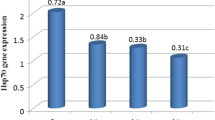
Abstract
The present experiment was conducted to investigate the interactive effects between dietary glutamine (Gln, 0 and 5 g/kg) and gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA, 0 and 100 mg/kg) on growth performance and amino acid (AA) metabolism of broilers under hot environment. A total of 360 22-day-old Arbor Acres male chickens were randomly assigned to five treatment groups under thermoneutral chamber (PC, 23 °C) and cyclic heat stress (HS, 30–34 °C cycling) conditions. Compared with the PC group, cyclic HS decreased (P < 0.05) daily weight gain (DWG), daily feed consumption (DFC), the concentrations of Gln, glutamate (Glu), and GABA, and the activities of glutaminase and glutamic acid decarboxylase (GAD) in breast muscle at 28, 35, and 42 days, while it increased (P < 0.05) the activities of glutamine synthetase (GS) and gamma-aminobutyric acid transaminase (GABA-T) at 28, 35, and 42 days. Dietary Gln and GABA improved (P < 0.05) DWG and DFC of broilers under cyclic HS during 28–42 days. In breast muscle, the Gln supplementation increased (P < 0.05) the concentrations of Gln (28, 35, and 42 days), Glu (28, 35, and 42 days), and GABA (42 days) and the activities of glutaminase (28, 35, and 42 days) and GAD (28, 35, and 42 days) but decreased (P < 0.05) GS activities at 28, 35, and 42 days and GABA-T activities at 28 days. The addition of GABA increased (P < 0.05) the concentrations of Gln and Glu and activities of glutaminase and GAD, while it decreased (P < 0.05) GABA-T activities at 28, 35, and 42 days. Significant interactions (P < 0.05) between Gln and GABA were found on breast skeletal muscle Gln concentrations, glutaminase activities, GS activities at 28 and 35 days, and DWG, GABA concentrations, and GABA-T activities at 28, 35, and 42 days in broilers under cyclic HS. In conclusion, the present results indicated that the interactions of exogenous Gln and GABA could offer a potential nutritional strategy to prevent HS-related depression in skeletal muscle Gln and GABA metabolism of broilers.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aksit M, Yalcin S, Özkan S, Metin K, Ozdemir D (2006) Effects of temperature during rearing and crating on stress parameters and meat quality of broilers. Poult Sci 85:1867–1874. doi:10.1093/ps/85.11.1867
Bartell SM, Batal AB (2007) The effect of supplemental glutamine on growth performance, development of the gastrointestinal tract, and humoral immune response of broilers. Poult Sci 86:1940–1947. doi:10.1093/ps/86.9.1940
Biggio G, Corda MG, Demontis G, Concas A, Gessa GL (1980) Sudden decrease in cerebellar GABA binding induced by stress. Pharmacol Res Commun 12:489–493. doi:10.1016/S0031-6989(80)80120-2
Chand N, Naz S, Khan A, Khan S, Khan RU (2014) Performance traits and immune response of broiler chicks treated with zinc and ascorbic acid supplementation during cyclic heat stress. Int J Biometeorol 58:2153–2157. doi:10.1007/s00484-014-0815-7
Chen Z, Tang J, Sun YQ, Xie J (2013) Protective effect of γ-aminobutyric acid on antioxidation function in intestinal mucosa of Wenchang chicken induced by heat stress. J Anim Plant Sci 23:1634–1641
Chen Z, Xie J, Wang B, Tang J (2014) Effect of γ-aminobutyric acid on digestive enzymes, absorption function, and immune function of intestinal mucosa in heat-stressed chicken. Poult Sci 93:2490–2500. doi:10.3382/ps.2013-03398
Dai SF, Wang LK, Wen AY, Wang LX, Jin GM (2009) Dietary glutamine supplementation improves growth performance, meat quality and colour stability of broilers under heat stress. Brit Poult Sci 50:333–340. doi:10.1080/00071660902806947
Dai SF, Gao F, Zhang WH, Song SX, Xu XL, Zhou GH (2011) Effects of dietary glutamine and gamma-aminobutyric acid on performance, carcass characteristics and serum parameters in broilers under circular heat stress. Anim Feed Sci Technol 168:51–60. doi:10.1016/j.anifeedsci.2011.03.005
Dai SF, Gao F, Xu XL, Zhang WH, Song SX, Zhou GH (2012) Effects of dietary glutamine and gamma- aminobutyric acid on meat colour, pH, composition, and water-holding characteristic in broilers under cyclic heat stress. Brit Poult Sci 53:471–481. doi:10.1080/00071668.2012.719148
Dalvi A, Rodgers RJ (2001) Anxiolytic effects of valproate and diazepam in mice are differentially sensitive to picrotoxin antagonism. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 68:23–32. doi:10.1016/S0091-3057(00)00408-1
Erecińska M, Silver IA (1990) Metabolism and role of glutamate in mammalian brain. Prog Neurobiol 35:245–296. doi:10.1016/0301-0082(90)90013-7
