Abstract
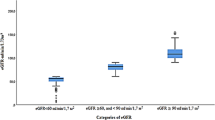
World Kidney Day (WKD) is intended to raise awareness and increase detection of chronic kidney disease (CKD), but most emphasis is placed on adults rather than children. We examined yield of screening for CKD and hypertension among poor children in Mexico. On WKD (2006, 2007), children (age < 18 years) without known CKD were invited to participate at two screening stations. We measured body mass index (BMI), blood pressure, and serum creatinine, and performed dipstick urinalysis. The Schwartz equation was used to estimate glomerular filtration rate (GFR; reduced GFR defined as < 60 ml/min per 1.73 m2). Proteinuria and hematuria were defined by a reading of ≥ 1+ protein or blood on dipstick. Hypertension was defined by gender, age, and height-specific norms. In total, 240 children were screened (mean age 8.9 ± 4.1 years; 44.2% male). Proteinuria and hematuria were detected in 38 (16.1%) and 41 (17.5%), respectively; 15% had BMI > 95th percentile for age. Reduced GFR was detected in four (1.7%) individuals. Systolic hypertension was more prevalent in younger children (age 0–8 years, 19.6%; age 9–13 years, 7.1%; age 14–17 years, 5.3%) suggesting a possible white-coat effect. Hematuria, proteinuria, hypertension and obesity were frequently detected among children in a community based screening program in Mexico. This form of screening might be useful in identifying children with CKD and hypertension in developing nations.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Levey AS, Andreoli SP, DuBose T, Provenzano R, Collins AJ (2007) Chronic kidney disease: common, harmful and treatable-World Kidney Day 2007. Pediatr Nephrol 22:321–325
Jafar TH (2006) The growing burden of chronic kidney disease in Pakistan. N Engl J Med 354:995–997
Mani MK (2005) Experience with a program for prevention of chronic renal failure in India. Kidney Int 67:S75–S78
Plata R, Silva C, Yahuita J, Perez L, Schieppati A, Remuzzi G (1998) The first clinical and epidemiological programme on renal disease in Bolivia: a model for prevention and early diagnosis of renal diseases in the developing countries. Nephrol Dial Transplant 13:3034–3036
Amato D, Alvarez-Aguilar C, Castaneda-Limones R, Rodriguez E, Avila-Diaz M, Arreola F, Gomez A, Ballesteros H, Becerril R, Paniagua R (2005) Prevalence of chronic kidney disease in an urban Mexican population. Kidney Int 68:S11–S17
Rosas M, Attie F, Pastelin G, Lara A, Velazquez O, Tapia-Conyer R, Martinez-Reding J, Mendez A, Lorenzo-Negrete A, Herrera-Acosta J (2005) Prevalance of proteinuria in Mexico: a conjunctive consolidation approach with other cardiovascular risk factors: the Mexican Health Survey 2000. Kidney Int 68:S112–S119
Lawlor DA, Smith GD (2005) Early life determinants of adult blood pressure. Curr Opin Nephrol Hypertens 14:259–264
Cutler JA, Roccella EJ (2006) Salt reduction for preventing hypertension and cardiovascular disease: a population approach should include children. Hypertension 48:818–819
Encuesta Nacional de Salud y Nutricion (2006) Resultados por Entidad Federativa, Jalisco Instituto Nacional de Salud Publica Cuernavaca, Morelos, Mexico.
Instituto Nacional de Geografia y Estadistica. Jalisco. Informacion Estadistica. Defunciones generales por principales causas de defuncion. Available at: https://doi.org/www.inegi.gob.mx. Accessed 17 December 2007
Consejo Nacional de Poblacion (CONAPO). Indicadores Demograficos Basicos, Jalisco Available at: https://doi.org/www.conapo.gob.mx. Accessed 20 August 2008
National High Blood Pressure Education Program Working Group on High Blood Pressure in Children and Adolescents (2004) The fourth report on the diagnosis, evaluation, and treatment of high blood pressure in children and adolescents. Pediatrics 114:555–576
Chobanian AV, Bakris GL, Black HR, Cushman WC, Green LA, Izzo JL Jr, Jones DW, Materson BJ, Oparil S, Wright JT Jr, Roccella EJ (2003) The Seventh Report of the Joint National Committee on Prevention, Detection, Evaluation, and Treatment of High Blood Pressure: the JNC 7 report. JAMA 289:2560–2572
Schwartz GJ, Haycock GB, Edelmann CM Jr, Spitzer A (1976) A simple estimate of glomerular filtration rate in children derived from body length and plasma creatinine. Pediatrics 58:259–263
Schwartz GJ, Gauthier B (1985) A simple estimate of glomerular filtration rate in adolescent boys. J Pediatr 106:522–526
Schwartz GJ, Feld LG, Langford DJ (1984) A simple estimate of glomerular filtration rate in full-term infants during the first year of life. J Pediatr 104:849–854
Hogg RJ, Furth S, Lemley KV, Portman R, Schwartz GJ, Coresh J, Balk E, Lau J, Levin A, Kausz AT, Eknoyan G, Levey AS (2003) National Kidney Foundation′s Kidney Disease Outcomes Quality Initiative clinical practice guidelines for chronic kidney disease in children and adolescents: evaluation, classification, and stratification. Pediatrics 111:1416–1421
