Abstract
Background
Morbidity and mortality with necrotizing enterocolitis (NEC) remains a significant challenge. Acute kidney injury (AKI) has been shown to worsen survival in critically ill neonates. To our knowledge, this study is the first to evaluate the prevalence of AKI and its impact on outcomes in neonatal NEC.
Methods
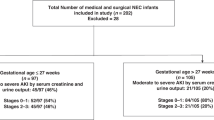
We carried out a single-center retrospective chart review of all neonates treated for NEC between 2003 and 2015 (N = 181). AKI is defined as a rise in serum creatinine (SCr) from a previous trough according to neonatal modified KDIGO criteria (stage 1 = SCr rise 0.3 mg/dL or SCr 150 < 200%, stage 2 = SCr rise 200 < 300%, stage 3 = SCr rise ≥300%, SCr 2.5 mg/dL or dialysis). Primary outcome was in-hospital mortality and secondary outcomes were hospital length of stay (LOS) and need for and type of surgery.
Results
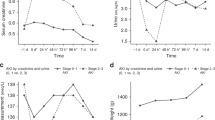
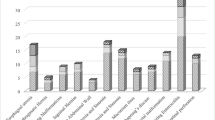
Acute kidney injury occurred in 98 neonates (54%), with 39 stage 1 (22%), 31 stage 2 (18%), and 28 stage 3 (16%), including 5 requiring dialysis. Non-AKI and AKI groups were not statistically different in age, weight, Bell’s NEC criteria, and medication exposure (vasopressors, vancomycin, gentamicin, or diuretic). Neonates with AKI had higher mortality (44% vs 25.6%, p = 0.008) and a higher chance of death (HR 2.4, CI 1.2–4.8, p = 0.009), but the effect on LOS on survivors did not reach statistical significance (79 days, interquartile range [IQR] 30–104 vs 54 days, IQR 30–92, p = 0.09). Overall, 48 (27.9%) patients required surgical intervention.
Conclusions
This study shows that AKI not only occurs in over half of patients with NEC, but that it is also associated with more than a two-fold higher mortality, highlighting the importance of early recognition and potentially early intervention for AKI.

Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- AKI:
-
Acute kidney injury
- NEC:
-
Necrotizing enterocolitis
- NICU:
-
Neonatal intensive care unit
- KDIGO:
-
Kidney Disease Improving Global Outcomes
- DIC:
-
Disseminated intravascular coagulopathy
- VON:
-
Vermont Oxford Network
References
Kliegman RM, Fanaroff AA (1981) Neonatal necrotizing enterocolitis: a nine-year experience. Am J Dis Child 135:603–607
Abdullah F, Zhang Y, Camp M, Mukherjee D, Gabre-Kidan A, Colombani PM, Chang DC (2010) Necrotizing enterocolitis in 20,822 infants: analysis of medical and surgical treatments. Clin Pediatr (Phila) 49:166–171
Stey A, Barnert ES, Tseng CH, Keeler E, Needleman J, Leng M, Kelley-Quon LI, Shew SB (2015) Outcomes and costs of surgical treatments of necrotizing enterocolitis. Pediatrics 135:e1190–e1197
Selewski DT, Charlton JR, Jetton JG, Guillet R, Mhanna MJ, Askenazi DJ, Kent AL (2015) Neonatal acute kidney injury. Pediatrics 136:e463–e473
Carmody JB, Swanson JR, Rhone ET, Charlton JR (2014) Recognition and reporting of AKI in very low birth weight infants. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol 9:2036–2043
Viswanathan S, Manyam B, Azhibekov T, Mhanna MJ (2012) Risk factors associated with acute kidney injury in extremely low birth weight (ELBW) infants. Pediatr Nephrol 27:303–311
Askenazi DJ, Griffin R, McGwin G, Carlo W, Ambalavanan N (2009) Acute kidney injury is independently associated with mortality in very low birthweight infants: a matched case-control analysis. Pediatr Nephrol 24:991–997
Gadepalli SK, Selewski DT, Drongowski RA, Mychaliska GB (2011) Acute kidney injury in congenital diaphragmatic hernia requiring extracorporeal life support: an insidious problem. J Pediatr Surg 46:630–635
Mammen C, Al Abbas A, Skippen P, Nadel H, Levine D, Collet JP, Matsell DG (2012) Long-term risk of CKD in children surviving episodes of acute kidney injury in the intensive care unit: a prospective cohort study. Am J Kidney Dis 59:523–530
Menon S, Kirkendall ES, Nguyen H, Goldstein SL (2014) Acute kidney injury associated with high nephrotoxic medication exposure leads to chronic kidney disease after 6 months. J Pediatr 165(522–527):e522
Bruel A, Roze JC, Quere MP, Flamant C, Boivin M, Roussey-Kesler G, Allain-Launay E (2016) Renal outcome in children born preterm with neonatal acute renal failure: IRENEO-a prospective controlled study. Pediatr Nephrol 31:2365–2373
Maqsood S, Fung N, Chowdhary V, Raina R, Mhanna MJ (2017) Outcome of extremely low birth weight infants with a history of neonatal acute kidney injury. Pediatr Nephrol 32:1035–1043
Harer MW, Pope CF, Conaway MR, Charlton JR (2017) Follow-up of acute kidney injury in neonates during childhood years (FANCY): a prospective cohort study. Pediatr Nephrol 32:1067–1076
Jetton JG, Askenazi DJ (2012) Update on acute kidney injury in the neonate. Curr Opin Pediatr 24:191–196
