Abstract
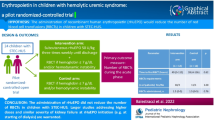
Background
Although erythropoietin (EPO) deficiency has been reported in children with post-diarrheal hemolytic uremic syndrome (D + HUS), very limited clinical data on EPO use in this disease are currently available. In this case–control study we examined whether EPO administration would reduce the number of red blood cell (RBC) transfusions in D + HUS patients under our care.
Methods
Data from children treated exclusively with RBC transfusions (controls; n = 21) were retrospectively compared with data on those who also received EPO for the treatment of anemia (cases; n = 21).
Results
Both patient groups were similar in age (p = 0.9), gender (p = 0.12), weight (p = 1.00) and height (p = 0.66). Acute phase severity was also comparable, as inferred by the need for dialysis (p = 0.74), the duration of dialysis (p = 0.3), length of hospitalization (p = 0.81), presence of severe bowel (p = 1.00) or neurological injury (p = 0.69), arterial hypertension (p = 1.00) and death (p = 1.00). No differences in the hemoglobin level at admission (p = 0.51) and discharge (p = 0.28) were noted. Three children treated with EPO and two controls did not require any RBC transfusion (p = 1.00). Median number of RBC transfusions needed by cases and controls was 2 (p = 0.52).
Conclusion
Treatment with EPO did not reduce the number of RBC transfusions in D + HUS children. Assessment of EPO efficacy in D + HUS merits further studies.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Gianantonio C, Vitacco M, Mendilaharzu F, Rutti A, Mendilaharzu J (1964) The hemolytic uremic syndrome. J Pediatr 64:478–491
Scheiring J, Rosales A, Zimmerhackl LB (2010) Clinical practice. Today’s understanding of the haemolytic uraemic syndrome. Eur J Pediatr 169:7–13
Exeni R, Donato H, Rendo P, Antonuccio M, Rapetti MC, Grimoldi I, Exeni A, de Galvagni A, Trepacka E, Amore A (1998) Low levels of serum erythropoietin in children with endemic hemolytic uremic syndrome. Pediatr Nephrol 12:226–230
Scheiring J, Andreoli S, Zimmerhackl L (2008) Treatment and outcome of Shiga-toxin-associated hemolytic uremic syndrome (HUS). Pediatr Nephrol 23:1749–1760
Iijima K, Kamioka I, Nozu K (2008) Management of diarrheaassociated hemolytic uremic syndrome in children. Clin Exp Nephrol 12:16–19
Pape L, Ahlenstiel T, Kreuzer M, Drube J, Froede K, Franke D, Ehrich JH, Haubitz M (2009) Early erythropoietin reduced the need for red blood cell transfusion in childhood hemolytic uremic syndrome: a randomized prospective pilot trial. Pediatr Nephrol 24:1061–1064
Spizzirri F, Rahman R, Bibiloni N, Ruscasso J, Amoreo O (1997) Childhood hemolytic uremic syndrome in Argentina: long-term follow-up and prognostic features. Pediatr Nephrol 11:156–160
Koshy SM, Geary DF (2008) Anemia in children with chronic kidney disease. Pediatr Nephrol 23:209–219
Rahman R, Cobeñas C, Drut R, Amoreo O, Ruscasso J, Spizzirri A, Suarez A, Zalba J, Ferrari C, Gatti M (2012) Hemorrhagic colitis in postdiarrheal hemolytic uremic syndrome: retrospective analysis of 54 children. Pediatr Nephrol 27:229–233
de Buys Roessingh AS, de Lagausie P, Baudoin V, Loirat C, Aigrain Y (2007) Gastrointestinal complications of post-diarrheal hemolytic uremic syndrome. Eur J Pediatr Surg 17:328–334
National High Blood Pressure Education Program Working Group on Hypertension Control in Children and Adolescents (2004) The fourth report on the diagnosis, evaluation, and treatment of high blood pressure in children and adolescents. Pediatrics 114[Suppl 2]:S555–S576
