Abstract
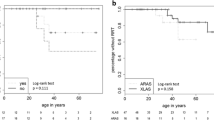
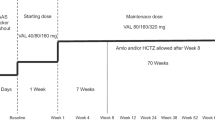
Ten pediatric patients with Alport syndrome received enalapril for 5 years. There were nine boys. Eight patients have the X-linked form of the disease and two the autosomal recessive form. The median age at the start of treatment was 10.25 years. Only one patient was hypertensive. The starting dose of enalapril was 0.05 mg/kg; the target dose was 0.5 mg/kg per day. The median dose given effectively was 0.24, 0.37, 0.45, 0.43, and 0.49 mg/kg per day at years of study 1, 2, 3, 4, and 5, respectively. The median urinary protein/creatinine ratio was 1.58 g/g (range 0.49–4.60) before treatment. This decreased to 0.98, 1.09, 1.35, 1.11, and 1.38 g/g after 1, 2, 3, 4, and 5 years, respectively. The median creatinine clearance at baseline was 100 ml/min per 1.73 m2 (range 82–133) and after 5 years 92 ml/min per 1.73 m2 (range 22–115). Three patients did not reach the target dose of enalapril because of orthostatic hypotension. One of them was the only patient to develop chronic renal failure within 5 years. The present study indicates that enalapril reduces urinary protein excretion and preserves glomerular filtration in Alport patients as a group. However, there was individual variation, as in most studies of patients with proteinuric nephropathies given inhibitors of the angiotensin-converting enzyme.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anderson S, Meyer TW, Rennke HG, Brenner BM (1985) Control of glomerular hypertension limits glomerular injury in rats with reduced renal mass. J Clin Invest 76:612–619
Zatz R, Dunn BR, Meyer TW, Anderson S, Rennke HG, Brenner BM (1986) Prevention of diabetic nephropathy by pharmacological amelioration of glomerular capillary hypertension. J Clin Invest 77:1925–1930
Marinides GN, Groggel GC, Cohen AH, Border WA (1990) Enalapril and low protein reverse chronic puromycin aminonucleoside nephropathy. Kidney Int 37:749–757
Verseput GH, Provoost AP, Braam BB, Weening JJ, Koomans HA (1997) Angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibition in the prevention and treatment of chronic renal damage in the hypertensive fawn-hooded rat. J Am Soc Nephrol 8:249–259
Remuzzi A, Fassi A, Bertani T, Perico N, Remuzzi G (1999) ACE inhibition induces regression of proteinuria and halts progression of renal damage in a genetic model of progressive nephropathy. Am J Kidney Dis 34:626–632
Parving HH, Hommel E, Schmidt UM (1988). Protection of kidney function and decrease of albuminuria by captopril in insulin dependent diabetics with nephropathy. BMJ 297:1086–1091
Chaturvedi N, Stevenson J, Fuller JH, Rottiers R, Ferriss B. The EUCLID Study Group (1997) Randomised placebo-controlled trial of lisinopril in normotensive patients with insulin-dependent diabetes and normoalbuminuria or microalbuminuria. Lancet 349:1787–1792
Jafar TH, Schmid CH, Landa M, Giatras I, Toto R, Remuzzi G, Maschio G, Brenner B, Kamper A, Zucchelli P, Becker G, Himmelmann A, Bannister K, Landais P, Shahinfar S, Jong P de, Zeeuw D de, Lau J, Levey AS, the ACE inhibition in Progressive Renal Disease Study Group (2001) Angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors and progression of nondiabetic renal disease. A meta-analysis of patient-level data. Ann Intern Med 135:73–87
Trachtman H, Gauthier B (1988) Effect of angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitor therapy on proteinuria in children with renal disease. J Pediatr 112:295–298
Proesmans W, Van Wambeke I, Van Dyck M (1996) Long-term therapy with enalapril in patients with nephrotic-range proteinuria. Pediatr Nephrol 10:587–589
Lama G, Salsano ME, Pedulla M, Grassia C, Ruocco G (1997) Angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors and reflux nephropathy: 2 year follow-up. Pediatr Nephrol 11:714–718
Yüksel H, Darcan S, Kabasakal C, Cura A, Mir S, Mavi E (1998) Effect of enalapril on proteinuria, phosphaturia and calciuria in insulin-dependent diabetes. Pediatr Nephrol 12:648–650
Proesmans W, Knockaert H, Trouet D (2000) Enalapril in pediatric patients with Alport syndrome: 2 years’ experience. Eur J Pediatr 159:430–433
Maschio G, Alberti D, Janin G, Locatelli F, Mann JF, Motolese M, Ponticelli C, Ritz E, Zucchelli P, and the Angiotensin Converting Enzyme Inhibition in Progressive Renal Insufficiency Study Group (1996) Effect of the angiotensin-converting-enzyme inhibitor benazepril on the progression of chronic renal insufficiency. N Engl J Med 334:939–945
The GISEN group (1997) Randomized placebo-controlled trial of effect of ramipril on decline in glomerular filtration rate and risk of terminal renal failure in proteinuric, non-diabetic nephropathy. Lancet 349:1857–1863
Ruggenenti P, Perna A, Gherardi G, Gaspari F, Benini R, Remuzzi G (1998) Renal function and requirement of dialysis in chronic nephropathy patients on long-term ramipril: REIN follow-up trial. Lancet 352:1252–1256
Tryggvason K, Zhou J, Hostikka Sl, Shows TB (1993) Molecular genetics of Alport syndrome. Kidney Int 43:38–44
Grodecki KM, Gains MJ, Baumal R, Osmond DH, Cotter B, Valli VE, Jacobs RM (1997) Treatment of X-linked hereditary nephritis in Samoyed dogs with angiotensin converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitor. J Comp Pathol 117:209–225
Taal MW, Brenner BM (2002) Combination ACEI and ARB therapy: additional effect in renoprotection? Curr Opin Nephrol Hypertens 11:377–381
Bhattacharjee R, Filler G (2002) Additive antiproteinuric effect of ACE inhibitor and losartan in IgA nephropathy. Pediatr Nephrol 17:302–304
Fogo AB (2003) Editorial review: the potential for regression of renal scarring. Curr Opin Nephrol Hypertens 12:223–225
Gross O, Koepke ML, Schulze-Lohoff E (2003) Current concepts in prevention of renal fibrosis and renal failure in children with Alport syndrome: lessons from preemptive medical therapy in mice (abstract). Nephrol Dial Transpl 18 [Suppl 4]:373
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Proesmans, W., Van Dyck, M. Enalapril in children with Alport syndrome. Pediatr Nephrol 19, 271–275 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00467-003-1366-z
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00467-003-1366-z