Abstract
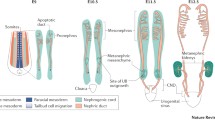
Branching morphogenesis, defined as the growth and branching of epithelial tubules, is a fundamental developmental process involved in the formation of a variety of mammalian tissues, including the kidney. Defective renal branching may result in a number of clinically relevant abnormalities, including renal agenesis, renal dysplasia, multiplex kidneys, and hypertension. In this review we describe the morphological events that generate the characteristic tree-like structure of the mammalian collecting system. We also highlight new knowledge related to both established and novel signaling systems that are important for stimulating and inhibiting branching morphogenesis.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Piscione TD, Rosenblum ND (2002) The molecular control of renal branching morphogenesis: current knowledge and emerging insights. Differentiation 70:227–246
Costantini F (2006) Renal branching morphogenesis: concepts, questions, and recent advances. Differentiation 74:402–421
Shah MM, Sampogna RV, Sakurai H, Bush KT, Nigam SK (2004) Branching morphogenesis and kidney disease. Development 131:1449–1462
Osathanondh V, Potter E (1963) Development of the human kidney as shown by microdissection III. Formation and interrelationships of collecting tubules and nephrons. Arch Pathol 76:290–302
Watanabe T, Costantini F (2004) Real-time analysis of ureteric bud branching morphogenesis in vitro. Dev Biol 271:98–108
Pachnis V, Mankoo B, Costantini F (1993) Expression of the c-ret proto-oncogene during mouse embryogenesis. Development 119:1005–1017
Majumdar A, Vainio S, Kispert A, McMahon J, McMahon AP (2003) Wnt11 and Ret/Gdnf pathways cooperate in regulating ureteric branching during metanephric kidney development. Development 130:3175–3185
Schmidt-Ott KM, Yang J, Chen X, Wang H, Paragas N, Mori K, Li JY, Lu B, Costantini F, Schiffer M, Bottinger E, Barasch J (2005) Novel regulators of kidney development from the tips of the ureteric bud. J Am Soc Nephrol 16:1993–2002
Li Z, Stuart RO, Qiao J, Pavlova A, Bush KT, Pohl M, Sakurai H, Nigam SK (2000) A role for timeless in epithelial morphogenesis during kidney development. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 97:10038–10043
Michael L, Sweeney DE, Davies JA (2007) The lectin Dolichos biflorus agglutinin is a sensitive indicator of branching morphogenetic activity in the developing mouse metanephric collecting duct system. J Anat 210:89–97
Michael L, Davies JA (2004) Pattern and regulation of cell proliferation during murine ureteric bud development. J Anat 204:241–255
Hellmich HL, Kos L, Cho ES, Mahon KA, Zimmer A (1996) Embryonic expression of glial cell-line derived neurotrophic factor (GDNF) suggests multiple developmental roles in neural differentiation and epithelial-mesenchymal interactions. Mech Dev 54:95–105
Pichel JG, Shen L, Sheng HZ, Granholm AC, Drago J, Grinberg A, Lee EJ, Huang SP, Saarma M, Hoffer BJ, Sariola H, Westphal H (1996) GDNF is required for kidney development and enteric innervation. Cold Spring Harbor Symp Quant Biol 61:445–457
Sainio K, Suvanto P, Davies J, Wartiovaara J, Wartiovaara K, Saarma M, Arumae U, Meng X, Lindahl M, Pachnis V, Sariola H (1997) Glial-cell-line-derived neurotrophic factor is required for bud initiation from ureteric epithelium. Development 124:4077–4087
Schuchardt A, D'Agati V, Larsson-Blomberg L, Costantini F, Pachnis V (1994) Defects in the kidney and enteric nervous system of mice lacking the tyrosine kinase receptor Ret. Nature 367:380–383
Schuchardt A, D'Agati V, Pachnis V, Costantini F (1996) Renal agenesis and hypodysplasia in ret-k- mutant mice result from defects in ureteric bud development. Development 122:1919–1929
Enomoto H, Araki T, Jackman A, Heuckeroth RO, Snider WD, Johnson EM Jr, Milbrandt J (1998) GFR alpha1-deficient mice have deficits in the enteric nervous system and kidneys. Neuron 21:317–324
Jain S, Encinas M, Johnson EM Jr, Milbrandt J (2006) Critical and distinct roles for key RET tyrosine docking sites in renal development. Genes Dev 20:321–333
Fisher CE, Michael L, Barnett MW, Davies JA (2001) Erk MAP kinase regulates branching morphogenesis in the developing mouse kidney. Development 128:4329–4338
Tang MJ, Cai Y, Tsai SJ, Wang YK, Dressler GR (2002) Ureteric bud outgrowth in response to RET activation is mediated by phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase. Dev Biol 243:128–136
Mendelsohn C, Batourina E, Fung S, Gilbert T, Dodd J (1999) Stromal cells mediate retinoid-dependent functions essential for renal development. Development 126:1139–1148
Quinlan J, Kaplan F, Sweezey N, Goodyer P (2007) LGL1, a novel branching morphogen in developing kidney, is induced by retinoic acid. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol 293:F987–993
Basson MA, Akbulut S, Watson-Johnson J, Simon R, Carroll TJ, Shakya R, Gross I, Martin GR, Lufkin T, McMahon AP, Wilson PD, Costantini FD, Mason IJ, Licht JD (2005) Sprouty1 is a critical regulator of GDNF/RET-mediated kidney induction. Dev Cell 8:229–239
