Abstract
Background
This study investigated the impact of body composition in the arterial stiffness of children with chronic kidney disease (CKD).
Methods
Fat mass (FM), fat tissue index (FTI), fat-free mass (FFM), fat-free tissue index (FFTI), and FFTI/FTI were measured in 26 patients and 25 healthy controls by bio-impedance analysis. Data on patient’s body mass index (BMI) for height-age, serum albumin, glomerular filtration rate (GFR), blood pressure status, and pulse wave velocity (PWV) were collected in patients.
Results
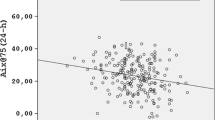
Patients presented lower levels of FM and FFM compared to healthy controls (p = 0.04 and p = 0.055 respectively). In patient group, BMI height-age z-score was positively correlated to FTI (r2 = 0.574, p < 0.001) and FFTI (r2 = 0.338, p = 0.001) and negatively correlated to FFTI/FTI (r2 = 0.263, p = 0.007). Serum albumin was positively correlated only with FFM among body composition data (r2 = 0.169, p = 0.037). PWV z-score was positively correlated to FFTI (r2 = 0.421, p = 0.006) and inversely correlated to FFTI/FTI ≥ 2.5 (r2 = 0.317, p = 0.003). Patients with FFTI/FTI ≥ 2.5 presented lower levels of PWV regardless the need for antihypertensive treatment. Serum albumin ≥ 3.8 mg/dl and FFTI/FTI ≥ 2.5 were independently associated with a lower risk for high PWV, after adjustment for age, sex, and GFR (OR 0.009, 95% CI 0.000–0.729 and OR 0.039, 95% CI 0.002–0.680). All underweight [2 (7.7%)] and overweight [4 (15.4%)] patients presented high PWV. Among normal weight patients, FFTI/FTI ratio ≥ 2.5 was significantly associated with lower PWV z-score (p = 0.013).
Conclusions
Both underweight and overweight are associated with arterial stiffness. Targeting FFTI/FTI ≥ 2.5 could be protective against cardiovascular disease in normal weight children.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Mitsnefes MM (2012) Cardiovascular disease in children with chronic kidney disease. J Am Soc Nephrol 23:578–585
Shroff R, Weaver DJ, Mitsnefes MM (2011) Cardiovascular complications in children with chronic kidney disease. Nat Rev Nephrol 7:642–649
Savant JD, Furth SL, Meyers KE (2014) Arterial stiffness in children: pediatric measurement and considerations. Pulse (Basel) 2:69–80
Stabouli S, Papakatsika S, Kotronis G, Papadopoulou-Legbelou K, Rizos Z, Kotsi (2015) Arterial stiffness and SBP variability in children and adolescents. J Hypertens 33:88–95
Kotsis V, Antza C, Doundoulakis I, Stabouli S (2017) Markers of early vascular ageing. Curr Pharm Des 23:3200–3204
Patange AR, Valentini RP, Du W, Pettersen MD (2012) Vitamin D deficiency and arterial wall stiffness in children with chronic kidney disease. Pediatr Cardiol 33:122–128
Kis E, Cseprekál O, Bíró E, Kelen K, Ferenczi D, Kerti A, Szabó AJ, Szabó A, Reusz GS (2009) Effects of bone and mineral metabolism on arterial elasticity in chronic renal failure. Pediatr Nephrol 24:2413–2420
Shroff RC, Donald AE, Hiorns MP, Watson A, Feather S, Milford D, Ellins EA, Storry C, Ridout D, Deanfield J, Rees L (2007) Mineral metabolism and vascular damage in children on dialysis. J Am Soc Nephrol 18:2996–3003
Schmidt BMW, Sugianto RI, Thurn D, Azukaitis K, Bayazit AK, Canpolat N, Eroglu AG, Caliskan S, Doyon A, Duzova A, Karagoz T, Anarat A, Deveci M, Mir S, Ranchin B, Shroff R, Baskin E, Litwin M, Özcakar ZB, Büscher R, Soylemezoglu O, Dusek J, Kemper MJ, Matteucci MC, Habbig S, Laube G, Wühl E, Querfeld U, Sander A, Schaefer F, Melk A, 4C Study Consortium (2018) Early effects of renal replacement therapy on cardiovascular comorbidity in children with end-stage kidney disease. Transplantation 102:484–492
