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (2004) Lyme disease – United States, 2001–2002. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep 53: 365–369
Brown RN, Lane RS (1992) Lyme disease in California: a novel enzootic transmission cycle of Borrelia burgdorferi. Science 256: 1439–1442
Schneider BS, Zeidner NS, Burkot TR, Maupin GO, Piesman J (2000) Borrelia isolates in northern Colorado identifies Borrelia bissettii. J Clin Microbiol 38: 3103–3105
Gern L, Pierre-Francois H (2002) Ecology of Borrelia burgdorferi sensu lato in Europe. In: Gray JS, Kahl O, Lane RS, Stanek G (eds) Lyme borreliosis: biology, epidemiology and control. CABI Publishing, Oxford, pp 149–174
Dennis DT, Hayes EB (2002) Epidemiology of Lyme Borreliosis. In: Gray JS, Kahl O, Lane RS, Stanek G (eds) Lyme borreliosis: biology, epidemiology and control. CABI Publishing, Oxford, pp 251–280
Masuzawa T (2004) Terrestrial Distribution of the Lyme Borreliosis Agent Borrelia burgdorferi sensu lato in East Asia. Jpn J Infect Dis 57: 229–235
Burgdorfer W, Barbour AG, Hayes SF, Benach JL, Grunwaldt E, Davis JP (1982) Lyme disease – a tick-borne spirochetosis? Science 216: 1317–1319
Fraser CM, Casjens S, Huang WM, Sutton GG, Clayton R, Lathigra R, et al (1997) Genomic sequence of a Lyme disease spirochete, Borrelia burgdorferi. Nature 390: 580–586
Casjens S, Palmer N, Van Vugt R, Mun Huang W, Stevenson B, Rosa P, et al (2000) A bacterial genome in flux: the twelve linear and nine circular extrachromosomal DNAs in an infectious isolate of the Lyme disease spirochete Borrelia burgdorferi. Mol Microbiol 35: 490–516
Zhang JR, Hardham JM, Barbour AG, Norris SJ (1997) Antigenic variation in Lyme disease borreliae by promiscuous recombination of VMP-like sequence cassettes. Cell 89: 275–285
Bono JL, Elias AF, Kupko JJ III, Stevenson B, Tilly K, Rosa P (2000) Efficient targeted mutagenesis in Borrelia burgdorferi. J Bacteriol 182: 2445–2452
Cabello FC, Sartakova ML, Dobrikova EY (2001) Genetic manipulation of spirochetes – light at the end of the tunnel. Trends Microbiol 9: 245–248
Stewart PE, Thalken R, Bono JL, Rosa P (2001) Isolation of a circular plasmid region sufficient for autonomous replication and transformation of infectious Borrelia burgdorferi. Mol Microbiol 39: 714–721
Schwan TG, Piesman J (2000) Temporal changes in outer surface proteins A and C of the Lyme disease-associated spirochete, Borrelia burgdorferi, during the chain of infection in ticks and mice. J Clin Microbiol 38: 382–388
Ohnishi J, Piesman J, de Silva AM (2001) Antigenic and genetic heterogeneity of Borrelia burgdorferi populations transmitted by ticks. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 98: 670–675
Ramamoorthi N, Narasimhan S, Pal U, Bao F, Yang XF, Fish D, et al (2005) The Lyme disease agent exploits a tick protein to infect the mammalian host. Nature 436: 573–577
Hu LT, Perides G, Noring R, Klempner MS (1995) Binding of human plasminogen to Borrelia burgdorferi. Infect Immun 63: 3491–3496
Coleman JL, Gebbia JA, Pieman J, Degen JL, Bugge TH, Benach JL (1997) Plasminogen is required for efficient dissemination of B. burgdorferi in ticks and for enhancement of spirochetemia in mice. Cell 89: 1111–1119
Kraiczy P, Hartmann K, Hellwage J, Skerka C, Kirschfink M, Brade V, et al (2004) Immunological characterization of the complement regulator factor H-binding CRASP and Erp proteins of Borrelia burgdorferi. Int J Med Microbiol 293: 152–157
Hellwage J, Meri T, Heikkila T, Alitalo A, Panelius J, Lahdenne P, et al (2001) The complement regulator factor H binds to the surface protein OspE of Borrelia burgdorferi. J Biol Chem 276: 8427–8435
