Abstract
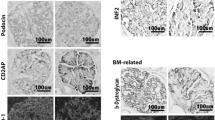
Recently, nephrin, podocin, α-actinin, and WT1, which are located at the slit diaphragm and expressed by the podocyte, were found to be causative in congenital/familial nephrotic syndrome (NS), but their role in acquired NS remains unclear. We studied their expression in NS with the aim of disclosing their possible role in the development of proteinuria. Immunofluorescence, confocal microscopy, and image analysis were used to study the expression and the distribution in 19 children with primary NS, 9 with isolated hematuria, and 9 controls. All the children with NS presented with heavy proteinuria and foot process effacement was identified by electron microscopy. No proteinuria and foot process effacement was seen in the group with hematuria. A dramatic decrease of podocin expression was found in NS (86.66±22.74) compared with control groups (P=0.014). Furthermore, we also found the pattern of distribution of nephrin, podocin, and α-actinin changed in children with NS. In conclusion, a dramatic decrease of podocin expression and abnormal distribution of nephrin, podocin, and α-actinin were found in children with NS. No differences were found in children with isolated hematuria, suggesting involvement of these molecules in the development of proteinuria in primary NS.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Tryggvason K (1999) Unraveling the mechanisms of glomerular ultrafiltration: nephrin, a key component of the slit diaphragm. J Am Soc Nephrol 10:2440–2445
Boute N, Gribouval O, Roselli S, Benessy F, Lee H, Fuchshuber A, Dahan K, Gubler MC, Niaudet P, Antignac C (2000) NPHS2, encoding the glomerular protein podocin, is mutated in autosomal recessive steroid-resistant nephrotic syndrome. Nat Genet 24:349–354
Kaplan JM, Kim SH, North KN, Rennke H, Correia LA, Tong HQ, Mathis BJ, Rodríguez-Pérez JC, Allen PG, Beggs AH, Pollak MR (2000) Mutations in ACTN4, encoding α-actinin-4, cause familial focal segmental glomerulosclerosis. Nat Genet 24:251–256
Jeanpierre C, Denamur E, Henry I, Cabanis MO, Luce S, Cecille A, Elion J, Peuchmaur M, Loirat C, Niaudet P, Gubler MC, Junien C (1998) Identification of constitutional WT1 mutations, in patients with isolated diffuse mesangial sclerosis, and analysis of genotype/phenotype correlations by use of a computerized mutation database. Am J Hum Genet 62:824–833
Roselli S, Gribouval O, Boute N, Sich M, Benessy F, Attie T, Gubler MC, Antignac C (2002) Podocin localizes in the kidney to the slit diaphragm area. Am J Pathol 160:131–139
Sellin L, Huber TB, Gerke P, Quack I, Pavenstädt H, Walz G (2003) NEPH1 defines a novel family of podocin interacting proteins. FASEB J 17:115–117
Reiser J, Kriz W, Kretzler M, Mundel P (2000) The glomerular slit diaphragm is a modified adherens junction. J Am Soc Nephrol 11:1–8
Schnabel E, Anderson JM, Farquhar MG (1990) The tight junction protein ZO-1 is concentrated along slit diaphragms of the glomerular epithelium. J Cell Biol 111:1255–1263
Li C, Ruotsalainen V, Tryggvason K, Shaw AS, Miner JH (2000) CD2AP is expressed with nephrin in developing podocytes and is found widely in mature kidney and elsewhere. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol 279: F785–F792
Srivastava T, Garola RE, Whiting JM, Alon US (2001) Synaptopodin expression in idiopathic nephrotic syndrome of childhood. Kidney Int 59:118–125
Mundel P, Heid HW, Mundel TM, Kruger M, Reiser J, Kriz W (1997) Synaptopodin: an actin-associated protein in telencephalic dendrites and renal podocytes. J Cell Biol 139:193–204
Putaala H, Soininen R, Kilpelainen P, Wartiovaara J, Tryggvason K (2001) The murine nephrin gene is specifically expressed in kidney, brain and pancreas: inactivation of the gene leads to massive proteinuria and neonatal death. Hum Mol Genet 10:1–8
Ruotsalainen V, Patrakka J, Tissari P, Reponen P, Hess M, Kestilä M, Holmberg C, Salonen R, Heikinheimo M, Wartiovaara J, Tryggvason K, Jalanko H (2000) Role of nephrin in cell junction formation in human nephrogenesis. Am J Pathol 157:1905–1916
