Abstract
Background
Recently, we demonstrated that urinary angiotensinogen (AGT) levels are increased and reflect intrarenal renin–angiotensin system (RAS) status in pediatric patients with chronic glomerulonephritis. Therefore, this study was performed to test the hypothesis that urinary AGT (UAGT) levels provide a specific index of intrarenal RAS status associated with RAS blockade treatment in pediatric IgA nephropathy (IgAN) patients.
Methods
We measured plasma and UAGT levels and urinary transforming growth factor beta (TGF-β) levels, after which we performed immunohistochemical analysis of AGT, angiotensin II (Ang II), and TGF-β in 24 pediatric IgAN patients treated with RAS blockades for 2 years. Paired tests were used to analyze the changes from baseline to study end.
Results
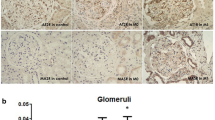
Although there was no change in plasma AGT levels, UAGT and TGF-β levels were significantly decreased after RAS blockade, which was accompanied by the expression levels of AGT, Ang II, and TGF-β, as well as the magnitude of glomerular injury. Baseline UAGT levels positively correlated with diastolic blood pressure, urinary protein levels, scores for mesangial hypercellularity, and the expression levels of AGT, Ang II, and TGF-β in renal tissues.
Conclusions
These data indicate that UAGT is a useful biomarker of intrarenal RAS activation, which is associated with glomerular injury during RAS blockade in pediatric IgAN patients.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kobori H, Urushihara M (2013) Augmented intrarenal and urinary angiotensinogen in hypertension and chronic kidney disease. Pflugers Arch 465:3–12
Dzau VJ, Re R (1994) Tissue angiotensin system in cardiovascular medicine. A paradigm shift. Circulation 89:493–498
Navar LG, Harrison-Bernard LM, Nishiyama A, Kobori H (2002) Regulation of intrarenal angiotensin II in hypertension. Hypertension 39:316–322
Baltatu O, Silva JA Jr, Ganten D, Bader M (2000) The brain renin-angiotensin system modulates angiotensin II-induced hypertension and cardiac hypertrophy. Hypertension 35:409–412
Dell’Italia LJ, Meng QC, Balcells E, Wei CC, Palmer R, Hageman GR, Durand J, Hankes GH, Oparil S (1997) Compartmentalization of angiotensin II generation in the dog heart. Evidence for independent mechanisms in intravascular and interstitial spaces. J Clin Invest 100:253–258
Danser AH, Admiraal PJ, Derkx FH, Schalekamp MA (1998) Angiotensin I-to-II conversion in the human renal vascular bed. J Hypertens 16:2051–2056
Kobori H, Nangaku M, Navar LG, Nishiyama A (2007) The intrarenal renin-angiotensin system: From physiology to the pathobiology of hypertension and kidney disease. Pharmacol Rev 59:251–287
Katsurada A, Hagiwara Y, Miyashita K, Satou R, Miyata K, Ohashi N, Navar LG, Kobori H (2007) Novel sandwich ELISA for human angiotensinogen. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol 293:F956–960
Kobori H, Alper AB Jr, Shenava R, Katsurada A, Saito T, Ohashi N, Urushihara M, Miyata K, Satou R, Hamm LL, Navar LG (2009) Urinary angiotensinogen as a novel biomarker of the intrarenal renin-angiotensin system status in hypertensive patients. Hypertension 53:344–350
Kobori H, Urushihara M, Xu JH, Berenson GS, Navar LG (2010) Urinary angiotensinogen is correlated with blood pressure in men (Bogalusa Heart Study). J Hypertens 28:1422–1428
Kobori H, Ohashi N, Katsurada A, Miyata K, Satou R, Saito T, Yamamoto T (2008) Urinary angiotensinogen as a potential biomarker of severity of chronic kidney diseases. J Am Soc Hypertens 2:349–354
Urushihara M, Kondo S, Kagami S, Kobori H (2010) Urinary angiotensinogen accurately reflects intrarenal Renin-Angiotensin system activity. Am J Nephrol 31:318–325
