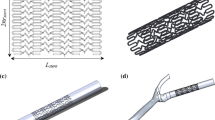
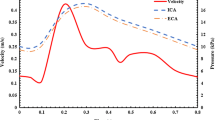
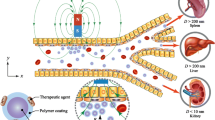
Abstract
A multi-physics model was developed to study the delivery of magnetic nanoparticles (MNPs) to the stent-implanted region under an external magnetic field. The model is firstly validated by experimental work in literature. Then, effects of external magnetic field strength, magnetic particle size, and flow velocity on MNPs’ targeting and binding have been analyzed through a parametric study. Two new dimensionless numbers were introduced to characterize relative effects of Brownian motion, magnetic force induced particle motion, and convective blood flow on MNPs motion. It was found that larger magnetic field strength, bigger MNP size, and slower flow velocity increase the capture efficiency of MNPs. The distribution of captured MNPs on the vessel along axial and azimuthal directions was also discussed. Results showed that the MNPs density decreased exponentially along axial direction after one-dose injection while it was uniform along azimuthal direction in the whole stented region (averaged over all sections). For the beginning section of the stented region, the density ratio distribution of captured MNPs along azimuthal direction is center-symmetrical, corresponding to the center-symmetrical distribution of magnetic force in that section. Two different generation mechanisms are revealed to form four main attraction regions. These results could serve as guidelines to design a better magnetic drug delivery system.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Chen GJ, Wang LF (2011) Design of magnetic nanoparticles-assisted drug delivery system. Curr Pharm Des 17(22):2331–2351
Yigit MV, Moore A, Medarova Z (2012) Magnetic nanoparticles for cancer diagnosis and therapy. Pharm Res-Dordr 29(5):1180–1188. doi:10.1007/s11095-012-0679-7
Azhar SL, Lotfipour F (2012) Magnetic nanoparticles for antimicrobial drug delivery. Die Pharmazie 67(10):817–821
Park H, Yang J, Seo S, Kim K, Suh J, Kim D, Haam S, Yoo KH (2008) Multifunctional nanoparticles for photothermally controlled drug delivery and magnetic resonance imaging enhancement. Small 4(2):192–196. doi:10.1002/smll.200700807
Dave SR, Gao X (2009) Monodisperse magnetic nanoparticles for biodetection, imaging, and drug delivery: a versatile and evolving technology. Wiley Interdiscip Rev Nanomed Nanobiotechnol 1(6):583–609. doi:10.1002/wnan.51
McGill SL, Cuylear CL, Adolphi NL, Osinski M, Smyth HD (2009) Magnetically responsive nanoparticles for drug delivery applications using low magnetic field strengths. IEEE Trans Nanobiosci 8(1):33–42. doi:10.1109/TNB.2009.2017292
Liu Y, Shah S, Tan J (2012) Computational modeling of nanoparticle targeted drug delivery. Rev Nanosci Nanotechnol 1(1):66–83. doi:10.1166/rnn.2012.1014
Chorny M, Fishbein I, Yellen BB, Alferiev IS, Bakay M, Ganta S, Adamo R, Amiji M, Friedman G, Levy RJ (2010) Targeting stents with local delivery of paclitaxel-loaded magnetic nanoparticles using uniform fields. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 107(18):8346–8351. doi:10.1073/pnas.0909506107
Dobson J (2006) Magnetic nanoparticles for drug delivery. Drug Develop Res 67(1):55–60. doi:10.1002/Ddr.20067
Grief AD, Richardson G (2005) Mathematical modelling of magnetically targeted drug delivery. J Magn Magn Mater 293(1):455–463. doi:10.1016/j.jmmm.2005.02.040
Tzirtzilakis EE, Loukopoulos VC (2005) Biofluid flow in a channel under the action of a uniform localized magnetic field. Comput Mech 36(5):360–374. doi:10.1007/s00466-005-0659-4
Liu Y, Tan J, Thomas A, Ou-Yang D, Muzykantov VR (2012) The shape of things to come: importance of design in nanotechnology for drug delivery. Ther Deliv 3(2):181–194