Patrakka J, Kestilä M, Wartiovaara J, Ruotsalainen V, Tissari P, Lenkkeri U, Männikkö M, Visapää I, Holmberg C, Rapola J, Tryggvason K, Jalanko H (2000) Congenital nephrotic syndrome (NPHS1): features resulting from different mutations in Finnish patients. Kidney Int 58:972–980
Schwarz K, Simons M, Reiser J, Saleem MA, Faul C, Kriz W, Shaw AS, Holzman LB, Mundel P (2001) Podocin, a raft-associated component of the glomerular slit diaphragm, interacts with CD2AP and nephrin. J Clin Invest 108:1621–1629
Blanchard A, Ohanian V, Critchley D (1989) The structure and function of α-actinin. J Muscle Res Cell Motil 10:280–289
Honda K, Yamada T, Endo R, Ino Y, Gotoh M, Tsuda H, Yamada Y, Chiba H, Hirohashi S (1998) Actinin-4, a novel actin-bundling protein associated with cell motility and cancer invasion. J Cell Biol 140:1383–1393
Beggs AH, Byers TJ, Knoll JH, Boyce FM, Bruns GA, Kunkel LM (1992) Cloning and characterization of two human skeletal muscle α-actinin genes located on chromosomes 1 and 11. J Biol Chem 267:9281–9288
Lachapelle M, Bendayan M (1991) Contractile proteins in podocytes: immunocytochemical localization of actin and alpha-actinin in normal and nephrotic rat kidneys. Virchows Arch [B] 60:105–111
Drenckhahn D, Franke RP (1988) Ultrastructural organization of contractile and cytoskeletal proteins in glomerular podocytes of chicken, rat, and man. Lab Invest 59:673–682
Ohtaka A, Ootaka T, Sato H, Soma J, Sato T, Saito T, Ito S (2002) Significance of early phenotypic change of glomerular podocytes detected by Pax2 in primary focal segmental glomerulosclerosis. Am J Kidney Dis 39:475–485
Huber TB, Kottgen M, Schilling B, Walz G, Benzing T (2001) Interaction with podocin facilitates nephrin signaling. J Biol Chem 276:41543–41546
Tryggvason K, Wartiovaara J (2001) Molecular basis of glomerular permselectivity. Curr Opin Nephrol Hypertens 10:543–549
Khoshnoodi J, Tryggvason K (2001) Unraveling the molecular make-up of the glomerular podocyte slit diaphragm. Exp Nephrol 9:355–359
Kerjaschki D (2001) Caught flat-footed: podocyte damage and the molecular bases of focal glomerulosclerosis. J Clin Invest 108:1583–1587
Yuan H, Takeuchi E, Salant DJ (2002) Podocyte slit-diaphragm protein nephrin is linked to the actin cytoskeleton. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol 282:F585–F591
Jalanko H, Patrakka J, Tryggvason K, Holmberg C (2001) Genetic kidney diseases disclose the pathogenesis of proteinuria. Ann Med 33:526–533
Saleem MA, Ni L, Witherden I, Tryggvason K, Ruotsalainen V, Mundel P, Mathieson PW (2002) Co-localization of nephrin, podocin, and the actin cytoskeleton: evidence for a role in podocyte foot process formation. Am J Pathol 161:1459–1466
Doublier S, Ruotsalainen V, Salvidio G, Lupia E, Biancone L, Conaldi PG, Reponen P, Tryggvason K, Camussi G (2001) Nephrin redistribution on podocytes is a potential mechanism for proteinuria in patients with primary acquired nephrotic syndrome. Am J Pathol 158:1723–1731
Guan N, Ding J, Zhang JJ, Xiao HJ, Liu JC, Yang JY (2001) Nephrin expression in kidneys of children with acquired renal diseases. Chin J Pediatr 39:718–721
Patrakka J, Ruotsalainen V, Ketola I, Holmberg C, Heikinheimo M, Tryggvason K, Jalanko H (2001) Expression of nephrin in pediatric kidney diseases. J Am Soc Nephrol 12:289–296
Furness PN, Hall LL, Shaw JA, Pringle JH (1999) Glomerular expression of nephrin is decreased in acquired human nephrotic syndrome. Nephrol Dial Transplant 14:1234–1237
Kim BK, Hong HK, Kim JH, Lee HS (2002) Differential expression of nephrin in acquired human proteinuric diseases. Am J Kidney Dis 40:964–973
Acknowledgements.
This study was supported by National Nature Science Foundation of China (30170992). We are grateful to Professor Karl Tryggvason (Sweden) and Corinne Antignac (France) for their kind gift of antibodies. We also thank Jianping Huang, Yong Yao, Huijie Xiao, and Jingcheng Liu for their support of this project.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Guan, N., Ding, J., Zhang, J. et al. Expression of nephrin, podocin, α-actinin, and WT1 in children with nephrotic syndrome. Pediatr Nephrol 18, 1122–1127 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00467-003-1240-z
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00467-003-1240-z