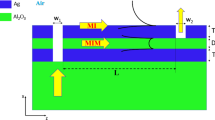
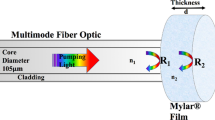
Summary
In industry, a vast variety of processes can be optimized by means of online measurement of chemical properties of fluids in order to reduce costs for maintenance or increase productivity as well as production quality. In this contribution, we report on the design of a fully integrated infrared absorption sensor, which is capable to determine chemical properties by investigating infrared absorption at selected distinct wavelengths in the mid-infrared region. For example, in order to reduce the frequency of scheduled maintenance of lubrication oil, e.g., in combustion engines, the quality of the deteriorated oil has to be determined, which has been selected as pilot application for our development. Based on results of transmission spectroscopy, we show that by means of a properly designed optical waveguide structure, a sensitivity similar to that obtained by transmission spectroscopy, as used in the laboratory, can be achieved. To achieve a highly sensitive absorption element, a planar mono-mode waveguide is utilized which requires an appropriate coupler to couple the infrared light into the waveguide. The employed grating couplers have been modeled in order to derive a design yielding the desired sensor performance. As the targeted wavelength is located in the mid-infrared region, a suitable infrared source or detector, respectively, can be fabricated by thermal components. Finally, we report on the ongoing technological development to establish the required thin-film processes.
Zusammenfassung
Bei industriellen Anlagen existiert eine Vielzahl von Prozessen für die, durch Online-Messung von chemischen Eigenschaften von Flüssigkeiten und Gasen, die Kosten für Wartung reduziert und/oder eine Zunahme der Produktivität sowie eine Erhöhung der Produktqualität erreicht werden kann. Der vorliegende Beitrag beschäftigt sich mit dem Design eines integrierten Infrarotabsorptionssensors, der chemische Eigenschaften anhand vordefinierter Wellenlängen im mittleren Infrarotbereich bestimmen kann. Beispielsweise werden in vielen industriellen Anlagen (z. B. Verbrennungskraftmaschinen) Schmiermittel in definierten Wartungsintervallen gewechselt. Um die tatsächliche Lebensdauer eines Schmieröls ausnutzen zu können, muss die Qualität des abgenutzten Öls festgestellt werden. Diese Anwendung wurde als Pilotanwendung ausgewählt. Basierend auf Resultaten der Transmissionsspektroskopie wird gezeigt, dass eine geeignet dimensionierte Wellenleiterstruktur eine zum, in Labors verwendeten, Durchlichtverfahren vergleichbare Empfindlichkeit erreicht. Als hoch empfindliches Absorptionselement wird ein planarer optischer Monomode-Wellenleiter eingesetzt, welcher eine geeignete Kopplerstruktur zur Ein- und Auskopplung der verwendeten Infrarotstrahlung benötigt. Die verwendeten Gitterkoppler wurden simuliert, um ein Design zu entwickeln, welches die gewünschten Sensorcharakteristiken realisiert. Da die zu untersuchende Wellenlänge im mittleren Infrarotbereich liegt, werden zur Erzeugung und Detektion der Infrarotstrahlung thermische Elemente verwendet. Abschließend wird ein Überblick über die laufenden Arbeiten zur Entwicklung der benötigten technologischen Dünnschichtprozesse gegeben.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Agoston, A., Ötsch, C., Zhuravleva, J., Jakoby, B. (2004): An IR-Absorption Sensor System for the Determination of Engine, Proceedings IEEE Sensor: 463–466
Ahmed, A. H. Z., Tait, R. N. (2004): Fabrication of a self-absorbing, self-supported complementary metal-oxide-semiconductor compatible micromachined bolometer. J Vac Sci Technol A, 22 (3): 842–846
Chen, W. R., Chang, S. J., Su, Y. K., Lan, W. H. (2000): RIE of ZnSe, ZnSSe, ZnCdSe and ZnMgSSe by H2/Ar and Ch4/H2/Ar. Jpn J Appl Phys, 39 (1): 3308–3313
Crystran (2007): http://www.crystran.co.uk/
Ezema, F. I., Ekwealor, A. B. C., Osuji, R. U. (2006): Effect of thermal annealing on the band GAP and optical properties of CBD znSe thin films. Turk J Phys, 30: 157–163
Harris, J. H., Winn, R. K., Dalgoutte, D. G. (1972): Theory and design of periodic couplers. Applied Optics, 11 (10): 2234–2241
Jiang, H., Pandey, R., Darrigan, C., Rérat, M. (2003): First-principles study of structural, electronic and optical properties of BaF2 in its cubic, orthorhombic and hexagonal phases. J Phys Condens Matter, 15 (4): 709–718
Kohl, F., Keplinger, F., Jachimowicz, A., Schalko, J. (2004): A model of metal film resistance bolometers based on the electro-thermal feedback effect. Sensors Actuators A, 115: 308–317
Langwieser, C. (1990): Wachstum von Bariumfluorid-Volumskristallen. Master thesis, Johannes Kepler University Linz
Lifante, G. (2003): Integrated Photonics: Fundamentals. Chichester: Wiley
Madelung, O., Schulz, M., Weiss, H. (1982): Landolt-Börnstein, Semiconductors 17b. Berlin: Springer: 388–403
Moharam, M. G., Pommet, D. A., Grann, E. B. (1995): Stable implementation of the rigorous coupled-waveanalysis for surface-relief gratings: enhanced transmittance matrix approach. J Opt Soc Am A, 12 (5): 1077–1086
Mahalingam, T., Kathalingam, A., Lee, S., Moon, S., Kim, Y. D. (2007): Studies of electrosynthesized ZnSe thin Films. J New Mat Electrochem Syst, 10: 15–19
Neviére, M., Popov, E. (2003): Light Propagation in Periodic Media. New York: Marcel Dekker
Pearton, S. J., Ren, F. (1993): Plasma etching of ZnS, ZnSe, CdS and CdTe in electron cylotron resonance Ch4/H2/Ar and H2/Ar discharge. J Vac Sci Technol B, 11: 15–19
Pollock, C., Lipson, M. (2003): Integrated Photonics. Dordrecht: Kluwer
Taillaert, D. (2004): Grating couplers as Interface between Optical Fibres and Nanophotonic Waveguides. PhD, Gent University
Venkatachalam, S., Mangalaraj, D., Narayandass, Sa. K. (2007): Characterization of vacuum-evaporated ZnSe thin film. Physica B, 393: 47–55
Venkata Subbaiah, Y. P., Prathap, P., Devika, M., Ramakrishna Reddy, K. T. (2005): Close-spaced evaporated ZnSe film: preperation and characterization. Physica B, 365: 240–246
Wolffenbuttel, R. F. (2004): State-of-the-art in integrated optical microspectrometers. IEEE Trans Instrum Meas, 53 (1): 197–202
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kasberger, J., Saeed, A., Hilber, W. et al. Towards an integrated IR-absorption microsensor for the online monitoring of fluids. Elektrotech. Inftech. 125, 65–70 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00502-008-0508-1
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00502-008-0508-1