Schaefer F, Doyon A, Azukaitis K, Bayazit A, Canpolat N, Duzova A, Niemirska A, Sözeri B, Thurn D, Anarat A, Ranchin B, Litwin M, Caliskan S, Candan C, Baskin E, Yilmaz E, Mir S, Kirchner M, Sander A, Haffner D, Melk A, Wühl E, Shroff R, Querfeld U, 4C Study Consortium (2017) Cardiovascular phenotypes in children with CKD: the 4C study. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol 12:19–28
Marcelli D, Usvyat LA, Kotanko P, Bayh I, Canaud B, Etter M, Gatti E, Grassmann A, Wang Y, Marelli C, Scatizzi L, Stopper A, van der Sande FM, Kooman J, MONitoring Dialysis Outcomes (MONDO) Consortium (2015) Body composition and survival in dialysis patients: results from an international cohort study. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol 10:1192–1200
Lin TY, Peng CH, Hung SC, Tarng DC (2018) Body composition is associated with clinical outcomes in patients with non–dialysis-dependent chronic kidney disease. Kidney Int 93:733–740
Beddhu S, Pappas LM, Ramkumar N, Samore M (2003) Effects of body size and body composition on survival in hemodialysis patients. J Am Soc Nephrol 14:2366–2372
Schwartz GJ, Muñoz A, Schneider MF, Mak RH, Kaskel F, Warady BA, Furth SL (2009) New equations to estimate GFR in children with CKD. J Am Soc Nephrol 20:629–637
Cole TJ, Bellizzi MC, Flegal KM, Dietz WH (2000) Establishing a standard definition for child overweight and obesity worldwide: international survey. BMJ 320:1240–1243
Oliveira EA, Cheung WW, Toma KG, Mak RH (2018) Muscle wasting in chronic kidney disease. Pediatr Nephrol 33:789–798
Van Bortel LM, Laurent S, Boutouyrie P, Chowienczyk P, Cruickshank JK, De Backer T, Filipovsky J, Huybrechts S, Mattace-Raso FU, Protogerou AD, Schillaci G, Segers P, Vermeersch S, Weber T, Artery Society; European Society of Hypertension Working Group on Vascular Structure and Function; European Network for Noninvasive Investigation of Large Arteries (2012) Expert consensus document on the measurement of aortic stiffness in daily practice using carotid-femoral pulse wave velocity. J Hypertens 30:445–448
Reusz GS, Cseprekal O, Temmar M, Kis E, Cherif AB, Thaleb A, Fekete A, Szabó AJ, Benetos A, Salvi P (2010) Reference values of pulse wave velocity in healthy children and teenagers. Hypertension 56:217–224
Rees L, Jones H (2013) Nutritional management and growth in children with chronic kidney disease. Pediatr Nephrol 28:527–536
Mak RH, Cheung WW, Zhan JY, Shen Q, Foster BJ (2012) Cachexia and protein-energy wasting in children with chronic kidney disease. Pediatr Nephrol 27:173–181
Abraham AG, Mak RH, Mitsnefes M, White C, Moxey-Mims M, Warady B, Furth SL (2014) Protein energy wasting in children with chronic kidney disease. Pediatr Nephrol 29:1231–1238
Foster BJ, Kalkwarf HJ, Shults J, Zemel BS, Wetzsteon RJ, Thayu M, Foerster DL, Leonard MB (2011) Association of chronic kidney disease with muscle deficits in children. J Am Soc Nephrol 22:377–386
Apostolou A, Printza N, Karagiozoglou-Lampoudi T, Dotis J, Papachristou F (2014) Nutrition assessment of children with advanced stages of chronic kidney disease-a single center study. Hippokratia 18:212–216