Seinost G, Dykhuizen DE, Dattwyler RJ, Golde WT, Dunn JJ, Wang IN, et al (1999) Four clones of Borrelia burgdorferi sensu stricto cause invasive infection in humans. Infect Immun 67: 3518–3524
Probert WS, Johnson BJB (1998) Identification of a 47 kDa fibronectin-binding protein expressed by Borrelia burgdorferi isolate B31. Mol Microbiol 30: 1003–1015
Coburn J, Cugini C (2003) Targeted mutation of the outer membrane protein P66 disrupts attachment of the Lyme disease agent, Borrelia burgdorferi, to integrin alphavbeta3. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 100: 7301–7306
Leong JL, Morrissey PE, Ortega-Barria E, Pereira MEA, Coburn J (1995) Hemagglutination and proteoglycan binding by the Lyme disease spirochete, Borrelia burgdorferi. Infect Immun 63: 874–883
Guo BP, Brown EL, Dorward DW, Rosenberg LC, Hook M (1998) Decorin-binding adhesins from Borrelia burgdorferi. Mol Microbiol 30: 711–723
Cadavid D, Thomas DD, Crawley R, Barbour AG (1994) Variability of a bacterial surface protein and disease expression in a possible mouse model of systemic Lyme borreliosis. J Experi Med 179: 631–642
Wooten RM, Ma Y, Yoder RA, Brown JP, Weis JH, Zachary JF, et al (2002) Toll-like receptor 2 is required for innate, but not acquired, host defense to Borrelia burgdorferi. J Immunol 168: 348–355
Talkington J, Nickell SP (2001) Role of Fc gamma receptors in triggering host cell activation and cytokine release by Borrelia burgdorferi. Infect Immun 69: 413–419
Mullegger RR, McHugh G, Ruthazer R, Binder B, Kerl H, Steere AC (2000) Differential expression of cytokine mRNA in skin specimens from patients with erythema migrans or acrodermatitis chronica atrophicans. J Invest Dermatol 115: 1115–1123
Salazar JC, Pope CD, Sellati TJ, Feder HMJ, Kiely TG, Dardick KR, et al (2003) Coevolution of markers of innate and adaptive immunity in skin and peripheral blood of patients with erythema migrans. J Immunol 171: 2660–2670
Kumar H, Belperron A, Barthold SW, Bockenstedt LK (2000) Cutting edge: CD1d deficiency impairs murine host defense against the spirochete, Borrelia burgdorferi. J Immunol 165: 4797–4801
Nguyen TP, Lam TT, Barthold SW, Telford SR 3rd, Flavell RA, Fikrig E (1994) Partial destruction of Borrelia burgdorferi within ticks that engorged on OspE- or OspF-immunized mice. Infect Immun 62: 2079–2084
Steere AC, Glickstein L (2004) Elucidation of Lyme arthritis. Nature Reviews Immunology 4: 143–152
Dong Z, Edelstein M, Glickstein LJ (1997) CD8+ T cells are activated during the early Th1 and Th2 immune responses in the murine Lyme disease model. Infect Immun 65: 5334–5337
Liang FT, Jacobs MB, Bowers LC, Philipp MT (2002) An immune evasion mechanism for spirochetal persistence in Lyme borreliosis. J Experi Med 195: 415–422
Barthold SW, Beck DS, Hansen GM, Terwilliger GA, Moody KD (1990) Lyme borreliosis in selected strains and ages of laboratory mice. J Infect Dis 162: 133–138
Ma Y, Seiler KP, Eichwals EJ, Weis JH, Teuscher C, Weiss JJ (1998) Distinct characteristics of resistance to Borrelia burgdorferi-induced arthritis in C57BL/6N mice. Infect Immun 66: 161–168
Brown JP, Zachary JF, Teuscher C, Weis JJ, Wooten RM (1999) Dual role of interleukin-10 in murine Lyme disease: regulation of arthritis severity and host defense. Infect Immun 67: 5142–5150
Anguita J, Rincon M, Samanta S, Barthold SW, Flavell RA, Fikrig E (1998) Borrelia burgdorferi-infected, interleukin-6-deficient mace have decreased Th2 responses and increased Lyme arthritis. J Infect Dis 178: 1512–1515
