Abstract
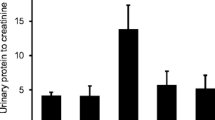
Combinations of antiproteinurics, including angiotensin I-converting enzyme inhibitors + angiotensin II receptor antagonist + statins, are promising choices in the treatment of steroid-resistant nephrotic syndrome. We aimed to investigate the effects of high doses of immunoglobulin in addition to these combinations in rats with adriamycin-induced nephrosis. The study included 40 rats allocated into five groups: control, nephrotic syndrome without treatment, dual therapy (DT) with enalapril + losartan, triple therapy (TT) with enalapril + losartan + simvastatin, and quadruple therapy (QT) with enalapril + losartan + simvastatin + a high dose of immunoglobulin. The proteinuria levels were not statistically different between DT, TT and QT groups at weeks 5, 8, 12 and 16. At week 16, serum creatinine levels in the QT group were significantly lower than those in the control, DT and TT groups. The glomerulosclerosis index in the DT group was significantly lower than in the TT and QT groups. The scores for interstitial fibrosis and TGF-β staining were similar among treatment groups. In conclusion, we showed that quadruple therapy including immunoglobulin had a beneficial effect on renal function in the late phase, but it had no additional effects in reducing proteinuria or in glomerulosclerosis score in experimental nephrotic syndrome. Further studies with angiotensin I-converting enzyme inhibitors (ACEIs), angiotensin II receptor antagonists (AIIRAs) and immunoglobulin combinations would offer some benefits in the treatment of nephrotic syndrome.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Grond J, Weening JJ, Elema JD (1984) Glomerular sclerosis in nephrotic rats. Comparison of the long-term effects of adriamycin and aminonucleoside. Lab Invest 51:277–285
Sakemi T, Ohtsuka N, Tomiyoshi Y, Morito F (1996) Sex difference in progression of adriamycin-induced nephropathy in rats. Am J Nephrol 16:540–547
Okasora T, Takikawa T, Utsunomiya Y, Senoh I, Hayashibara H, Shiraki K, Kasagi T, Shimizu F (1992) Suppressive effect of superoxide dismutase on adriamycin nephropathy. Nephron 60:199–203
Van den Branden C, Ceyssens B, De Craemer D, Pauwels M, Vanden Houte K, De Bleser P, Hellemans K, Geerts A, Verbeelen D (2000) Renal antioxidant enzymes and fibrosis-related markers in the rat adriamycin model. Nephron 86:167–175
Ozen S, Usta Y, Sahin-Erdemli I, Orhan D, Gumusel B, Yang B, Gursoy Y, Tulunay O, Dalkara T, Bakkaloglu A, El-Nahas M (2001) Association of nitric oxide production and apoptosis in a model of experimental nephropathy. Nephrol Dial Transplant 16:32–38
Bricio T, Molina A, Mampaso F (1992) Effect of anti-interleukin-1 administration to rats with adriamycin-induced nephrosis. APMIS 100:401–407
Abbate M, Zoja C, Rottoli D, Corna D, Perico N, Bertani T, Remuzzi G (1999) Antiproteinuric therapy while preventing the abnormal protein traffic in proximal tubule abrogates protein and complement-dependent interstitial inflammation in experimental renal disease. J Am Soc Nephrol 10:804–813
Zoja C, Donadelli R, Corna D, Testa D, Facchinetti D, Maffi R, Luzzana E, Colosio V, Bertani T, Remuzzi G (1997) The renoprotective properties of angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors in a chronic model of membranous nephropathy are solely due to the inhibition of angiotensin II: evidence based on comparative studies with a receptor antagonist. Am J Kidney Dis 29:254–264
Perico N, Amuchastegui SC, Colosio V, Sonzogni G, Bertani T, Remuzzi G (1994) Evidence that an angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitor has a different effect on glomerular injury according to the different phase of the disease at which the treatment is started. J Am Soc Nephrol 5:1139–1146
Taal MW, Brenner BM (2000) Renoprotective benefits of RAS inhibition: from ACEI to angiotensin II antagonists. Kidney Int 57:1803–1817