Bonthuis M, van Stralen KJ, Verrina E, Groothoff JW, Alonso Melgar Á, Edefonti A, Fischbach M, Mendes P, Molchanova EA, Paripović D, Peco-Antic A, Printza N, Rees L, Rubik J, Stefanidis CJ, Sinha MD, Zagożdżon I, Jager KJ, Schaefer F (2013) Underweight, overweight and obesity in paediatric dialysis and renal transplant patients. Nephrol Dial Transplant 28:iv195–iv204
Miliku K, Bakker H, Dorresteijn EM, Cransberg K, Franco OH, Felix JF, Jaddoe VW (2017) Childhood estimates of glomerular filtration rate based on creatinine and cystatin C: importance of body composition. Am J Nephrol 45:320–326
Ayestaran FW, Schneider MF, Kaskel FJ, Srivaths PR, Seo-Mayer PW, Moxey-Mims M, Furth SL, Warady BA, Greenbaum LA (2016) Perceived appetite and clinical outcomes in children with chronic kidney disease. Pediatr Nephrol 31:1121–1127
Ku E, Glidden DV, Hsu CY, Portale AA, Grimes B, Johansen KL (2016) Association of body mass index with patient-centered outcomes in children with ESRD. J Am Soc Nephrol 27:551–558
Wong CS, Gipson DS, Gillen DL, Emerson S, Koepsell T, Sherrard DJ, Watkins SL, Stehman-Breen C (2000) Anthropometric measures and risk of death in children with end-stage renal disease. Am J Kidney Dis 36:811–819
Mastrangelo A, Paglialonga F, Edefonti A (2014) Assessment of nutritional status in children with chronic kidney disease and on dialysis. Pediatr Nephrol 29:1349–1358
Cochat P, Braillon P, Feber J, Hadj-Aïssa A, Dubourg L, Liponski I, Saïd MH, Glastre C, Meunier PJ, David L (1996) Body composition in children with renal disease: use of dual energy X-ray absorptiometry. Pediatr Nephrol 10:264–268
Gao T, Leonard MB, Zemel B, Kalkwarf HJ, Foster BJ (2012) Interpretation of body mass index in children with CKD. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol 7:558–564
Weber DR, Leonard MB, Shults J, Zemel BS (2014) A comparison of fat and lean body mass index to BMI for the identification of metabolic syndrome in children and adolescents. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 99:3208–3216
Bohn B, Müller MJ, Simic-Schleicher G, Kiess W, Siegfried W, Oelert M, Tuschy S, Berghem S, Holl RW, APV Initiative and the German BMBF Competence Network Obesity (2015) BMI or BIA: is body mass index or body fat mass a better predictor of cardiovascular risk in overweight or obese children and adolescents? A German/Austrian/Swiss multicenter APV analysis of 3,327 children and adolescents. Obes Facts 8:156–165
Lin TY, Lim PS, Hung SC (2018) Normal-weight obesity and clinical outcomes in nondiabetic chronic kidney disease patients: a cohort study. Am J Clin Nutr 107:664–672
Sgambat K, Roem J, Mitsnefes M, Portale AA, Furth S, Warady B, Moudgil A (2018) Waist-to-height ratio, body mass index, and cardiovascular risk profile in children with chronic kidney disease. Pediatr Nephrol. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00467-018-3987-2
Fantuzzi G, Mazzone T (2007) Adipose tissue and atherosclerosis exploring the connection. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 27:996–1003
Hardy OT, Czech MP, Corvera S (2012) What causes the insulin resistance underlying obesity? Curr Opin Endocrinol Diabetes Obes 19:81–87
Srikanthan P, Karlamangla AS (2011) Relative muscle mass is inversely associated with insulin resistance and prediabetes. Findings from the third National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 96:2898–2903
Kim K, Park SM (2018) Association of muscle mass and fat mass with insulin resistance and the prevalence of metabolic syndrome in Korean adults: a cross-sectional study. Sci Rep 8:2703
