Abstract
Objective
To estimate the accuracy of Neutrophil Gelatinase-Associated Lipocalin (NGAL) as a biomarker for acute kidney injury (AKI) in children.
Methods
A systematic review of the literature was performed. The review protocol was registered at PROSPERO (CRD 42015024153). We conducted searches in the following databases: Medline (PubMed), LILACS (BVS), SCOPUS (Elsevier), Embase (OVID), Cochrane Central Register of Controlled Trials (CENTRAL), Biomed Central, and ISI Web of Science, from January 1990 to October 2016. For inclusion, studies measured NGAL levels in plasma and urine for AKI in children. For each study, 2 × 2 contingency tables were developed. For statistical analysis we calculated the sensitivity, specificity and diagnostic odds ratio. For methodological assessment, we used Quality Assessment of Diagnostic Accuracy Studies–2. Software used for analysis was Stata 14, and RevMan 5.3.
Results
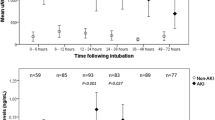
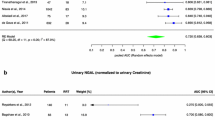
In total 13 studies were analyzed, which included 1629 children. For urinary NGAL, the pooled sensitivity was 0.76 (95% CI 0.62–0.85) and a pooled specificity 0.93 (95% CI 0.88–0.96). The diagnostic odds ratio (DOR) for the detection of AKI was 43 (95% CI 16–115) and the Area under the curve (AUC) was 0.94 (95% CI 0.92–0.96). For plasma NGAL the combined sensitivity was 0.80 (95% CI 0.64–0.90) and a combined specificity was 0.87 (95% CI 0.74–0.94). The DOR was 26 (95% CI 8.0–82) and AUC was 0.90 (95% CI 0.87–0.94) for the detection of AKI in children.
Conclusion
The data suggest that NGAL levels can be an important biomarker for the early detection of AKI in children.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kaddourah A, Basu RK, Bagshaw SM, Goldstein SL (2017) Epidemiology of acute kidney injury in critically ill children and young adults. N Engl J Med 376:11–20
American Society of Nephrology (2005) American Society of Nephrology renal research report. J Am Soc Nephrol 16:1886–1903
Basu RK, Wheeler D (2011) Approaches to the management of acute kidney injury in children. Recent Pat Biomark 1:49–59
Haase-Fielitz A, Haase M, Devarajan P (2014) Neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin as a biomarker of acute kidney injury: a critical evaluation of current status. Ann Clin Biochem 51:335–351
Devarajan P (2008) Neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin (NGAL): a new marker of kidney disease. Scand J Clin Lab Invest Suppl 241:89–94
Schmidt-Ott KM, Mori K, Li JY, Kalandadze A, Cohen DJ, Devarajan P, Barasch J (2007) Dual action of neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin. J Am Soc Nephrol 18:407–413
Yang J, Goetz D, Li JY, Wang W, Mori K, Setlik D, Du T, Erdjument-Bromage H, Tempst P, Strong R, Barasch J (2002) An iron delivery pathway mediated by a lipocalin. Mol Cell 10:1045–1056
Bellomo R, Ronco C, Kellum JA, Mehta RL, Palevsky P (2004) Acute dialysis quality initiative workgroup: acute renal failure -definition, outcome measures, animal models, fluid therapy and information technology needs: the second international consensus conference of the acute dialysis quality initiative (ADQI) group. Crit Care 8:R204–R212
Mehta RL, Kellum JA, Shah SV, Molitoris BA, Ronco C, Warnock DG, Levin A (2007) Acute kidney injury Network: acute kidney injury Network: report of an initiative to improve outcomes in acute kidney injury. Crit Care 11:R31
Kidney Disease Improving Global Outcomes Kidney Disease Improving Global Outcomes (KDIGO) (2012) KDIGO clinical practice guideline for acute kidney injury. Kidney Int 2:1–138
