Abstract
Background
The aim of this study was to evaluate the association of serum intact fibroblast growth factor 23 (FGF23) concentrations with indexed left ventricular mass in children with non-dialysis stages 3–5 of chronic kidney disease (CKD).
Methods
The study cohort comprised 83 children (51 boys; mean age 12.1 ± 3.2 years) with a mean estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR) of 32.3 ± 14.6 ml/min/1.73 m2 who underwent clinic and ambulatory blood pressure measurement (ABPM), echocardiography and evaluation of biochemical markers of CKD-associated mineral bone disease.
Results
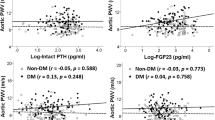
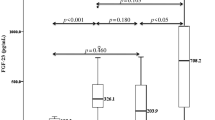
The mean left ventricular mass index (LVMI) was 35.9 ± 8.5 g/m2.7 (± standard deviation), with 30 (36.1 %) children showing left ventricular hypertrophy (LVH), all eccentric, as defined using age-specific criteria. For all subjects, the mean FGF23 concentration was 142.2 ± 204.4 ng/l and the normalised distribution following log transformation was 1.94 ± 0.39. There was significant univariate correlation of LVMI with GFR, body mass index (BMI) z-score and calcium intake, but not with 24-h systolic ABPM z-score, log intact parathyroid hormone or log FGF23. On multivariate analysis following adjustment for confounders, only elemental calcium content (g/kg/day) estimated from prescribed calcium-based phosphate binder dose (β = 154.9, p < 0.001) and BMI z-score (β = 2.397, p = 0.003) maintained a significant positive relationship with LVMI (model r 2 = 0.225).
Conclusions
We observed no significant relationship of FGF23 with LVMI. Larger studies in children are needed to clarify the roles of calcium-containing phosphate binders and FGF23 with LV mass and their roles in the evolution of the development of adverse cardiovascular outcomes.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Mitsnefes MM, Laskin BL, Dahhou M, Zhang X, Foster BJ (2013) Mortality risk among children initially treated with dialysis for end-stage kidney disease. JAMA 309:1921–1929
Mitsnefes MM (2012) Cardiovascular disease in children with chronic kidney disease. J Am Soc Nephrol 23:578–585
Wolf M (2010) Forging forward with 10 burning questions on FGF23 in kidney disease. J Am Soc Nephrol 21:1427–1435
van Husen M, Fischer AK, Lehnhardt A, Klaassen I, Möller K, Müller-Wiefel DE, Kemper MJ (2010) Fibroblast growth factor 23 and bone metabolism in children with chronic kidney disease. Kidney Int 78:200–206
Sinha MD, Turner C, Dalton RN, Rasmussen P, Waller S, Booth CJ, Goldsmith DJ (2012) Investigating FGF23 levels and its relationship with declining renal function in paediatric patients with pre-dialysis CKD stage 3–5. Nephrol Dial Transplant 27:4361–4368
Wesseling-Perry K, Pereira RC, Wang H, Elashoff RM, Sahney S, Gales B, Juppner H, Salusky IB (2009) Relationship between plasma fibroblast growth factor-23 concentration and bone mineralization in children with renal failure on peritoneal dialysis. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 94:511–517
Bacchetta J, Dubourg L, Harambat J, Ranchin B, Abou-Jaoude P, Arnaud S, Carlier MC, Richard M, Cochat P (2010) The influence of glomerular filtration rate and age on fibroblast growth factor 23 serum levels in pediatric chronic kidney disease. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 95:1741–1748
Wan M, Smith C, Shah V, Gullet A, Wells D, Rees L, Shroff R (2013) Fibroblast growth factor 23 and soluble klotho in children with chronic kidney disease. Nephrol Dial Transplant 28:153–161
Portale AA, Wolf M, Jüppner H, Messinger S, Kumar J, Wesseling-Perry K, Schwartz GJ, Furth SL, Warady BA, Salusky IB (2014) Disordered FGF23 and mineral metabolism in children with CKD. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol 9:344–353