Brasher C, Siegler RL (1981) The hemolytic-uremic syndrome. West J Med 134:193–197
Schifferli A, von Vigier RO, Fontana M, Spartà G, Schmid H, Bianchetti MG, Rudin C, Unit SPS (2010) Hemolytic-uremic syndrome in Switzerland: a nationwide surveillance 1997–2003. Eur J Pediatr 169:591–598
Cavagnaro F, Gana JC, Lagomarsino E, Vogel A, Gederlini A (2005) Hemolytic uremic syndrome: the experience of a pediatric Center. Rev Med Chil 133:781–787
Lumbreras Fernández J, Cruz Rojo J, Iñigo Martín G, Muley Alonso R, Vara Martín J (2010) Hemolytic uremic syndrome: long term renal injury. An Pediatr (Barc) 72:309–316
Srivastava RN, Moudgil A, Bagga A, Vasudev AS (1991) Hemolytic uremic syndrome in children in northern India. Pediatr Nephrol 5:284–288
Oh G, Lau KK (2012) Characteristics of children with sporadic hemolytic uremic syndrome in a single Northern California center. Int Urol Nephrol 44:1467–1472
Caletti MG, Balestracci A, Missoni M, Vezzani C (2013) Additive antiproteinuric effect of enalapril and losartan in children with hemolytic uremic syndrome. Pediatr Nephrol 28:745–750
Boyer O, Niaudet P (2011) Hemolytic uremic syndrome: new developments in pathogenesis and treatment. Int J Nephrol 2011:908407
Walters MD, Matthei IU, Kay R, Dillon MJ, Barratt TM (1989) The polymorphonuclear leucocyte count in childhood haemolytic uraemic syndrome. Pediatr Nephrol 3:130–134
Coad N, Marshall T, Rowe B, Taylor CM (1991) Changes in the postenteropathic form of the hemolytic uremic syndrome in children. Clin Nephrol 35:10–16
Lopez Devoto Lopez EL, Devoto S, Fayad A, Canepa C, Morrow AL, Cleary TG (1992) Association between severity of gastrointestinal prodrome and long-term prognosis in classic hemolytic-uremic syndrome. J Pediatr 120:210–215
Gianviti A, Tozzi AE, De Petris L, Caprioli A, Ravà L, Edefonti A, Ardissino G, Montini G, Zacchello G, Ferretti A, Pecoraro C, De Palo T, Caringella A, Gaido M, Coppo R, Perfumo F, Miglietti N, Ratsche I, Penza R, Capasso G, Maringhini S, Li Volti S, Setzu C, Pennesi M, Bettinelli A, Peratoner L, Pela I, Salvaggio E, Lama G, Maffei S, Rizzoni G (2003) Risk factors for poor renal prognosis in children with hemolytic uremic syndrome. Pediatr Nephrol 18:1229–1235
Spinale JM, Ruebner RL, Copelovitch L, Kaplan BS (2013) Long-term outcomes of Shiga toxin hemolytic uremic syndrome. Pediatr Nephrol 28:2097–3105
Nathanson S, Kwon T, Elmaleh M, Charbit M, Launay EA, Harambat J, Brun M, Ranchin B, Bandin F, Cloarec S, Bourdat-Michel G, Piètrement C, Champion G, Ulinski T, Deschênes G (2010) Acute neurological involvement in diarrhea-associated hemolytic uremic syndrome. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol 5:1218–1228
Oakes R, Siegler R, McReynolds M, Pysher T, Pavia A (2006) Predictors of fatality in postdiarrheal hemolytic uremic syndrome. Pediatrics 117:1656–1662
Hadtstein C, Schaefer F (2008) Hypertension in children with chronic kidney disease: pathophysiology and management. Pediatr Nephrol 23:363–371
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Balestracci, A., Martin, S.M., Toledo, I. et al. Early erythropoietin in post-diarrheal hemolytic uremic syndrome: a case–control study. Pediatr Nephrol 30, 339–344 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00467-014-2911-7
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00467-014-2911-7