Kim SI, Kim HJ, Han DC, Lee HB (2000) Effect of lovastatin on small GTP binding proteins and on TGF-b1 and fibronectin expression. Kidney Int 58:S88–S92
Hundt M, Manger K, Dorner T, Grimbacher B, Kalden P, Rascu A, Weber D, Burmester GR, Peter HH, Kladen JR, Schmidt RE (2000) Treatment of acute exacerbation of systemic lupus erythematosus with high-dose intravenous immunoglobulin. Rheumatology 39:1301–1302
Yokoyama H, Goshima S, Wada T, Takaeda M, Furuichi K, Kobayashi K, Kida H (1999) The short- and long-term outcomes of membranous nephropathy treated with intravenous immune globulin therapy. Kanazawa study group for renal diseases and hypertension. Nephrol Dial Transplant 14:2379–2386
Rostoker G, Desvaux-Belghiti D, Pilatte Y, Petit-Phar M, Philippon C, Deforges L, Terzidis H, Intrator L, André C, Adnot S, Bonin P, Bierling P, Rémy P, Lagrue G, Lang P, Weil B (1994) High-dose immunoglobulin therapy for severe IgA nephropathy and Henoch-Schönlein purpura. Ann Intern Med 120:476–484
Jungi TW, Brcic M, Kuhnert P, Spycher MO, Li F, Nydegger UE (1990) Effect of IgG for intravenous use on Fc receptor-mediated phagocytosis by human monocytes. Clin Exp Immunol 82:163–169
Abe Y, Horiuchi A, Miyake M, Kimura S (1994) Anti-cytokine nature of natural human immunoglobulin: one possible mechanism of the clinical effect of intravenous immunoglobulin therapy. Immunol Rev 139:5–19
Andersson UG, Bjork L, Skansén-Saphir U, Andersson JP (1993) Down-regulation of cytokine production and interleukin-2 receptor expression by pooled human IgG. Immunology 79:211–216
Basta M, Fries LF, Frank MM (1991) High doses of intravenous Ig inhibit in vitro uptake of C4 fragments onto sensitized erythrocytes. Blood 77:376–380
Dietrich G, Kaveri SV, Kazatchkine MD (1992) Modulation of autoimmunity by intravenous immune globulin through interaction with the function of the immune/idiotypic network. Clin Immunol Immunopathol 62:S73–S81
Blanchette VS, Kirby MA, Turner C (1992) Role of intravenous immunoglobulin G in autoimmune hematologic disorders. Semin Hematol 29:72–82
Toungouz M, Denys CH, De Groote D, Dupont E (1995) In vitro inhibition of tumour necrosis factor-alpha and interleukin-6 production by intravenous immunoglobulins. Br J Haematol 89:698–703
Shalhoub RJ (1974) Pathogenesis of lipoid nephrosis: a disorder of T-cell function. Lancet 2:556–560
Yap HK, Cheung W, Murugasu B, Sim SK, Seah CC, Jordan SC (1999) Th1 and Th2 cytokine mRNA profiles in childhood nephrotic syndrome: evidence for increased IL-13 mRNA expression in relapse. J Am Soc Nephrol 10:529–537
Stefanoviç V, Goluboviç E, Mitic-Zlatkovic M, Vlahovic P, Jovanovic O, Bogdanovic R (1998) Interleukin-12 and interferon-gamma production in childhood idiopathic nephrotic syndrome. Pediatr Nephrol 12:463–466
Sahali D, Pawlak A, Le Gouvello S, Lang P, Valanciute A, Remy P, Loirat C, Niaudet P, Bensman A, Guellaen G (2001) Transcriptional and post-transcriptional alterations of IκBα in active minimal-change nephrotic syndrome. J Am Soc Nephrol 12:1648–1658
Cao C, Lu S, Dong C, Zhao R (2001) Abnormal DNA-binding of transcription factors in minimal-change nephrotic syndrome. Pediatr Nephrol 16:790–795
Erisir S, Akbas H, Koyun M, Akman S (2006) The efficiency of intraperitoneal high-dose immunoglobulin in experimental nephrotic syndrome. Pediatr Nephrol 21:39–45
Okuda S, Oh Y, Tsuruda H, Onoyama K, Fujimi S, Fujishima M (1986) Adriamycin-induced nephropathy as a model of chronic progressive glomerular disease. Kidney Int 29:502–510
Diamond JR, Anderson S (1990) Irreversible tubulointerstitial damage associated with chronic aminonucleoside nephrosis. Amelioration by angiotensin I converting enzyme inhibition. Am J Pathol 137:1323–1332
Attia DM, Feron O, Goldschmeding R, Radermakers LH, Vaziri ND, Boer P, Balligand JL, Koomans HA, Joles JA (2004) Hypercholesterolemia in rats induces podocyte stress and decreases renal cortical nitric oxide synthesis via an angiotensin II type 1 receptor-sensitive mechanism. J Am Soc Nephrol 15:949–957
