Abstract
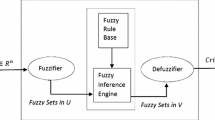
In this paper, a new hybrid method based on fuzzy neural network (FNN) for approximate solution of fuzzy linear systems of the form \(Ax=d,\) where \(A\) is a square matrix of fuzzy coefficients, \(x\) and \(d\) are fuzzy number vectors, is presented. Here a neural network is considered as a part of a large field called neural computing or soft computing. Moreover, in order to find the approximate solution of an \(n\times n\) system of fuzzy linear equations that supposedly has a unique fuzzy solution, a simple algorithm from the cost function of the FNN is proposed. Finally, we illustrate our approach by some numerical examples.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abbasbandy S, Alavi M (2005) A method for solving fuzzy linear systems. Iran J Fuzzy Syst 2:37–43
Abbasbandy S, Otadi M (2006) Numerical solution of fuzzy polynomials by fuzzy neural network. Appl Math Comput 181:1084–1089
Abbasbandy S, Jafarian A, Ezzati R (2005a) Conjugate gradient method for fuzzy symmetric positive definite system of linear equations. Appl Math Comput 171:1184–1191
Abbasbandy S, Nieto JJ, Alavi M (2005b) Tuning of reachable set in one dimensional fuzzy differential inclusions. Chaos Solitons Fractals 26:1337–1341
Abbasbandy S, Ezzati R, Jafarian A (2006) LU decomposition method for solving fuzzy system of linear equations. Appl Math Comput 172:633–643
Abbasbandy S, Otadi M, Mosleh M (2008a) Minimal solution of general dual fuzzy linear systems. Chaos Solitons Fractals 178:1113–1124
Abbasbandy S, Otadi M, Mosleh M (2008b) Numerical solution of a system of fuzzy polynomials by fuzzy neural network. Inf Sci 178:1948–1960
Alefeld G, Herzberger J (1983) Introduction to interval computations. Academic Press, New York
Asady B, Abbasbandy S, Alavi M (2005) Fuzzy general linear systems. Appl Math Comput 169:34–40
Buckley JJ, Eslami E (1997) Neural net solutions to fuzzy problems: the quadratic equation. Fuzzy Sets Syst 86:289–298
Caldas M, Jafari S (2005) θ-Compact fuzzy topological spaces. Chaos Solitons Fractals 25:229–232
Dehghan M, Hashemi B, Ghatee M (2007) Solution of the fully fuzzy linear systems using iterative techniques. Chaos Solitons Fractals 34:316–336
Dubois D, Prade H (1978) Operations on fuzzy numbers. J Syst Sci 9:613–626
Elnaschie MS (2004a) A review of E-infinity theory and the mass spectrum of high energy particle physics. Chaos Solitons Fractals 19:209–236
Elnaschie MS (2004b) The concepts of E infinity: an elementary introduction to the Cantorian-fractal theory of quantum physics. Chaos Solitons Fractals 22:495–511
Elnaschie MS (2005) On a fuzzy Kãhler manifold which is consistent with the two slit experiment. Int J Nonlinear Sci Numer Simul 6:95–98
Elnaschie MS (2006a) Elementary number theory in superstrings, loop quantum mechanics, twistors and E-infinity high energy physics. Chaos Solitons Fractals 27:297–330
Elnaschie MS (2006b) Superstrings, entropy and the elementary particles content of the standard model. Chaos Solitons Fractals 29:48–54
Feng G, Chen G (2005) Adaptive control of discrete-time chaotic systems: a fuzzy control approach. Chaos Solitons Fractals 23:459–467
Feuring TH, Lippe W-M (1995) Fuzzy neural networks are universal approximators. In: IFSA World Congress 1995, vol 2, Sao Paulo, Brazil, pp 659–662
Friedman M, Ma M, Kandel A (1998) Fuzzy linear systems. Fuzzy Sets Syst 96:201–209
Friedman M, Ma M, Kandel A (2000) Duality in fuzzy linear systems. Fuzzy Sets Syst 109:55–58
Jiang W, Guo-Dong Q, Bin D (2005) H ∞ variable universe adaptive fuzzy control for chaotic system. Chaos Solitons Fractals 24:1075–1086
Hayashi Y, Buckley JJ, Czogala E (1993) Fuzzy neural network with fuzzy signals and weights. Int J Intell Syst 8:527–537
Ishibuchi H, Nii M (2001) Numerical analysis of the learning of fuzzified neural networks from fuzzy if-then rules. Fuzzy Sets Syst 120:281–307
Ishibuchi H, Kwon K, Tanaka HA (1995) A learning algorithm of fuzzy neural networks with triangular fuzzy weights. Fuzzy Sets Syst 71:277–293
Kaleva O (1987) Fuzzy differential equations. Fuzzy Sets Syst 24:301–317
Kaufmann A, Gupta MM (1985) Introduction fuzzy arithmetic. Van Nostrand Reinhold, New York
Li HX, Li LX, Wang JY (2003) Interpolation functions of feedforward neural networks. Comput Math Appl 46:1861–1874
Ma M, Friedman M, Kandel A (1999) A new fuzzy arithmetic. Fuzzy Sets Syst 108:83–90
Muzzioli S, Reynaerts H (2006) Fuzzy linear systems of the form A 1 x + b 1 = A 2 x + b 2. Fuzzy Sets Syst 157:939–951
Nozari K, Fazlpour B (2007) Some consequences of spacetime fuzziness. Chaos Solitons Fractals 34:224–234
Park JH (2004) Intuitionistic fuzzy metric spaces. Chaos Solitons Fractals 22:1039–1046
Rumelhart DE, McClelland JL, the PDP Research Group (1986) Parallel distributed processing, vol 1. MIT Press, Cambridge
Tanaka Y, Mizuno Y, Kado T (2005) Chaotic dynamics in the Friedman equation. Chaos Solitons Fractals 24:407–422
Wang X, Zhong Z, Ha M (2001) Iteration algorithms for solving a system of fuzzy linear equations. Fuzzy Sets Syst 119:121–128
Wang K, Chen G, Wei Y (2009) Perturbation analysis for a class of fuzzy linear systems. J Comput Appl Math 224:54–65
Zadeh LA (1975) The concept of a linguistic variable and its application to approximate reasoning. Inf Sci 8:199–249
Acknowledgments
We would like to offer particular thanks to Dr M. A. Rezvani for the editing of this paper. We would also like to thank the referees for valuable suggestions.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Otadi, M., Mosleh, M. & Abbasbandy, S. Numerical solution of fully fuzzy linear systems by fuzzy neural network. Soft Comput 15, 1513–1522 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00500-010-0685-9
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00500-010-0685-9