Kang I, Barthold SW, Persing DH, Bockenstedt LK (1997) T-helper-cell cytokines in the early evolution of murine Lyme arthritis. Infect Immun 65: 3107–3111
Zeider N, Mbow ML, Dolan M, Massung R, Baca E, Piesman J (1997) Effects of Ixodes scapularis and Borrelia burgdorferi on modulation of the host immune response: induction of a TH2 cytokine response in Lyme diseasesusceptible (C3H/HeJ) mice but not in disease-resistant (BALB/c) mice. Infect Immun 65: 3100–3106
Baranton G, Seinost G, Theodore G, Postic D, Dykhuizen D (2001) Distinct levels of genetic diversity of Borrelia burgdorferi are associated with different aspects of pathogenicity. Res Microbiol 152: 149–156
Strle F, Nadelman RB, Cimperman J, Nowakowski J, Picken RN, Schwartz I, et al (1999) Comparison of culture-confirmed erythema migrans caused by Borrelia burgdorferi sensu stricto in New York state and by Borrelia afzelii in Slovenia. Ann Intern Med 130: 32–36
Steere AC (2001) Lyme disease. N Engl J Med 345: 115–125
Steere AC, Dhar A, Hernandez J, Fischer PA, Sikand VK, Schoen RT, et al (2003) Systemic symptoms without erythema migrans as the presenting picture of early Lyme disease. Am J Med 114: 58–62
Nowakowski J, Schwartz I, Liveris D, Wang G, Aguero-Rosenfeld ME, Girao G, et al (2001) Laboratory diagnostic techniques for patients with early Lyme disease associated with erythema migrans: a comparison of different techniques. Clin Infect Dis 33: 2023–2027
Wormser GP, Bittker S, Cooper D, Nowakowski J, Nadelman RB, Pavia C (2001) Yield of large-volume blood cultures in patients with early Lyme disease. J Infect Dis 184: 1070–1072
Nocton JJ, Dressler F, Rutledge BJ, Rys PN, Persing DH, Steere AC (1994) Detection of Borrelia burgdorferi DNA by polymerase chain reaction in synovial fluid in Lyme arthritis. N Engl J Med 330: 229–234
Bradley JF, Johnson RC, Goodman JL (1994) The persistence of spirochetal nucleic acids in active Lyme arthritis. Ann Intern Med 120: 487–489
Nocton JJ, Bloom BJ, Rutledge BJ, Persing DH, Logigian EL, Schmid CH, et al (1996) Detection of Borrelia burgdorferi DNA by polymerase chain reaction in cerebrospinal fluid in patients with Lyme neuroborreliosis. J Infect Dis 174: 623–627
Lebech AM (2002) Polymerase chain reaction in diagnosis of Borrelia burgdorferi infections and studies on taxonomic classification. APMIS [Suppl]: 1–40
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (1995) Recommendations for test performance and interpretation from the Second International Conference on serologic diagnosis of Lyme disease. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep 44: 590–591
Dressler F, Whalen JA, Reinhardt BN, Steere AC (1993) Western blotting in the serodiagnosis of Lyme disease. J Infect Dis 167: 392–400
Robertson J, Guy E, Andrews N, Wilske B, Anda P, Granstrom M, et al (2000) Immunoblot interpretation criteria for serodiagnosis of early Lyme disease. J Clin Microbiol 33: 419–427
Liang FT, Steere AC, Marques AR, Johnson BJ, Miller JN, Philipp MT (1999) Sensitive and specific serodiagnosis of Lyme disease by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay with a peptide based on an immunodominant conserved region of Borrelia burgdorferi VlsE. J Clin Microbiol 37: 3990–3996
Bacon RM, Biggerstaff BJ, Schriefer ME, Gilmore RD, Philipp MT, Steere AC, et al (2003) Serodiagnosis of Lyme disease by kinetic enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay using recombinant VlsE1 or peptide antigens of Borrelia burgdorferi compared with 2-tiered testing using whole-cell lysates. J Infect Dis 187: 1187–1199
