Abstract
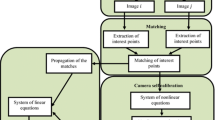
This paper presents a complete pipeline of the reconstruction and the modeling of the unknown complex 3D scenes from a sequence of unconstrained images. The proposed system is based on the formulation of a nonlinear cost function by determining the relationship between 2D points of the images and the cameras parameters; the optimization of this function by a genetic algorithm makes finding the optimal cameras parameters. The determination of these parameters allows thereafter to estimate the 3D points of the observed scene. Then, the mesh of the 3D points is achieved by 3D Crust algorithm and the texture mapping is performed by multiple dependent viewpoints. Extensive experiments on synthetic and real data are performed to validate the proposed approach, and the results indicate that our system is robust and can achieve a very satisfactory reconstruction quality.












Similar content being viewed by others
References
Amenta N (1999) The crust algorithm for 3D surface reconstruction. In: Proceedings of symposium on computational geometry, pp 423–424
Amenta N, Choi S, Kolluri RK (2001) The power crust. In: Proceedings of the sixth ACM symposium on solid modeling and applications, University of Texas at Austin, pp 249–266
Anam S, Islam MS, Kashem MA, Islam MN, Islam MR, Islam MS (2009) Face recognition using genetic algorithm and back propagation neural network. In: International multi conference of engineers and computer scientists, vol I
Baumgart BG et al (1974) Geometric modeling for computer vision. Doctoral dissertation, Stanford University
Cazals F, Giesen J (2004) Delaunay triangulation based surface reconstruction: ideas and algorithms. Technical report, RR-5393, INRIA
Chang CC, Kuo Y-T (2008) Genetic-based approach for synthesizing texture. Int J Artif Intell Tools 17(04):731–743
Craciun DI (2011) Modélisation des équivalents dynamiques des réseaux électriques. Thèse, Université de Grenoble, p 174
Dipanda A, Woo S, Marzani F, Bilbault JM (2003) 3D shape reconstruction in an active stereo vision system using genetic algorithms. J Pattern Recognit Soc 36:2143–2159
El Hazzat S, Saaidi A, Satori K (2014) Euclidean 3D reconstruction of unknown objects from multiple images. J Emerg Technol Web Intell 6(1):59–63
Faugeras O, Luong QT, Papadopoulou T (2001) The geometry of multiple images: the laws that govern the formation of images of a scene and some of their applications. MIT Press, Cambridge
Franco J (2010) Efficient polyhedral modeling from silhouettes. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell 31(3):853–861
Fuhrmann S et al (2015) MVE—an image-based reconstruction environment. Comput Graph 53:44–53
Furukawa Y, Ponce J (2010) Accurate, dense, and robust multi-view stereopsis. Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell 32(8):1362–1376
Furukawa Y, Curless B, Seitz SM, Szeliski R (2010) Towards internet-scale multi-view stereo. In: Conference on computer vision and pattern recognition
Goldberg DE (1989) Genetic algorithms in search, optimization & machine learning. Addison-Wesley, Boston
Goldberg DE, Deb K (1991) A comparative analysis of selection scheme used in genetic algorithms. In: Rawlins G (ed) Foundations of genetic algorithms. Morgan Kaufman, San Mateo, pp 69–93
Harris C, Stephens M (1988) A combined corner et edge detector. In: 4th Alvey vision conference, pp 147–151
Hartley RI, Zisserman A (2000) Multiple view geometry in computer vision. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, p 265. ISBN: 0521623049
Holland JH (1992) Adaptation in natural and artificial systems. MIT Press, Cambridge
Hornung A, Kobbelt L, (2006) Robust reconstruction of watertight 3D models from non-uniformly sampled point-clouds without normal information. In: Eurographics symposium on geometry processing, pp 41–50
Janko Z, Chetverikov D, Ekart A (1995) Using genetic algorithms in computer vision: registering images to 3D surface model. Acta Cybern 18(2):193–212
Jean-Denis D, Adrien B, Pierre G (1998) Interactive 3D modeling from multiple images using scene regularities. Lecture notes in computer science, vol, 1506, pp 236–252
Jean-Denis D, Adrien B, Pierre G (2010) Shape-from-texture revisited. In: Francophone congress of pattern recognition and artificial intelligence, pp 1–8
Johnson CM, Bhat A, et Thibault W (2006) An evolutionary approach to camera-based projector calibration. In: Genetic and evolutionary computation conference, pp 1871–1872
Kazhdan M, Hoppe H (2013) Screened Poisson surface reconstruction. ACM Trans Graph 32(3):1–29
Kolev K, Klodt M et al (2009) Continuous global optimization in multiview 3D reconstruction. Int J Comput Vis 4(1):80–96