Rembold CM (1998) Number needed to screen: development of a statistic for disease screening. BMJ 317:307–312
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Available at: https://doi.org/www.cdc.gov/growthcharts. Accessed 13 June 2008
Himes JH, Dietz WH (1994) Guidelines for overweight in adolescent preventive services: recommendations from an expert committee. The Expert Committee on Clinical Guidelines for Overweight in Adolescent Preventive Services. Am J Clin Nutr 59:307–316
Sorof JM, Lai D, Turner J, Poffenbarger T, Portman RJ (2004) Overweight, ethnicity, and the prevalence of hypertension in school-aged children. Pediatrics 113:475–482
Stergiou GS, Yiannes NJ, Rarra VC, Alamara CV (2005) White-coat hypertension and masked hypertension in children. Blood Press Monit 10:297–300
Pall D, Katona E, Fulesdi B, Zrinyi M, Zatik J, Bereczki D, Polgar P, Kakuk G (2003) Blood pressure distribution in a Hungarian adolescent population: comparison with normal values in the USA. J Hypertens 21:41–47
Genovesi S, Giussani M, Pieruzzi F, Vigorita F, Arcovio C, Cavuto S, Stella A (2005) Results of blood pressure screening in a population of school-aged children in the province of Milan: role of overweight. J Hypertens 23:493–497
Jago R, Harrell JS, McMurray RG, Edelstein S, El Ghormli L, Bassin S (2006) Prevalence of abnormal lipid and blood pressure values among an ethnically diverse population of eighth-grade adolescents and screening implications. Pediatrics 117:2065–2073
Sorof JM, Portman RJ (2000) White coat hypertension in children with elevated casual blood pressure. J Pediatr 137:493–497
Ogden CL, Flegal KM, Carroll MD, Johnson CL (2002) Prevalence and trends in overweight among US children and adolescents, 1999–2000. JAMA 288:1728–1732
Francischetti EA, Genelhu VA (2007) Obesity-hypertension: an ongoing pandemic. Int J Clin Pract 61:269–280
Ardissino G, Dacco V, Testa S, Bonaudo R, Claris-Appiani A, Taioli E, Marra G, Edefonti A, Sereni F (2003) Epidemiology of chronic renal failure in children: data from the ItalKid project. Pediatrics 111:e382–e387
Dirks JH, Robinson SW, Alderman M, Couser WG, Grundy SM, Smith SC, Remuzzi G, Unwin N (2006) Meeting report on the Bellagio conference ‘prevention of vascular diseases in the emerging world: an approach to global health equity’. Kidney Int 70:1397–1402
Dirks JH, de Zeeuw D, Agarwal SK, Atkins RC, Correa-Rotter R, D′Amico G, Bennett PH, El Nahas M, Valdes RH, Kaseje D, Katz IJ, Naicker S, Rodriguez-Iturbe B, Schieppati A, Shaheen F, Sitthi-Amorn C, Solez K, Viberti G, Remuzzi G, Weening JJ (2005) Prevention of chronic kidney and vascular disease: toward global health equity—the Bellagio 2004 declaration. Kidney Int 68:S1–S6
Mani MK (2006) Nephrologists sans frontieres: preventing chronic kidney disease on a shoestring. Kidney Int 70:821–823
Geleijnse JM, Hofman A, Witteman JC, Hazebroek AA, Valkenburg HA, Grobbee DE (1997) Long-term effects of neonatal sodium restriction on blood pressure. Hypertension 29:913–917
Brenner BM, Mackenzie HS (1997) Nephron mass as a risk factor for progression of renal disease. Kidney Int Suppl 63:S124–S127
Srinivasan SR, Myers L, Berenson GS (2006) Changes in metabolic syndrome variables since childhood in prehypertensive and hypertensive subjects: the Bogalusa Heart Study. Hypertension 48:33–39
Pugia MJ, Lott JA, Kajima J, Saambe T, Sasaki M, Kuromoto K, Nakamura R, Fusegawa H, Ohta Y (1999) Screening school children for albuminuria, proteinuria and occult blood with dipsticks. Clin Chem Lab Med 37:149–157
Haysom L, Williams R, Hodson E, Lopez-Vargas P, Roy LP, Lyle D, Craig JC (2009) Diagnostic accuracy of urine dipsticks for detecting albuminuria in indigenous and non-indigenous children in a community setting. Pediatr Nephrol 24:323–331
Haycock GB (1989) Creatinine, body size and renal function. Pediatr Nephrol 3:22–24
Zappitelli M, Joseph L, Gupta IR, Bell L, Paradis G (2007) Validation of child serum creatinine-based prediction equations for glomerular filtration rate. Pediatr Nephrol 22:272–281
Acknowledgments
Drs. Tonelli and Hemmelgarn are supported by Population Health Investigator Awards from the Alberta Heritage Foundation for Medical Research (AHFMR) and by New Investigator Awards from the Canadian Institutes of Health Research. Dr. Koshy is supported by a Clinical Fellowship award from AHFMR. This study was funded by a grant from the Foundation of the Hospitales Civiles de Guadalajara. The sponsor did not participate in analyses or influence the decision to submit this article for publication. The authors have no relevant competing financial interests to disclose.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Koshy, S.M., Garcia-Garcia, G., Pamplona, J.S. et al. Screening for kidney disease in children on World Kidney Day in Jalisco, Mexico. Pediatr Nephrol 24, 1219–1225 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00467-009-1136-7
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00467-009-1136-7