Abstract
Background
Surveillance biopsies (SBs) are performed in some pediatric kidney transplant programs, based on data obtained in earlier immunosuppressive eras that the treatment of subclinical acute rejection results in better graft survival. The benefit of SBs for patients on modern immunosuppression regimens is unclear. We have therefore evaluated the clinical utility of SBs in a population of children receiving a kidney transplant.
Methods
We have performed SBs at 3, 6 and 12 months post-transplantation as standard of care at our institution since 2013 in patients on a regimen of rabbit anti-thymocyte globulin, tacrolimus, mycophenolate and rapid steroid taper (RST; steroids maintained in some exceptions). We reviewed pathology reports of 82 SBs from 34 transplants in 34 children for all abnormal findings and adequacy of specimens. Clinical records were reviewed for changes in management resulting from SB findings and for significant procedure complications.
Results
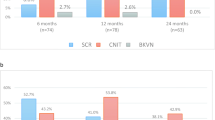
Of the 82 biopsies, 41 (50%) had abnormal findings separate from fibrosis, including five Banff Grade I rejections, ten borderline rejections, six calcineurin-inhibitor nephrotoxicity, four BK-virus nephropathy, five recurrent disease and three acute pyelonephritis. Moderate or more fibrosis was present in nine of the 82 (11%) biopsies. Management changes due to SB findings occurred in nine cases (11.0%). The proportion of abnormal findings or management changes did not differ between the RST or steroid-based groups. Patients performing clean intermittent catheterization showed inflammatory changes often read as rejection, but were managed differently. Three biopsies were deemed inadequate. No significant complications occurred.
Conclusions
A high percentage of the SBs performed under modern immunosuppression showed abnormal findings even when fibrosis was excluded. However, management changes due to the SB findings were less frequent, although they occurred in a clinically meaningful percentage of cases. Complications or inadequate specimens were rare.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Rush D (2006) Protocol transplant biopsies: an underutilized tool in kidney transplantation. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol 1:138–143
Rush D, Nickerson P, Gough J, McKenna R, Grimm P, Cheang M, Trpkov K, Solez K, Jeffery J (1998) Beneficial effects of treatment of early subclinical rejection: a randomized study. J Am Soc Nephrol 9:2129–2134
Rush D, Arlen D, Boucher A, Busque S, Cockfield SM, Girardin C, Knoll G, Lachance JG, Landsberg D, Shapiro J, Shoker A, Yilmaz S (2007) Lack of benefit of early protocol biopsies in renal transplant patients receiving TAC and MMF: a randomized study. Am J Transplant 7:2538–2545
Dharnidharka VR, Abdulnour HA, Araya CE (2011) The BK virus in renal transplant recipients—review of pathogenesis, diagnosis, and treatment. Pediatr Nephrol 26:1763–1774
Mengel M, Chapman JR, Cosio FG, Cavaille-Coll MW, Haller H, Halloran PF, Kirk AD, Mihatsch MJ, Nankivell BJ, Racusen LC, Roberts IS, Rush DN, Schwarz A, Seron D, Stegall MD, Colvin RB (2007) Protocol biopsies in renal transplantation: insights into patient management and pathogenesis. Am J Transplant 7:512–517
Birk PE (2012) Surveillance biopsies in children post-kidney transplant. Pediatr Nephrol 27:753–760
Loupy A, Haas M, Solez K, Racusen L, Glotz D, Seron D, Nankivell BJ, Colvin RB, Afrouzian M, Akalin E, Alachkar N, Bagnasco S, Becker JU, Cornell L, Drachenberg C, Dragun D, de Kort H, Gibson IW, Kraus ES, Lefaucheur C, Legendre C, Liapis H, Muthukumar T, Nickeleit V, Orandi B, Park W, Rabant M, Randhawa P, Reed EF, Roufosse C, Seshan SV, Sis B, Singh HK, Schinstock C, Tambur A, Zeevi A, Mengel M (2017) The Banff 2015 kidney meeting report: current challenges in rejection classification and prospects for adopting molecular pathology. Am J Transplant 17:28–41
Sar A, Worawichawong S, Benediktsson H, Zhang J, Yilmaz S, Trpkov K (2011) Interobserver agreement for polyomavirus nephropathy grading in renal allografts using the working proposal from the 10th Banff conference on allograft pathology. Hum Pathol 42:2018–2024
Mehta R, Cherikh W, Sood P, Hariharan S (2017) Kidney allograft surveillance biopsy practices across US transplant centers: a UNOS survey. Clin Transpl 31. https://doi.org/10.1111/ctr.12945
Shishido S, Asanuma H, Nakai H, Mori Y, Satoh H, Kamimaki I, Hataya H, Ikeda M, Honda M, Hasegawa A (2003) The impact of repeated subclinical acute rejection on the progression of chronic allograft nephropathy. J Am Soc Nephrol 14:1046–1052
Seikku P, Krogerus L, Jalanko H, Holmberg C (2005) Better renal function with enhanced immunosuppression and protocol biopsies after kidney transplantation in children. Pediatr Transplant 9:754–762
Hymes LC, Warshaw BL, Hennigar RA, Amaral SG, Greenbaum LA (2009) Prevalence of clinical rejection after surveillance biopsies in pediatric renal transplants: does early subclinical rejection predispose to subsequent rejection episodes? Pediatr Transplant 13:823–826
Naesens M, Salvatierra O, Benfield M, Ettenger RB, Dharnidharka V, Harmon W, Mathias R, Sarwal MM, for the SNSNIHCMT (2012) Subclinical inflammation and chronic renal allograft injury in a randomized trial on steroid avoidance in pediatric kidney transplantation. Am J Transplant 12:2730–2743
Kanzelmeyer NK, Ahlenstiel T, Drube J, Froede K, Kreuzer M, Broecker V, Ehrich JH, Melk A, Pape L (2010) Protocol biopsy-driven interventions after pediatric renal transplantation. Pediatr Transplant 14:1012–1018
Kanzelmeyer NK, Ahlenstiel T, Kreuzer M, Becker JU, Pape L (2013) Correlations with six-month protocol biopsy findings in pediatric transplant recipients on low- and regular-dose CNI regimens. Clin Transpl 27:319–323
Birk PE, Blydt-Hansen TD, Dart AB, Kaita LM, Proulx C, Taylor G (2007) Low incidence of adverse events in outpatient pediatric renal allograft biopsies. Pediatr Transplant 11:196–200
Benfield MR, Herrin J, Feld L, Rose S, Stablein D, Tejani A (1999) Safety of kidney biopsy in pediatric transplantation: a report of the controlled clinical trials in pediatric transplantation trial of induction therapy study group. Transplantation 67:544–547
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
A retrospective analysis was conducted of all SBs since January 2013 performed in children receiving a kidney transplant at St Louis Children’s Hospital, under Institutional Review Board approval.
Additional information
Vikas R. Dharnidharka and Neil Vyas contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Dharnidharka, V.R., Vyas, N., Gaut, J.P. et al. The utility of surveillance biopsies in pediatric kidney transplantation. Pediatr Nephrol 33, 889–895 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00467-017-3864-4
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00467-017-3864-4