Abstract
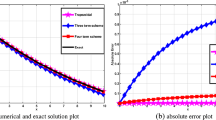
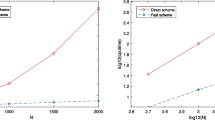
Differential Quadrature (DQ) is a numerical technique of high accuracy, but it is sensitive to grid distribution and requires that the number of grid points cannot be too large. These two requirements greatly restrict wider applications of DQ method. Through a simplified stability analysis in this paper, it is concluded that these two limitations are due to stability requirements. This analysis leads us to propose to localize differential quadrature to a small neighbourhood so as to keep the balance of accuracy and stability. The derivatives at a grid point are approximated by a weighted sum of the points in its neighbourhood rather than of all grid points. The method is applied to the one- and two-dimensional wave equations. Numerical examples show the present method produces very accurate results while maintaining good stability. The proposed method enables us to solve more complicated problems and enhance DQ's flexibility significantly.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Received: 23 October 2001 / Accepted: 3 July 2002
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zong, Z., Lam, K. A localized differential quadrature (LDQ) method and its application to the 2D wave equation. Computational Mechanics 29, 382–391 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00466-002-0349-4
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00466-002-0349-4