Harada K, Suzuki S, Ishii H, Aoki T, Hirayama K, Shibata Y, Negishi Y, Sumi T, Kawashima K, Kunimura A, Shimbo Y, Tatami Y, Kawamiya T, Yamamoto D, Morimoto R, Yasuda Y, Murohara T (2017) Impact of skeletal muscle mass on long-term adverse cardiovascular outcomes in patients with chronic kidney disease. Am J Cardiol 119:1275–1280
Kahraman S, Yilmaz R, Akinci D, Arici M, Altun B, Erdem Y, Yasavul U, Turgan C (2005) U-shaped association of body mass index with inflammation and atherosclerosis in hemodialysis patients. J Ren Nutr 15:377–386
Canpolat N, Caliskan S, Sever L, Tasdemir M, Ekmekci OB, Pehlivan G, Shroff R (2013) Malnutrition and its association with inflammation and vascular disease in children on maintenance dialysis. Pediatr Nephrol 28:2149–2156
Amodu A, Abramowitz MK (2016) Effects of metabolic acidosis on skeletal muscle. In: Wesson D (ed) Metabolic acidosis: a guide to clinical assessment and management, 1st edn. Springer, New York, pp 101–110
Mistretta A, Marventano S, Antoci M, Cagnetti A, Giogianni G, Nolfo F, Rametta S, Pecora G, Marranzano M (2017) Mediterranean diet adherence and body composition among Southern Italian adolescents. Obes Res Clin Pract 11:215–226
Chauveau P, Aparicio M, Bellizzi V, Campbell K, Hong X, Johansson L, Kolko A, Molina P, Sezer S, Wanner C, Ter Wee PM, Teta D, Fouque D, Carrero JJ, European Renal Nutrition (ERN) Working Group of the European Renal Association–European Dialysis Transplant Association (ERA-EDTA) (2018) Mediterranean diet as the diet of choice for patients with chronic kidney disease. Nephrol Dial Transplant 33:725–735
Roshanravan B, Gamboa J, Wilund K (2017) Exercise and CKD: skeletal muscle dysfunction and practical application of exercise to prevent and treat physical impairments in CKD. Am J Kidney Dis 69:837–852
Molina P, Vizcaíno B, Molina MD, Beltrán S, González-Moya M, Mora A, Castro-Alonso C, Kanter J, Ávila AI, Górriz JL, Estañ N, Pallardó LM, Fouque D, Carrero JJ (2018) The effect of high-volume online haemodiafiltration on nutritional status and body composition: the ProtEin Stores prEservaTion (PESET) study. Nephrol Dial Transplant 33:1223–1235
Dasgupta I, Keane D, Lindley E, Shaheen I, Tyerman K, Schaefer F, Wühl E, Müller MJ, Bosy-Westphal A, Fors H, Dahlgren J, Chamney P, Wabel P, Moissl U (2018) Validating the use of bioimpedance spectroscopy for assessment of fluid status in children. Pediatr Nephrol 33:1601–1607
Milani GP, Groothoff JW, Vianello FA, Fossali EF, Paglialonga F, Consolo S, Edefonti A, Consonni D, van Harskamp D, van Goudoever JB, Schierbeek H, Agostoni C, Oosterveld MJS (2018) Bioimpedance spectroscopy imprecisely assesses lean body mass in pediatric dialysis patients. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr 67:533–537
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
This study was approved by the local Ethics Committee and was conducted in accordance with the 1964 Helsinki Declaration or comparable standards. Informed consent was obtained from the parents of all the participants.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(DOCX 32 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Karava, V., Printza, N., Dotis, J. et al. Body composition and arterial stiffness in pediatric patients with chronic kidney disease. Pediatr Nephrol 34, 1253–1260 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00467-019-04224-8
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00467-019-04224-8