Saito T, Urushihara M, Kotani Y, Kagami S, Kobori H (2009) Increased urinary angiotensinogen is precedent to increased urinary albumin in patients with type 1 diabetes. Am J Med Sci 338:478–480
Sawaguchi M, Araki SI, Kobori H, Urushihara M, Haneda M, Koya D, Kashiwagi A, Uzu T, Maegawa H (2012) Association between urinary angiotensinogen levels and renal and cardiovascular prognoses in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. J Diabetes Investig 3:318–324
Roberts IS, Cook HT, Troyanov S, Alpers CE, Amore A, Barratt J, Berthoux F, Bonsib S, Bruijn JA, Cattran DC, Coppo R, D’Agati V, D’Amico G, Emancipator S, Emma F, Feehally J, Ferrario F, Fervenza FC, Florquin S, Fogo A, Geddes CC, Groene HJ, Haas M, Herzenberg AM, Hill PA, Hogg RJ, Hsu SI, Jennette JC, Joh K, Julian BA, Kawamura T, Lai FM, Li LS, Li PK, Liu ZH, Mackinnon B, Mezzano S, Schena FP, Tomino Y, Walker PD, Wang H, Weening JJ, Yoshikawa N, Zhang H (2009) The Oxford classification of IgA nephropathy: Pathology definitions, correlations, and reproducibility. Kidney Int 76:546–556
Yoshikawa N, Iijima K, Maehara K, Yoshiara S, Yoshiya K, Matsuo T, Okada S (1987) Mesangial changes in IgA nephropathy in children. Kidney Int 32:585–589
Takamatsu M, Urushihara M, Kondo S, Shimizu M, Morioka T, Oite T, Kobori H, Kagami S (2008) Glomerular angiotensinogen protein is enhanced in pediatric IgA nephropathy. Pediatr Nephrol 23:1257–1267
Fukuda M, Urushihara M, Wakamatsu T, Oikawa T, Kobori H (2012) Proximal tubular angiotensinogen in renal biopsy suggests nondipper BP rhythm accompanied by enhanced tubular sodium reabsorption. J Hypertens 30:1453–1459
Tanaka H, Suzuki K, Nakahata T, Tsugawa K, Konno Y, Tsuruga K, Ito E, Waga S (2004) Combined therapy of enalapril and losartan attenuates histologic progression in immunoglobulin A nephropathy. Pediatr Int 46:576–579
Yang Y, Ohta K, Shimizu M, Nakai A, Kasahara Y, Yachie A, Koizumi S (2005) Treatment with low-dose angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitor (ACEI) plus angiotensin II receptor blocker (ARB) in pediatric patients with IgA nephropathy. Clin Nephrol 64:35–40
Ballardie FW, Roberts IS (2002) Controlled prospective trial of prednisolone and cytotoxics in progressive IgA nephropathy. J Am Soc Nephrol 13:142–148
Cattran DC, Coppo R, Cook HT, Feehally J, Roberts IS, Troyanov S, Alpers CE, Amore A, Barratt J, Berthoux F, Bonsib S, Bruijn JA, D’Agati V, D’Amico G, Emancipator S, Emma F, Ferrario F, Fervenza FC, Florquin S, Fogo A, Geddes CC, Groene HJ, Haas M, Herzenberg AM, Hill PA, Hogg RJ, Hsu SI, Jennette JC, Joh K, Julian BA, Kawamura T, Lai FM, Leung CB, Li LS, Li PK, Liu ZH, Mackinnon B, Mezzano S, Schena FP, Tomino Y, Walker PD, Wang H, Weening JJ, Yoshikawa N, Zhang H (2009) The Oxford classification of IgA nephropathy: Rationale, clinicopathological correlations, and classification. Kidney Int 76:534–545
Kobori H, Katsurada A, Ozawa Y, Satou R, Miyata K, Hase N, Suzaki Y, Shoji T (2007) Enhanced intrarenal oxidative stress and angiotensinogen in IgA nephropathy patients. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 358:156–163
Nishiyama A, Konishi Y, Ohashi N, Morikawa T, Urushihara M, Maeda I, Hamada M, Kishida M, Hitomi H, Shirahashi N, Kobori H, Imanishi M (2011) Urinary angiotensinogen reflects the activity of intrarenal renin-angiotensin system in patients with IgA nephropathy. Nephrol Dial Transplant 26:170–177
Kim YG, Song SB, Lee SH, Moon JY, Jeong KH, Lee TW, Ihm CG (2011) Urinary angiotensinogen as a predictive marker in patients with immunoglobulin A nephropathy. Clin Exp Nephrol 15:720–726