Review Manager (RevMan) (2014) [computer program] version 5.3. The Cochrane collaboration. The Nordic Cochrane Centre, Copenhagen
Whiting PF, Rutjes AW, Westwood ME (2011) QUADAS-2: a revised tool for the quality assessment of diagnostic accuracy studies. Ann Intern Med 155:529–536
Irwig L, Tosteson AN, Gatsonis C, Lau J, Colditz G, Chalmers TC, Mosteller F (1994) Guidelines for meta-analyses evaluating diagnostic tests. Ann Intern Med 120:667–676
Schlesselman JJ, Stolley PD (1982) Case control studies: design, conduct, analysis. Oxford University Press, New York, pp 174–177
GRADEproGDT 2015 [Computer program] GRADEproGDT (2015) GRADEpro guideline development tool [http://www.guidelinedevelopment.org]. McMaster University (developed by Evidence Prime, Inc.), Hamilton
Higgins JPT, Deeks JJ (2011) Chapter 7: selecting studies and collecting data. In: Higgins JPT, Green S (eds). Cochrane handbook for systematic reviews of interventions version 5.1.0 [updated March 2011]. The Cochrane Collaboration, 2011. Available from www.cochrane-handbook.org
Yavuz S, Anarat A, Acartürk S, Dalay AC, Kesiktaş E, Yavuz M, Acartürk TO (2014) Neutrophil gelatinase associated lipocalin as an indicator of acute kidney injury and inflammation in burned children. Burns 40:648–654
Wheeler DS, Devarajan P, Ma Q, Harmon K, Monaco M, Cvijanovich N, Wong HR (2008) Serum neutrophil gelatinase-associated Lipocalin (NGAL) as a marker of acute kidney injury in critically ill children with septic shock. Crit Care Med 36:1297–1303
Parikh CR, Coca SG, Thiessen-Philbrook H, Shlipak MG, Koyner JL, Wang Z, Edelstein CL, Devarajan P, Patel UD, Zappitelli M, Krawczeski CD, Passik CS, Swaminathan M, Garg AX (2011) Postoperative biomarkers predict acute kidney injury and poor outcomes after pediatric cardiac surgery. J Am Soc Nephrol 22:1737–1747
Mishra J, Dent C, Tarabishi R, Mitsnefes MM, Ma Q, Kelly C, Ruff SM, Zahedi K, Shao M, Bean J, Mori K, Barasch J, Devarajan P (2005) Neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin (NGAL) as a biomarker for acute renal injury after cardiac surgery. Lancet 365:1231–1238
Krawczeski CD, Woo JG, Wang Y, Bennett MR, Ma Q, Devarajan P (2011) Neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin concentrations predict development of acute kidney injury in neonates and children after cardiopulmonary bypass. J Pediatr 158:1009–1015
Hirsch R, Dent C, Pfriem H, Allen J, Beekman RH 3rd, Ma Q, Dastrala S, Bennett M, Mitsnefes M, Devarajan P (2007) NGAL is an early predictive biomarker of contrast-induced nephropathy in children. Pediatr Nephrol 22:2089–2095
Fadel FI, Abdel Rahman AM, Mohamed MF, Habib SA, Ibrahim MH, Sleem ZS, Bazaraa HM, Soliman MM (2012) Plasma neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin as an early biomarker for prediction of acute kidney injury after cardio-pulmonary bypass in pediatric cardiac surgery. Arch Med Sci 8:250–255
Dent CL, Ma Q, Dastrala S, Bennett M, Mitsnefes MM, Barasch J, Devarajan P (2007) Plasma NGAL predicts acute kidney injury, morbidity and mortality after pediatric cardiac surgery: a prospective uncontrolled cohort study. Crit Care 11:R127
Zheng J, Xiao Y, Yao Y, Xu G, Li C, Zhang Q, Li H, Han L (2013) Comparison of urinary biomarkers for early detection of acute kidney injury after cardiopulmonary bypass surgery in infants and young children. Pediatr Cardiol 34:880–886
Zappitelli M, Washburn KK, Arikan AA, Loftis L, Ma Q, Devarajan P, Parikh CR, Goldstein SL (2007) Urine neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin is an early marker of acute kidney injury in critically ill children: a prospective cohort study. Crit Care 11:R84