Selewski DT, Cornell TT, Heung M, Troost JP, Ehrmann BJ, Lombel RM, Blatt NB, Luckritz K, Hieber S, Gajarski R, Kershaw DB, Shanley TP, Gipson DS (2014) Validation of the KDIGO acute kidney injury criteria in a pediatric critical care population. Intensive Care Med 40:1481–1488
Selewski DT, Jordan BK, Askenazi DJ, Dechert RE, Sarkar S (2013) Acute kidney injury in asphyxiated newborns treated with therapeutic hypothermia. J Pediatr 162:725–729.e1
Alabbas A, Campbell A, Skippen P, Human D, Matsell D, Mammen C (2013) Epidemiology of cardiac surgery-associated acute kidney injury in neonates: a retrospective study. Pediatr Nephrol 28:1127–1134
Gregory KE, DeForge CE, Natale KM, Phillips M, Van Marter LJ (2011) Necrotizing enterocolitis in the premature infant: neonatal nursing assessment, disease pathogenesis, and clinical presentation. Adv Neonatal Care 11:155–166
Sharma R, Tepas JJ III, Hudak ML, Wludyka PS, Mollitt DL, Garrison RD, Bradshaw JA, Sharma M (2005) Portal venous gas and surgical outcome of neonatal necrotizing enterocolitis. J Pediatr Surg 40:371–376
Bell MJ, Ternberg JL, Feigin RD, Keating JP, Marshall R, Barton L, Brotherton T (1978) Neonatal necrotizing enterocolitis. Therapeutic decisions based upon clinical staging. Ann Surg 187:1–7
Cox DR (1972) Regression models and life-tables. J R Stat Soc Ser B Stat Methodol 34:187–220
StataCorp (2013) Stata statistical software: release 13. College Station TSL, Houston
El-Badawy AA, Makar S, Abdel-Razek AR, Abd Elaziz D (2015) Incidence and risk factors of acute kidney injury among the critically ill neonates. Saudi J Kidney Dis Transpl 26:549–555
Al-Jboor W, Almardini R, Al Bderat J, Frehat M, Al Masri H, Alajloni MS (2016) Acute kidney injury in critically ill child. Saudi J Kidney Dis Transpl 27:740–747
Andreoli SP (2009) Acute kidney injury in children. Pediatr Nephrol 24:253–263
Zwiers AJ, de Wildt SN, Hop WC, Dorresteijn EM, Gischler SJ, Tibboel D, Cransberg K (2013) Acute kidney injury is a frequent complication in critically ill neonates receiving extracorporeal membrane oxygenation: a 14-year cohort study. Crit Care 17:R151
Koralkar R, Ambalavanan N, Levitan EB, McGwin G, Goldstein S, Askenazi D (2011) Acute kidney injury reduces survival in very low birth weight infants. Pediatr Res 69:354–358
Goldstein SL, Kirkendall E, Nguyen H, Schaffzin JK, Bucuvalas J, Bracke T, Seid M, Ashby M, Foertmeyer N, Brunner L, Lesko A, Barclay C, Lannon C, Muething S (2013) Electronic health record identification of nephrotoxin exposure and associated acute kidney injury. Pediatrics 132:e756–e767
Moffett BS, Goldstein SL (2011) Acute kidney injury and increasing nephrotoxic-medication exposure in noncritically-ill children. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol 6:856–863
Cuzzolin L, Fanos V, Pinna B, di Marzio M, Perin M, Tramontozzi P, Tonetto P, Cataldi L (2006) Postnatal renal function in preterm newborns: a role of diseases, drugs and therapeutic interventions. Pediatr Nephrol 21:931–938
Cataldi L, Leone R, Moretti U, De Mitri B, Fanos V, Ruggeri L, Sabatino G, Torcasio F, Zanardo V, Attardo G, Riccobene F, Martano C, Benini D, Cuzzolin L (2005) Potential risk factors for the development of acute renal failure in preterm newborn infants: a case-control study. Arch Dis Child Fetal Neonatal Ed 90:F514–F519
Goldstein SL (2011) Acute kidney injury in children: prevention, treatment and rehabilitation. Contrib Nephrol 174:163–172
Mathur NB, Agarwal HS, Maria A (2006) Acute renal failure in neonatal sepsis. Indian J Pediatr 73:499–502
Blatt NB, Srinivasan S, Mottes T, Shanley MM, Shanley TP (2014) Biology of sepsis: its relevance to pediatric nephrology. Pediatr Nephrol 29:2273–2287
Garg PM, Tatum R, Ravisankar S, Shekhawat PS, Chen YH (2015) Necrotizing enterocolitis in a mouse model leads to widespread renal inflammation, acute kidney injury, and disruption of renal tight junction proteins. Pediatr Res 78:527–532
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflicts of interest
The authors do not have any potential conflicts of interest, real or perceived; there are no financial sponsors for this study. No honorarium, grant, or other form of payment was given to anyone to produce the manuscript.
Electronic supplementary material
Supplemental Table 1
(DOCX 15 kb)
Supplemental Table 2
(DOCX 12 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Criss, C.N., Selewski, D.T., Sunkara, B. et al. Acute kidney injury in necrotizing enterocolitis predicts mortality. Pediatr Nephrol 33, 503–510 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00467-017-3809-y
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00467-017-3809-y