Tan JF, Shah S, Thomas A, Ou-Yang HD, Liu YL (2013) The influence of size, shape and vessel geometry on nanoparticle distribution. Microfluid Nanofluid 14(1–2):77–87. doi:10.1007/s10404-012-1024-5
Shah S, Liu YL, Hu W, Gao JM (2011) Modeling particle shape-dependent dynamics in nanomedicine. J Nanosci Nanotechnol 11(2):919–928. doi:10.1166/jnn.2011.3536
Wong BS, Low YG, Xin W, Jee-Hou H, ChingSeong T, Jong Boon O (2010) 3D finite element simulation of magnetic particle inspection. In: IEEE Conference on sustainable utilization and development in engineering and technology (STUDENT) Nov 20–2, pp. 50–55. doi:10.1109/student.2010.5687008
Furlani EP, Sahoo Y, Ng KC, Wortman JC, Monk TE (2007) A model for predicting magnetic particle capture in a microfluidic bioseparator. Biomed Microdevices 9(4):451–463. doi:10.1007/s10544-007-9050-x
Furlani EP (2006) Analysis of particle transport in a magnetophoretic microsystem. J Appl Phys 99(2):Artn 024912. doi:10.1063/1.2164531
Forbes ZG, Yellen BB, Halverson DS, Fridman G, Barbee KA, Friedman G (2007) Validation of high gradient magnetic field based drug delivery to magnetizable implants under flow. IEEE Trans Bio-Med Eng 55(2):643–649. doi:10.1109/Tbme.899347
Gay M, Zhang LT (2009) Numerical studies of blood flow in healthy, stenosed, and stented carotid arteries. Int J Numer Methods Fluids 61(4):453–472. doi:10.1002/Fld.1966
Sensenig R, Sapir Y, MacDonald C, Cohen S, Polyak B (2012) Magnetic nanoparticle-based approaches to locally target therapy and enhance tissue regeneration in vivo. Nanomedicine 7(9):1425–1442. doi:10.2217/Nnm.12.109
Chorny M, Fishbein I, Alferiev I, Levy RJ (2009) Magnetically responsive biodegradable nanoparticles enhance adenoviral gene transfer in cultured smooth muscle and endothelial cells. Mol Pharm 6(5):1380–1387. doi:10.1021/Mp900017m
Polyak B, Fishbein I, Chorny M, Alferiev I, Williams D, Yellen B, Friedman G, Levy RJ (2008) High field gradient targeting of magnetic nanoparticle-loaded endothelial cells to the surfaces of steel stents. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 105(2):698–703. doi:10.1073/pnas.0708338105
Chorny M, Polyak B, Alferiev IS, Walsh K, Friedman G, Levy RJ (2007) Magnetically driven plasmid DNA delivery with biodegradable polymeric nanoparticles. FASEB J 21(10):2510–2519. doi:10.1096/fj.06-8070com
Chorny M, Fishbein I, Forbes S, Alferiev I (2011) Magnetic nanoparticles for targeted vascular delivery. IUBMB Life 63(8):613–620. doi:10.1002/Iub.00479
Forbes ZG, Fridman G, Yellen BB, Chomy M, Friedman G, Barbeel KA (2004) Locally targeted drug delivery to magnetic stents for therapeutic applications. IEEE/EMBS international summer school on medical devices and biosensors (ISSS-MD)
Liu Y, Yang J, Zhou Y, Hu J (2013) Structure design of vascular stents. In: Multiscale simulations and mechanics of biological materials. Wiley, pp. 301–317. doi:10.1002/9781118402955.ch16
Gay M, Zhang L, Liu WK (2006) Stent modeling using immersed finite element method. Comput Method Appl Mech Eng 195(33–36):4358–4370. doi:10.1016/j.cma.2005.09.012
Liu WK, Liu YL, Farrell D, Zhang L, Wang XS, Fukui Y, Patankar N, Zhang YJ, Bajaj C, Lee J, Hong JH, Chen XY, Hsu HY (2006) Immersed finite element method and its applications to biological systems. Comput Method Appl Mech Eng 195(13–16):1722–1749. doi:10.1016/j.cma.2005.05.049
Gay M, Zhang LT (2009) Numerical studies on fluid-structure interactions of stent deployment and stented arteries. Eng Comput 25(1):61–72. doi:10.1007/s00366-008-0105-2
Cutnell J, Kenneth J (1998) Density of blood. Physics. Wiley, New York
Erica M. Cherrya JKE (2013) Simulation of magnetic particles in the bloodstream for magnetic drug targeting applications. Eighth international conference on multiphase flow