Shimada T, Urakawa I, Isakova T, Yamazaki Y, Epstein M, Wesseling-Perry K, Wolf M, Salusky IB, Jüppner H (2010) Circulating fibroblast growth factor 23 in patients with end-stage renal disease treated by peritoneal dialysis is intact and biologically active. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 95:578–585
Isakova T, Wahl P, Vargas GS, Gutiérrez OM, Scialla J, Xie H, Appleby D, Nessel L, Bellovich K, Chen J, Hamm L, Gadegbeku C, Horwitz E, Townsend RR, Anderson CA, Lash JP, Hsu CY, Leonard MB, Wolf M (2011) Fibroblast growth factor 23 is elevated before parathyroid hormone and phosphate in chronic kidney disease. Kidney Int 79:1370–1378
Gutiérrez OM, Mannstadt M, Isakova T, Rauh-Hain JA, Tamez H, Smith K, Lee H, Thadhani R, Jüppner H, Wolf M (2008) Fibroblast growth factor 23 and mortality among patients undergoing hemodialysis. N Engl J Med 359:584–592
Jean G, Terrat JC, Vanel T, Hurot JM, Lorriaux C, Mayor B, Chazot C (2009) High levels of serum fibroblast growth factor (FGF)-23 are associated with increased mortality in long haemodialysis patients. Nephrol Dial Transplant 24:2792–2796
Parker BD, Schurgers LJ, Brandenburg VM, Christenson RH, Vermeer C, Ketteler M, Shlipak MG, Whooley MA, Ix JH (2010) The associations of fibroblast growth factor 23 and uncarboxylated matrix Gla protein with mortality in coronary artery disease: the Heart and Soul Study. Ann Intern Med 152:640–648
Isakova T, Xie H, Yang W, Xie D, Anderson AH, Scialla J, Wahl P, Gutiérrez OM, Steigerwalt S, He J, Schwartz S, Lo J, Ojo A, Sondheimer J, Hsu CY, Lash J, Leonard M, Kusek JW, Feldman HI, Wolf M; Chronic Renal Insufficiency Cohort (CRIC) Study Group (2011) Fibroblast growth factor 23 and risks of mortality and end-stage renal disease in patients with chronic kidney disease. JAMA 305:2432–2439
Gutiérrez OM, Januzzi JL, Isakova T, Laliberte K, Smith K, Sarwar A, Hoffmann U, Coglianese E, Christenson R, Wang TJ, deFilippi C, Wolf M (2009) Fibroblast growth factor 23 and left ventricular hypertrophy in chronic kidney disease. Circulation 119:2545–2552
Mirza MA, Larsson A, Melhus H, Lind L, Larsson TE (2009) Serum intact FGF23 associate with left ventricular mass, hypertrophy and geometry in an elderly population. Atherosclerosis 207:546–551
Faul C, Amaral AP, Oskouei B, Hu MC, Sloan A, Isakova T, Gutiérrez OM, Aguillon-Prada R, Lincoln J, Hare JM, Mundel P, Morales A, Scialla J, Fischer M, Soliman EZ, Chen J, Go AS, Rosas SE, Nessel L, Townsend RR, Feldman HI, St John Sutton M, Ojo A, Gadegbeku C, Di Marco GS, Reuter S, Kentrup D, Tiemann K, Brand M, Hill JA, Moe OW, Kuro-O M, Kusek JW, Keane MG, Wolf M (2011) FGF23 induces left ventricular hypertrophy. J Clin Invest 121:4393–4408
Seeherunvong W, Abitbol CL, Chandar J, Rusconi P, Zilleruelo GE, Freundlich M (2012) Fibroblast growth factor 23 and left ventricular hypertrophy in children on dialysis. Pediatr Nephrol 27:2129–2136
National High Blood Pressure Education Program Working Group on High Blood Pressure in Children and Adolescents (2004) The fourth report on the diagnosis, evaluation and treatment of high blood pressure in children and adolescents. Pediatrics 114:555–576
Schwartz GJ, Haycock GB, Edelmann CM Jr, Spitzer A (1976) A simple estimate of glomerular filtration rate in children derived from body length and plasma creatinine. Pediatrics 58:259–263
Hogg RJ, Furth S, Lemley KV (2003) National kidney foundation’s kidney disease outcomes quality initiative clinical practice guidelines for chronic kidney disease in children and adolescents: evaluation, classification, and stratification. Pediatrics 11:1416–1421
Sinha MD, Tibby SM, Rasmussen P, Rawlins D, Turner C, Dalton N, Reid CJD, Rigden SPA, Booth CJB, Simpson JM (2011) Blood pressure control and left ventricular mass in children with chronic kidney disease. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol 6:543–551