Kolev K, Brox T, Cremers D (2012) Fast joint estimation of silhouettes and dense 3D geometry from multiple images. Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell 34(3):493–505
Kutulakos KN, Seitz SM (2000) A theory of shape by space carving. Int J Comput Vis 38(3):199–218
Lobay A, Forsyth DA (2006) Shape from texture without boundaries. Int J Comput Vis 67(1):71–91
Loh M, Hartley R (2005) Shape from non homogeneous, non-stationary, anisotropic, perspective texture. In: BMVC’05. Royaume-Uni, Oxford, pp 69–78
Ma Y, Soatto S, Kosecka J, Sastry SS (2003) An invitation to 3-D vision: from images to geometric models. Springer, Berlin
Matusik W, Buehler C, McMillan L (2001) Polyhedral visual hulls for real-time rendering. In: Euro graphics workshop on rendering, pp 115–125
Merras M, El Akkad N, Saaidi A, Nazih AG, Satori K (2014) Camera calibration with varying parameters based on improved genetic algorithm. WSEAS Trans Comput 13:129–137
Merras M et al (2015) Camera self calibration with varying parameters by an unknown three dimensional scene using the improved genetic algorithm. 3D Res 6(1):1–14
Merras M, El Hazzat S, Saaidi A, Nazih AG, Satori K (2016) 3D face reconstruction using images from cameras with varying parameters. Int J Autom Comput. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11633-016-0999-x
Nguyen MH et al (2011) Modeling of 3D object using unconstrained and uncalibrated images taken with a handheld camera. Comput Vis Imaging Comput Graph Theory Appl 274:1–5
Nguyen MH et al (2013) A hybrid image base modeling algorithm. In: Proceedings of the thirty sixth Australasian computer sciences conference, vol 135, pp 115–123
Nistér D (2005) Preemptive RANSAC for live structure and motion estimation. Mach Vis Appl 16(5):321–329
Olsson C, Enqvist O (2011) Stable structure from motion for unordered image collections. In: Scandinavian conference on image analysis, SCIA 2011
Pighin F (2002) Modeling and animating realistic faces from images. Int J Comput Vis 50(2):143–169
Pighin F, Hecker J, Dani L, Richard S, Salesin DH (1998) Synthesizing realistic facial expressions from photographs. Comput Graph. https://doi.org/10.1145/280814.280825
Pollefeys M, Koch R, Gool LV (1999) Self-calibration and metric reconstruction in spite of varying and unknown internal camera parameters. Int J Comput Vis 32(1):7–25
Quan L et al (2006) Image-based plant modeling. ACM Trans Graph 25(3):599–604
Ren Z-W, San Y, Chen J-F (2007) Hybrid implex-improved genetic algorithm for global numerical optimization. Acta Autom Sin 33(1):91–95
Roberts R, Szeliski R (2011) Structure from motion for scenes with large duplicate structures. In: Computer vision and pattern recognition, pp 3137–3144
Saaidi A, Tairi H, Satori K (2006) Fast stereo matching using rectification and correlation techniques. In: ISCCSP, second international symposium on communications, control and signal processing. Marrakech, Morrocco, pp 1–4
Salman N, Yvinec M (2010) Surface reconstruction from multi-view stereo of large-scale outdoor scenes. Int J Virtual Real 5(3):1–6
Seitz S, Curless B, Diebel J, Scharstein D, Szeliski R (2006) A comparison and evaluation of multi-view stereo reconstruction algorithms. In: Conference on computer vision and pattern recognition
Snavely N, Seitz SM, Szeliski R (2006) Photo tourism: exploring photo collections in 3D. ACM Trans Graph 25:835–846
Tan P et al (2006) Image based tree graphics. ACM Trans Graph 27(3):418–433
Triggs B, McLauchlan P, Hartley RI, Fitzgibbon A (1999) Bundle adjustment—a modern synthesis. In: Vision algorithms, pp 298–372
Wang G, Wu QMJ (2009) Perspective 3-d Euclidean reconstruction with varying camera parameters. IEEE Trans Circuits Syst Video Technol 19(12):1793–1803
Wilczkowiak M, Boyer E, Sturm P (2001) Camera calibration and 3D reconstruction from single images using parallelepipeds. In: ICCV. Vancouver, Canada, pp 142–148
Wojciech et al (2000) Image based visual hulls. In: 27th conference on computer graphics and interactive techniques, pp 369–374
Wu C (2013) Towards linear-time incremental structurefrom motion. In: International conference on 3D vision, pp 127–134
Wu C, Agarwal S, Curless B, Seitz S (2011) Multicore bundle adjustment. In: Conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, pp 3057–3064
Xiao J et al (2008) Image based façade modeling. ACM Trans Graph 27(5):26–34
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Additional information
Communicated by A. Di Nola.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Merras, M., Saaidi, A., El Akkad, N. et al. Multi-view 3D reconstruction and modeling of the unknown 3D scenes using genetic algorithms. Soft Comput 22, 6271–6289 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00500-017-2966-z
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00500-017-2966-z