Jang HR, Kim SM, Lee YJ, Lee JE, Huh W, Kim DJ, Oh HY, Kim YG (2012) The origin and the clinical significance of urinary angiotensinogen in proteinuric IgA nephropathy patients. Ann Med 44:448–457
Ingelfinger JR, Zuo WM, Fon EA, Ellison KE, Dzau VJ (1990) In situ hybridization evidence for angiotensinogen messenger RNA in the rat proximal tubule. An hypothesis for the intrarenal renin angiotensin system. J Clin Invest 85:417–423
Lantelme P, Rohrwasser A, Gociman B, Hillas E, Cheng T, Petty G, Thomas J, Xiao S, Ishigami T, Herrmann T, Terreros DA, Ward K, Lalouel JM (2002) Effects of dietary sodium and genetic background on angiotensinogen and Renin in mouse. Hypertension 39:1007–1014
Rohrwasser A, Morgan T, Dillon HF, Zhao L, Callaway CW, Hillas E, Zhang S, Cheng T, Inagami T, Ward K, Terreros DA, Lalouel JM (1999) Elements of a paracrine tubular renin-angiotensin system along the entire nephron. Hypertension 34:1265–1274
Nakano D, Kobori H, Burford JL, Gevorgyan H, Seidel S, Hitomi H, Nishiyama A, Peti-Peterdi J (2012) Multiphoton imaging of the glomerular permeability of angiotensinogen. J Am Soc Nephrol 23:1847–1856
Ohashi N, Urushihara M, Satou R, Kobori H (2010) Glomerular angiotensinogen is induced in mesangial cells in diabetic rats via reactive oxygen species–ERK/JNK pathways. Hypertens Res 33:1174–1181
Brunner HR (1992) ACE inhibitors in renal disease. Kidney Int 42:463–479
Lafayette RA, Mayer G, Park SK, Meyer TW (1992) Angiotensin II receptor blockade limits glomerular injury in rats with reduced renal mass. J Clin Invest 90:766–771
Kohan DE (1998) Angiotensin II and endothelin in chronic glomerulonephritis. Kidney Int 54:646–647
Urushihara M, Kinoshita Y, Kondo S, Kagami S (2012) Involvement of the intrarenal renin-angiotensin system in experimental models of glomerulonephritis. J Biomed Biotechnol 2012:601786
Johnson RJ, Iida H, Alpers CE, Majesky MW, Schwartz SM, Pritzi P, Gordon K, Gown AM (1991) Expression of smooth muscle cell phenotype by rat mesangial cells in immune complex nephritis. Alpha-smooth muscle actin is a marker of mesangial cell proliferation. J Clin Invest 87:847–858
Gomez-Garre D, Ruiz-Ortega M, Ortego M, Largo R, Lopez-Armada MJ, Plaza JJ, Gonzalez E, Egido J (1996) Effects and interactions of endothelin-1 and angiotensin II on matrix protein expression and synthesis and mesangial cell growth. Hypertension 27:885–892
Minutolo R, Balletta MM, Catapano F, Chiodini P, Tirino G, Zamboli P, Fuiano G, Russo D, Marotta P, Iodice C, Conte G, De Nicola L (2006) Mesangial hypercellularity predicts antiproteinuric response to dual blockade of RAS in primary glomerulonephritis. Kidney Int 70:1170–1176
Border WA, Noble NA (1994) Transforming growth factor-beta in glomerular injury. Exp Nephrol 2:13–17
Kagami S, Border WA, Miller DE, Noble NA (1994) Angiotensin II stimulates extracellular matrix protein synthesis through induction of transforming growth factor-beta expression in rat glomerular mesangial cells. J Clin Invest 93:2431–2437
Urushihara M, Ohashi N, Miyata K, Satou R, Acres OW, Kobori H (2011) Addition of angiotensin II type 1 receptor blocker to CCR2 antagonist markedly attenuates crescentic glomerulonephritis. Hypertension 57:586–593
Acknowledgments
The authors acknowledge technical assistance from Ms. Naomi Okamoto and Ms. Chizuko Yamamoto. This study was supported by JSPS KAKENHI Grant Numbers 23591569 and 26461612.
Conflict of interest
None.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Urushihara, M., Nagai, T., Kinoshita, Y. et al. Changes in urinary angiotensinogen posttreatment in pediatric IgA nephropathy patients. Pediatr Nephrol 30, 975–982 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00467-014-3028-8
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00467-014-3028-8