Kim JJ, Booth CJ, Waller S, Rasmussen P, Reid CJD, Sinha MD (2013) The demographic characteristics of children with chronic kidney disease stages 3–5 in the South East of England over a 5 year period. Arch Dis Child 98:189–194
Wuhl E, Witte K, Soergel M, Mehls O, Schaefer F, German Working Group on Pediatric Hypertension (2002) Distribution of 24-h ambulatory blood pressure in children: normalised reference values and role of body dimensions. J Hypertens 20:1995–2007
Lang RM, Bierig M, Devereux RB, Flachskampf FA, Foster E, Pellikka PA, Picard MH, Roman MJ, Seward J, Shanewise JS, Solomon SD, Spencer KT, Sutton MS, Stewart WJ; Chamber Quantification Writing Group; American Society of Echocardiography’s Guidelines and Standards Committee; European Association of Echocardiography (2005) Recommendations for chamber quantification: a report from the American Society of Echocardiography’s Guidelines and Standards Committee and the Chamber Quantification Writing Group, developed in conjunction with the European Association of Echocardiography, a branch of the European Society of Cardiology. J Am Soc Echocardiogr 18:1440–1463
Devereux RB, Alonso DR, Lutas EM, Gottlieb GJ, Campo E, Sachs I, Reichek N (1986) Echocardiographic assessment of left ventricular hypertrophy: comparison to necropsy findings. Am J Cardiol 57:450–458
Khoury PR, Mitsnefes M, Daniels SR, Kimball TR (2009) Age-specific reference intervals for indexed left ventricular mass in children. J Am Soc Echocardiogr 22:709–714
de Simone G, Daniels SR, Kimball TR, Roman MJ, Romano C, Chinali M, Galderisi M, Devereux RB (2005) Evaluation of concentric left ventricular geometry in humans: evidence for age-related systematic underestimation. Hypertension 45:64–68
Dalton RN, Turner C (2010) Development of a reference MS/MS method for plasma creatinine. Clin Chim Acta 411:904–905
Ito N, Fukumoto S, Takeuchi Y, Yasuda T, Hasegawa Y, Takemoto F, Tajima T, Dobashi K, Yamazaki Y, Yamashita T, Fujita T (2005) Comparison of two assays for fibroblast growth factor (FGF)-23. J Bone Miner Metab 23:435–440
Yamazaki Y, Okazaki R, Shibata M, Hasegawa Y, Satoh K, Tajima T, Takeuchi Y, Fujita T, Nakahara K, Yamashita T, Fukumoto S (2002) Increased circulatory level of biologically active full-length FGF-23 in patients with hypophosphatemic rickets/osteomalacia. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 87:4957–4960
Casetta B, Jans I, Billen J, Vanderschueren D, Bouillon R (2009) Development of a method for the quantification of 1alpha,25(OH)2vitamin D3 in serum by liquid chromatography tandem mass spectrometry without derivatization. Eur J Mass Spectrom (Chichester, Eng) 16:81–89
Kidney Disease: Improving Global Outcomes (KDIGO) CKD-MBD Work Group (2009) KDIGO clinical practice guideline for the diagnosis, evaluation, prevention, and treatment of Chronic Kidney Disease-Mineral and Bone Disorder (CKD-MBD). Kidney Int Suppl 113:S1–S130
Sinha MD, Turner C, Goldsmith DJ (2013) FGF-23 concentrations measured using “intact” assays similar but not interchangeable. Int Urol Nephrol 45:1821–1823
Shimada T, Yamazaki Y, Takahashi M, Hasegawa H, Urakawa I, Oshima T, Ono K, Kakitani M, Tomizuka K, Fujita T, Fukumoto S, Yamashita T (2005) Vitamin D receptor-independent FGF23 actions in regulating phosphate and vitamin D metabolism. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol 289:F1088–F1095
Evenepoel P, Viaene L, Meijers B (2011) PTH, FGF23, and calcium: it takes three to tango? Kidney Int 80:1377
Wolf M (2012) Update on fibroblast growth factor 23 in chronic kidney disease. Kidney Int 82:737–747
