Abstract.
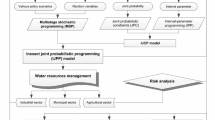
A vast array of techniques have been developed and applied to optimal operation of large-scale multireservoir systems. Researchers continue to be challenged by the highly complex, stochastic, nonlinear, and high dimensional nature of this dynamic optimization problem. An optimal control model is presented which incorporates chance-constraints on system state variables that assure satisfaction of operational restrictions under specified levels of reliability. The chance-constrained optimal control (CCOC) model is tested on a four-reservoir case study, and its performance assessed based on various quantitative and qualitative criteria, including maintenance of acceptable levels of risk and provision of risk-benefit trade-off information. The concepts of reliability, resiliency and vulnerability are utilized to characterize operating policies generated by the algorithm. CCOC is recommended for operational guidance of large-scale multireservoir systems due to its robustness, flexibility, modest computational requirements, and ability to include risk considerations directly impacting the choice of operational schemes.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ouarda, T., Labadie, J. Chance-constrained optimal control for multireservoir system optimization and risk analysis. Stochastic Environmental Research and Risk Assessment 15, 185–204 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1007/s004770100066
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s004770100066