Kim D, Dressler GR (2007) PTEN modulates GDNF/RET mediated chemotaxis and branching morphogenesis in the developing kidney. Dev Biol 307:290–299
Grieshammer U, Le M, Plump AS, Wang F, Tessier-Lavigne M, Martin GR (2004) SLIT2-mediated ROBO2 signaling restricts kidney induction to a single site. Dev Cell 6:709–717
Brophy PD, Ostrom L, Lang KM, Dressler GR (2001) Regulation of ureteric bud outgrowth by Pax2-dependent activation of the glial derived neurotrophic factor gene. Development 128:4747–4756
Xu PX, Adams J, Peters H, Brown MC, Heaney S, Maas R (1999) Eya1-deficient mice lack ears and kidneys and show abnormal apoptosis of organ primordia. Nat Genet 23:113–117
Gong KQ, Yallowitz AR, Sun H, Dressler GR, Wellik DM (2007) A Hox-Eya-Pax complex regulates early kidney developmental gene expression. Mol Cell Biol 27:7661–7668
Kume T, Deng K, Hogan BL (2000) Murine forkhead/winged helix genes Foxc1 (Mf1) and Foxc2 (Mfh1) are required for the early organogenesis of the kidney and urinary tract. Development 127:1387–1395
Dudley AT, Robertson EJ (1997) Overlapping expression domains of bone morphogenetic protein family members potentially account for limited tissue defects in BMP7 deficient embryos. Dev Dyn 208:349–362
Miyazaki Y, Oshima K, Fogo A, Hogan BL, Ichikawa I (2000) Bone morphogenetic protein 4 regulates the budding site and elongation of the mouse ureter. J Clin Invest 105:863–873
Michos O, Panman L, Vintersten K, Beier K, Zeller R, Zuniga A (2004) Gremlin-mediated BMP antagonism induces the epithelial-mesenchymal feedback signaling controlling metanephric kidney and limb organogenesis. Development 131:3401–3410
Bridgewater D, Cox B, Cain J, Lau A, Athaide V, Gill PS, Kuure S, Sainio K, Rosenblum ND (2008) Canonical WNT/beta-catenin signaling is required for ureteric branching. Dev Biol 317:83–94
Iglesias DM, Hueber PA, Chu L, Campbell R, Patenaude AM, Dziarmaga AJ, Quinlan J, Mohamed O, Dufort D, Goodyer PR (2007) Canonical WNT signaling during kidney development. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol 293:F494–500
Schwab KR, Patterson LT, Hartman HA, Song N, Lang RA, Lin X, Potter SS (2007) Pygo1 and Pygo2 roles in Wnt signaling in mammalian kidney development. BMC Biol 5:15
Hasegawa Y, Satoh K, Iizuka-Kogo A, Shimomura A, Nomura R, Akiyama T, Senda T (2007) Loss of ICAT gene function leads to arrest of ureteric bud branching and renal agenesis. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 362:988–994
Marose TD, Merkel CE, McMahon AP, Carroll TJ (2008) Beta-catenin is necessary to keep cells of ureteric bud/Wolffian duct epithelium in a precursor state. Dev Biol 314:112–126
Miyamoto N, Yoshida M, Kuratani S, Matsuo I, Aizawa S (1997) Defects of urogenital development in mice lacking Emx2. Development 124:1653–1664
Stark K, Vainio S, Vassileva G, McMahon AP (1994) Epithelial transformation of metanephric mesenchyme in the developing kidney regulated by Wnt-4. Nature 372:679–683
Kispert A, Vainio S, Shen L, Rowitch DH, McMahon AP (1996) Proteoglycans are required for maintenance of Wnt-11 expression in the ureter tips. Development 122:3627–3637
Lin Y, Liu A, Zhang S, Ruusunen T, Kreidberg JA, Peltoketo H, Drummond I, Vainio S (2001) Induction of ureter branching as a response to Wnt-2b signaling during early kidney organogenesis. Dev Dyn 222:26–39
Massague J (1998) TGF-beta signal transduction. Annu Rev Biochem 67:753–791
Dudley AT, Lyons KM, Robertson EJ (1995) A requirement for bone morphogenetic protein-7 during development of the mammalian kidney and eye. Genes Dev 9:2795–2807
Pelton RW, Saxena B, Jones M, Moses HL, Gold LI (1991) Immunohistochemical localization of TGF beta 1, TGF beta 2, and TGF beta 3 in the mouse embryo: expression patterns suggest multiple roles during embryonic development. J Cell Biol 115:1091–1105
Sanford LP, Ormsby I, Gittenberger-de Groot AC, Sariola H, Friedman R, Boivin GP, Cardell EL, Doetschman T (1997) TGFbeta2 knockout mice have multiple developmental defects that are non-overlapping with other TGFbeta knockout phenotypes. Development 124:2659–2670
Sims-Lucas S, Caruana G, Dowling J, Kett MM, Bertram JF (2008) Augmented and accelerated nephrogenesis in TGF-beta2 heterozygous mutant mice. Pediatr Res 63:607–612
Hartwig S, Bridgewater D, Di Giovanni V, Cain J, Mishina Y, Rosenblum ND (2008) BMP receptor ALK3 controls collecting system development. J Am Soc Nephrol 19:117–124
Brenner BM, Garcia DL, Anderson S (1988) Glomeruli and blood pressure. Less of one, more the other? Am J Hypertens 1:335–347
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bridgewater, D., Rosenblum, N.D. Stimulatory and inhibitory signaling molecules that regulate renal branching morphogenesis. Pediatr Nephrol 24, 1611–1619 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00467-008-1048-y
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00467-008-1048-y