Goodman WG, Goldin J, Kuizon BD, Yoon C, Gales B, Sider D, Wang Y, Chung J, Emerick A, Greaser L, Elashoff RM, Salusky IB (2000) Coronary-artery calcification in young adults with end-stage renal disease who are undergoing dialysis. N Engl J Med 342:1478–1483
Mitsnefes MM, Kimball TR, Kartal J, Witt SA, Glascock BJ, Khoury PR, Daniels SR (2005) Cardiac and vascular adaptation in pediatric patients with chronic kidney disease: role of calcium-phosphorus metabolism. J Am Soc Nephrol 16:2796–2803
Civilibal M, Caliskan S, Adaletli I, Oflaz H, Sever L, Candan C, Canpolat N, Kasapcopur O, Kuruoglu S, Arisoy N (2006) Coronary artery calcifications in children with end-stage renal disease. Pediatr Nephrol 21:1426–1433
Litwin M, Wühl E, Jourdan C, Trelewicz J, Niemirska A, Fahr K, Jobs K, Grenda R, Wawer ZT, Rajszys P, Tröger J, Mehls O, Schaefer F (2005) Altered morphologic properties of large arteries in children with chronic renal failure and after renal transplantation. J Am Soc Nephrol 16:1494–1500
Shroff R, Egerton M, Bridel M, Shah V, Donald AE, Cole TJ, Hiorns MP, Deanfield JE, Rees L (2008) A bimodal association of vitamin D levels and vascular disease in children on dialysis. J Am Soc Nephrol 19:1239–1246
Rees L, Shroff R (2010) Phosphate binders in CKD: chalking out the differences. Pediatr Nephrol 25:385–394
Rees L, Shroff R (2014) The demise of calcium-based phosphate binders—is this appropriate for children? Pediatr Nephrol. doi:10.1007/s00467-014-3017-y
Block GA, Wheeler DC, Persky MS, Kestenbaum B, Ketteler M, Spiegel DM, Allison MA, Asplin J, SmitsG HAN, Kooienga L, Thadhani R, Mannstadt M, Wolf M, Chertow GM (2012) Effects of phosphate binders in moderate CKD: The phosphate normalization trial (PNT). J Am Soc Nephrol 23:1407–1415
Mitsnefes M, Flynn J, Cohn S, Samuels J, Blydt-Hansen T, Saland J, Kimball T, Furth S, Warady B, CKiD Study Group (2010) Masked hypertension associates with left ventricular hypertrophy in children with CKD. J Am Soc Nephrol 21:137–144
Bakkaloglu SA, Borzych D, Soo Ha I, Serdaroglu E, Büscher R, Salas P, Patel H, Drozdz D, Vondrak K, Watanabe A, Villagra J, Yavascan O, Valenzuela M, Gipson D, Ng KH, Warady BA, Schaefer F; International Pediatric Peritoneal Dialysis Network (2011) Cardiac geometry in children receiving chronic peritoneal dialysis: findings from the International Pediatric Peritoneal Dialysis Network (IPPN) registry. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol 6:1926–1933
Matteucci MC, Chinali M, Rinelli G, Wühl E, Zurowska A, Charbit M, Pongiglione G, Schaefer F; ESCAPE Trial Group (2013) Change in cardiac geometry and function in CKD children during strict BP control: a randomized study. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol 8:203–210
Stenvinkel P, Carrero JJ, Axelson J, Lindholm B, Heimburger O, Massy Z (2008) Emerging biomarkers for evaluating cardiovascular risk in the chronic kidney disease patient: How do new pieces fit into the uraemic puzzle? Clin J Am Soc Nephrol 3:505–521
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to acknowledge Mr Anuj Sud for all his help with statistical analyses. MDS, DJAG and JMS acknowledge financial support from the Department of Health via the National Institute for Health Research (NIHR) comprehensive Biomedical Research Centre award to Guy’s & St Thomas’ NHS Foundation Trust in partnership with King’s College London and King’s College Hospital NHS Foundation Trust.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there are no conficts of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sinha, M.D., Turner, C., Booth, C.J. et al. Relationship of FGF23 to indexed left ventricular mass in children with non-dialysis stages of chronic kidney disease. Pediatr Nephrol 30, 1843–1852 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00467-015-3125-3
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00467-015-3125-3