Li SZ, Williams GD, Frisk TA, Arnold BW, Smith MB (1995) A computer-simulation of the static magnetic-field distribution in the human head. Magnet Reson Med 34(2):268–275. doi:10.1002/mrm.1910340219
Bhagwandien R (1994) Object Induced Geometry and Intensity Distortions in Magnetic Resonance Imaging: Met Een Samenvatting in Het Nederlands. Univerisiteit Utrecht, Faculteit Geneeskunde
Li SZ, Dardzinski BJ, Collins CM, Yang QX, Smith MB (1996) Three-dimensional mapping of the static magnetic field inside the human head. Magnet Reson Med 36(5):705–714. doi:10.1002/mrm.1910360509
Dames P, Gleich B, Flemmer A, Hajek K, Seidl N, Wiekhorst F, Eberbeck D, Bittmann I, Bergemann C, Weyh T, Trahms L, Rosenecker J, Rudolph C (2007) Targeted delivery of magnetic aerosol droplets to the lung. Nat Nanotechnol 2(8):495–499. doi:10.1038/nnano.2007.217
Alexandra Heidsieck BG (2010) Analysis of particle trajectories for magnetic drug targeting. COMSOL conference, Paris
Gleich B, Hellwig N, Bridell H, Jurgons R, Seliger C, Alexiou C, Wolf B, Weyh T (2007) Design and evaluation of magnetic fields for nanoparticle drug targeting in cancer. IEEE Trans Nanotechnol 6(2):164–170. doi:10.1109/Tnano.891829
Tan J, Wang S, Yang J, Liu Y (2013) Coupled particulate and continuum model for nanoparticle targeted delivery. Comput Struct 122:128–134. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.compstruc.2012.12.019
Liu YL, Guo QJ, Wang SQ, Hu W (2012) Electrokinetic effects on detection time of nanowire biosensor. Appl Phys Lett 100(15):Artn 153502. doi:10.1063/1.3701721
Tan JF, Thomas A, Liu YL (2012) Influence of red blood cells on nanoparticle targeted delivery in microcirculation. Soft Matter 8(6):1934–1946. doi:10.1039/C2sm06391c
Liu YL, Oh K, Bai JG, Chang CL, Yeo W, Chung JH, Lee KH, Liu WK (2008) Manipulation of nanoparticles and biomolecules by electric field and surface tension. Comput Method Appl Mech Eng 197(25–28):2156–2172. doi:10.1016/j.cma.2007.08.012
Wasilewski J, Mirota K, Peryt-Stawiarska S, Nowakowski A, Polonski L, Zembala M (2012) An introduction to computational fluid dynamics based on numerical simulation of pulsatile flow in the left coronary artery. Kardiochir Torakochi 9(3):366–374. doi:10.5114/kitp.2012.30851
Furlani EP, Ng KC (2006) Analytical model of magnetic nanoparticle transport and capture in the microvasculature. Phys Rev E 73(6):Artn 061919. doi:10.1103/Physreve.73.061919
Shire ES (1960) Classical electricity and magnetism. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge
Ravnik J, Hribersek M (2013) High gradient magnetic particle separation in viscous flows by 3D BEM. Comput Mech 51(4):465–474. doi:10.1007/s00466-012-0729-3
Zaremba LA (2003) Guidance for industry and FDA staff: criteria for significant risk investigations of magnetic resonance diagnostic devices. Center for Devices and Radiological Health
Petros RA, DeSimone JM (2010) Strategies in the design of nanoparticles for therapeutic applications. Nat Rev Drug Discov 9(8):615–627. doi:10.1038/Nrd2591
Wang J, Byrne JD, Napier ME, DeSimone JM (2011) More effective nanomedicines through particle design. Small 7(14):1919–1931. doi:10.1002/smll.201100442
Acknowledgments
The authors acknowledge the supports of this work from National Institute of Health (Grant EB015105) and National Science Foundation (Grant CBET-1113040, CBET-1067502).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
S. Wang and Y. Zhou contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, S., Zhou, Y., Tan, J. et al. Computational modeling of magnetic nanoparticle targeting to stent surface under high gradient field. Comput Mech 53, 403–412 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00466-013-0968-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00466-013-0968-y