Wormser GP, Nadelman RB, Dattwyler RJ, Dennis DT, Shapiro ED, Steere AC, et al (2000) Practice guidelines for the treatment of Lyme disease. Clin Infect Dis 31: S1–S14
Malawista SE (2000) Resolution of Lyme arthritis, acute or prolonged: a new look. Inflammation 24: 493–504
Carlson D, Hernandez J, Bloom BJ, Coburn J, Aversa JM, Steere AC (1999) Lack of Borrelia burgdorferi DNA in synovial samples in patients with antibiotic treatment-resistant Lyme arthritis. Arthritis Rheum 42: 2705–2709
Steere AC, Klitz W, Drouin EE, Falk BA, Kwok WW, Nepom GT, et al (2006) Antibiotic-refractory Lyme arthritis with HLA-DR molecules that bind a Borrelia burgdorferi peptide. J Experi Med 203: 961–971
Gross DM, Forsthuber T, Tary-Lehman M, Etling C, Ito K, Nagy ZA, et al (1998) Identification of LFA-1 as a candidate autoantigen in treatment-resistant Lyme arthritis. Science 281: 703–706
Chen J, Field JA, Glickstein L, Molloy PJ, Huber BT, Steere AC (1999) Association of antibiotic treatment-resistant Lyme arthritis with T cell responses to dominant epitopes of outer-surface protein A (OspA) of Borrelia burgdorferi. Arthritis Rheum 42: 1813–1822
Sigal LH (1990) Summary of the first 100 patients seen at a Lyme disease referral center. Am J Med 88: 577–581
Dinerman H, Steere AC (1992) Lyme disease associated with fibromyalgia. Ann Intern Med 117: 281–285
Klempner MS, Hu LT, Evans J, Schmid CH, Johnson GM, Trevino RP, et al (2001) Two controlled trials of antibiotic treatment in patients with persistent symptoms and a history of Lyme disease. N Engl J Med 345: 85–92
Steere AC (2002) A 58-year-old man with a diagnosis of chronic Lyme disease. JAMA 288: 1002–1010
Fikrig E, Barthold SW, Kantor FS, Flavell RA (1990) Protection of mice against the Lyme disease agent by immunizing with recombinant OspA. Science 250: 553–556
Simon MM, Schaible UE, Kramer MD, Eckerskorn C, Museteanu C, Muller-Hermelink HK, et al (1991) Recombinant outer surface protein A from Borrelia burgdorferi induces antibodies protective against spirochetal infection in mice. J Infect Dis 164: 123–132
Steere AC, Sikand VK, Meurice F, Parenti DL, Fikrig E, Schoen RT, et al (1998) Vaccination against Lyme disease with recombinant Borrelia burgdorferi outer-surface lipoprotein a with adjuvant. N Engl J Med 339: 209–215
Sigal LH, Zahradnik JM, Lavin P, Patella SJ, Bryant G, Haselby R, et al (1998) A vaccine consisting of recombinant Borrelia burgdorferi outer-surface protein A to prevent Lyme disease. Recombinant outer-surface protein A Lyme disease vaccine study consortium [see comments] [published erratum appears in N Engl J Med (1998) 339 (8): 571]. N Engl J Med 339: 216–222
Meltzer MI, Dennis DT, Orloski KA (1999) The cost effectiveness of vaccinating against Lyme disease. Emerg Infect Dis 5: 321–328
Shadick NA, Liang MH, Phillips CB, Fossel K, Kuntz KM (2001) The cost-effectiveness of vaccination against Lyme disease. Arch Intern Med 161: 554–561
Hanson MS, Edelman R (2003) Progress and controversy surrounding vaccines against Lyme disease. Future Drugs 2: 687–703
Anonymous (2006) When a vaccine is safe. Nature 439: 509
Hayes EB, Piesman J (2003) How can we prevent Lyme disease? N Engl J Med 348: 2424–2430
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Steere, A. Lyme borreliosis in 2005, 30 years after initial observations in Lyme Connecticut. Wien Klin Wochenschr 118, 625–633 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00508-006-0687-x
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00508-006-0687-x