Zoja C, Corna D, Rottoli D, Cattaneo D, Zanchi C, Tomasoni S, Abbate M, Remuzzi G (2002) Effect of combining ACE inhibitor and statin in severe experimental nephropathy. Kidney Int 61:1635–1645
Raij L, Azar S, Keane W (1984) Mesangial immune injury, hypertension, and progressive glomerular damage in Dahl rats. Kidney Int 26:137–143
Zoja C, Benigni A, Camozzi D, Corna D, Longaretti L, Todeschini M, Remuzzi G (2003) Combining lisinopril and l-arginine slows disease progression and reduces endothelin-1 in passive Heymann nephritis. Kidney Int 64:857–863
Coa Z, Cooper ME, Wu LL, Cox AJ, Jandeleit-Dahm K, Kelly DJ, Gilbert RE (2000) Blockade of the renin-angiotensin and endothelin systems on progressive renal injury. Hypertension 36:561–568
Wilkinson-Berka JL, Gibbs NJ, Cooper ME, Skinner SL, Kelly DJ (2001) Renoprotective and anti-hypertensive effects of combined valsartan and perindopril in progressive diabetic nephropathy in the transgenic (mRen-2)27 rat. Nephrol Dial Transplant 16:1343–1349
Bos H, Henning RH, De Boer E, Tiebosch AT, De Jong PE, De Zeeuw D, Navis G (2002) Addition of AT1 blocker fails to overcome resistance to ACE inhibition in adriamycin nephrosis. Kidney Int 61:473–480
Zoja C, Corna D, Camozzi D, Cattaneo D, Rottoli D, Batani C, Zanchi C, Abbate M, Remuzzi G (2002) How to fully protect the kidney in a severe model of progressive nephropathy: a multidrug approach. J Am Soc Nephrol 13:2898–2908
Branton MH, Kopp JB (1999) TGF-b and fibrosis. Microbes Infect 1:1349–1365
Khalil A, Tullus K, Bakhiet M, Burman LG, Jaremko G, Brauner A (2000) Angiotensin II type 1 receptor antagonist (losartan) down-regulates transforming growth factor-beta in experimental acute pyelonephritis. J Urol 164:186–191
Goumenos DS, Tsamandas AC, Oldroyd S, Sotsiou F, Tsakas S, Petropoulou C, Bonikos D, El Nahas AM, Vlachojannis JG (2001) Transforming growth factor-b1 in kidney and urine of patients with glomerular disease and proteinuria. Nephron 87:240–248
Taniguchi Y, Yorioka N, Masaki T, Yamashita K, Ito T, Ueda H, Yamakido M (2000) Role of transforming growth factor beta 1 in glomerulonephritis. J Int Med Res 25:71–80
Wasilewska AM, Zoch-Zwierz WM (2004) Transforming growth factor-β1 in nephrotic syndrome treated with cyclosporine and ACE inhibitors. Pediatr Nephrol 19:1349–1353
Zhang W, Li Q, Wang L, Yang X (2008) Simvastatin ameliorates glomerulosclerosis in Adriamycin-induced-nephropathy rats. Pediatr Nephrol 23:2185–2194
Adamczak M, Gross ML, Amnn K, Ritz E (2004) Reversal of glomerular lesions involves coordinated restructuring of glomerular microvasculature. J Am Soc Nephrol 15:3063–3072
Ma J, Nishimura H, Fogo A, Kon V, Inagami T, Ichikawa I (1998) Accelerated fibrosis and collagen deposition develop in the renal interstitium of angiotensin type 2 receptor null mutant mice during ureteral obstruction. Kidney Int 53:937–944
Benchetrit S, Golan E, Podjarny E, Green J, Rashid G, Bernheim J, Hershkovitz R, Bernheim J (2001) Low molecular weight heparin reduces proteinuria and modulates glomerular TNF alpha production in the early phase of adriamycin nephropathy. Nephron 87:155–160
Zima T, Tesar V, Stipek S, Crkovska J, Poledne R, Teminova J, Platenik J, Rychlik I, Merta M, Nemecek K (1997) The influence of cyclosporine on lipid peroxidation and superoxide dismutase in adriamycin nephropathy in rats. Nephron 75:464–468
Acknowledgments
The study was supported by a grant from the Turkish Society of Nephrology and the Scientific Research Fund of Akdeniz University.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Akman, S., Kalay, S., Akkaya, B. et al. Beneficial effect of triple treatment plus immunoglobulin in experimental nephrotic syndrome. Pediatr Nephrol 24, 1173–1180 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00467-009-1117-x
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00467-009-1117-x