Fluck E, Hogg S, Jones RB, Bourne R, File SE (1997) Changes in tonic immobility and the GABA- benzodiazepine system in response to handling in the chick. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 58:269–274. doi:10.1016/S0091-3057(96)00554-0
Gates RS, Zhang H, Colliver DG, Overhults DG (1995) Regional variation in temperature humidity index for poultry housing. Trans ASAE 38:197–206
Ghazi S, Amjadian T, Norouzi S (2015) Single and combined effects of vitamin C and oregano essential oil in diet, on growth performance, and blood parameters of broiler chicks reared under heat stress condition. Int J Biometeorol 59:1019–1024. doi:10.1007/s00484-014-0915-4
Gore DC, Wolfe RR (2002) Glutamine supplementation fails to affect muscle protein kinetics in critically ill patients. J Parenter Enter Nutr 26:342–350. doi:10.1177/0148607102026006342
Habibian M, Ghazi S, Moeini MM, Abdolmohammadi A (2014) Effects of dietary selenium and vitamin E on immune response and biological blood parameters of broilers reared under thermoneutral or heat stress conditions. Int J Biometeorol 58:741–752. doi:10.1007/s00484-013-0654-y
Khan RU, Naz S, Nikousefat Z, Tufarelli V, Javadani M, Rana N, Laudadio V (2011) Effect of vitamin E in heat-stressed poultry. World Poult Sci J 67:469–478. doi:10.1017/S0043933911000511
Khan RU, Naz S, Nikousefat Z, Selvaggi M, Laudadio V, Tufarelli V (2012) Effect of ascorbic acid in heat-stressed poultry. World Poult Sci J 68:477–490. doi:10.1017/S004393391200058X
NRC (1994) Nutrient requirements of poultry, 9th edn. National Academy Press, Washington, DC
Pascual JM, Carceller F, Roda JM, Cerdán S (1998) Glutamate, glutamine, and GABA as substrates for the neuronal and glial compartments after focal cerebral ischemia in rats. Stroke 29:1048–1057. doi:10.1161/01.STR.29.5.1048
Peng L, Hertz L, Huang R, Sonnewald U, Petersen SB, Westergaard N, Larsson O, Schousboe A (1993) Utilization of glutamine and of TCA cycle constituents as precursors for transmitter glutamate and GABA. Dev Neurosci 15:367–377. doi:10.1159/000111357
Sanami MN, Ghaedi B, Salary J, Matin HRH (2014) In ovo injection of L-arginine on performance and bone mineralization in broiler chicken. Res Opin Anim Vet Sci 4:394–397
Shekhar A, Johnson PL, Sajdyk TJ, Fitz SD, Keim SR, Kelley PE, Gehlert DR, DiMicco JA (2006) Angiotensin-II is a putative neurotransmitter in lactate-induced panic-like responses in rats with disruption of GABAergic inhibition in the dorsomedial hypothalamus. J Neurosci 26:9205–9219
SPSS (2004) Statistical package for social sciences (Release 13.0.) for windows. SPSS Inc, USA
Strużyńska L, Sulkowski G (2004) Relationships between glutamine, glutamate, and GABA in nerve endings under Pb-toxicity conditions. J Inorg Biochem 98:951–958. doi:10.1016/j.jinorgbio.2004.02.010
Watford M (1991) Regulation of expression of the genes for glutaminase and glutamine synthetase in the acidotic rat. Contrib Nephrol 92:211–217
Watford M, Wu G (2005) Glutamine metabolism in uricotelic species: variation in skeletal muscle glutamine synthetase, glutaminase, glutamine levels and rates of protein synthesis. Comp Biochem Physiol B 140:607–614. doi:10.1016/j.cbpc.2004.12.009
Xi P, Jiang Z, Zheng C, Lin Y, Wu G (2011) Regulation of protein metabolism by glutamine: implications for nutrition and health. Front Biosci 16:578–597. doi:10.2741/3707
Xie W, Hou X, Yan F, Sun G, Han R, Kang X (2013) Effect of gamma-aminobutyric acid on growth performance and immune function in chicks under beak trimming stress. Anim Sci J 84:121–129. doi:10.1111/j.1740-0929.2012.01051.x
Zhang M, Zou X, Li H, Dong X, Zhao W (2012) Effect of dietary gamma-aminobutyric acid on laying performance, egg quality, immune activity and endocrine hormone in heat-stressed Roman hens. Anim Sci J 83:141–147. doi:10.1111/j.1740-0929.2011.00939.x
Acknowledgments
This study was supported financially by Anhui Provincial Natural Science Foundation (1408085MC62, 1508085QC61), the research project of Anhui Science and Technology University (ZRC2014398), and the key discipline fund of Animal Science in Anhui Science and Technology University (AKZDXK2015B03). We would like to express our sincere appreciation to Prof. Guanghong Zhou for the assistance in the experimental design of this work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hu, H., Bai, X., Shah, A.A. et al. Interactive effects of glutamine and gamma-aminobutyric acid on growth performance and skeletal muscle amino acid metabolism of 22–42-day-old broilers exposed to hot environment. Int J Biometeorol 60, 907–915 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00484-015-1084-9
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00484-015-1084-9