Trachtman H, Christen E, Cnaan A, Patrick J, Mai V, Mishra J, Jain A, Bullington N, Devarajan P (2006) Urinary neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalcin in D+HUS: a novel marker of renal injury. Pediatr Nephrol 21:989–994
Elsharawy S, Raslan L, Morsy S, Hassan B, Khalifa N (2016) Plasma neutrophil gelatinase-associated Lipocalin as a marker for the prediction of worsening renal function in children hospitalized for acute heart failure. Saudi J Kidney Dis Transpl 27:49–54
Bennett M, Dent CL, Ma Q, Dastrala S, Grenier F, Workman R, Syed H, Ali S, Barasch J, Devarajan P (2008) Urine NGAL predicts severity of acute kidney injury after cardiac surgery: a prospective study. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol 3:665–673
Haase M, Bellomo R, Devarajan P, Schlattmann P, Haase-Fielitz A (2009) Accuracy of neutrophil gelatinase-associated Lipocalin (NGAL) in diagnosis and prognosis in acute kidney injury: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Am J Kidney Dis 54:1012–1024
Xin C, Yulong X, Yu C, Changchun C, Feng Z, Xinwei M (2008) Urine neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin and interleukin-18 predict acute kidney injury after cardiac surgery. Ren Fail 30:904–913
Herget-Rosenthal S, Marggraf G, Hüsing J, Göring F, Pietruck F, Janssen O, Philipp T, Kribben A (2004) Early detection of acute renal failure by serum cystatin C. Kidney Int 66:1115–1122
Askenazi DJ, Feig DI, Graham NM, Hui-Stickle S, Goldstein SL (2006) 3–5 year longitudinal follow-up of pediatric patients after acute renal failure. Kidney Int 69:184–189
Basu RK, Devarajan P, Wong H, Wheeler DS (2011) An update and review of acute kidney injury in pediatrics. Pediatr Crit Care Med 12:339–347
Lee EY, Kim MS, Park Y, Kim HS (2012) Serum neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin and interleukin-18 as predictive biomarkers for delayed graft function after kidney transplantation. J Clin Lab Anal 26:295–301
Mandelbaum T, Scott DJ, Lee J, Mark RG, Malhotra A, Waikar SS, Howell MD, Talmor D (2011) Outcome of critically ill patients with acute kidney injury using the acute kidney injury Network criteria. Crit Care Med 39:2659–2664
Susantitaphong P, Cruz DN, Cerda J, Abulfaraj M, Alqahtani F, Koulouridis I, Jaber BL (2013) World incidence of AKI: a meta-analysis. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol 8:1482–1493
Wagener G, Minhaz M, Mattis FA, Kim M, Emond JC, Lee HT (2011) Urinary neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin as a marker of acute kidney injury after orthotopic liver transplantation. Nephrol Dial Transplant 26:1717–1723
Acknowledgements
This review was funded by FAPESC (Santa Catarina State Foundation for Research).
Contribution to authorship
LTF, AJG, TC, ESPD and MIR designed the study. LTF, MIR, and ESPD selected included studies and evaluated their quality. AJG derived or calculated diagnostic parameters. All authors made substantial contributions to data interpretation and writing the first draft of the manuscript. LTF, AJG, TC, ESPD, and MIR critically revised the manuscript and approved the final version for publication.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
No ethical approval is necessary due to its exclusive use of secondary data.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Filho, L.T., Grande, A.J., Colonetti, T. et al. Accuracy of neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin for acute kidney injury diagnosis in children: systematic review and meta-analysis. Pediatr Nephrol 32, 1979–1988 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00467-017-3704-6
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00467-017-3704-6