Abstract
Objective
To acquaint with the presentation and management of the cystic artery aneurysm by enriching the reviewed literature with our own experience.
Background
Cystic artery pseudoaneurysm is an uncommon entity with varied clinical presentation. Inflammation and trauma are associated with most of the cases. Limited experience with the condition challenges the management of individual cases.
Materials and methods
We retrieved all the reported cases of cystic artery pseudoaneurysm, published up to December 2019, from the PubMed database and excluded those arising as postoperative complications. A total of 59 cases were analyzed, and we also included our experience of managing a case of cystic artery pseudoaneurysm.
Results
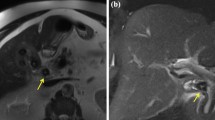
Abdominal pain (77.9%) was the most common presentation followed by upper GI bleed (64.4%), while 19 patients (32.2%) had presented with classic Quincke’s Triad. Most of the cases were diagnosed following the rupture of the pseudoaneurysm (n = 49, 83.05%). Fifteen patients presented with shock. Hyperbilirubinemia (59.3%) and anemia (55.9%) were the commonest laboratory findings. Although CT angiogram remains the investigation of choice, a conventional angiogram is the gold standard and sufficed as the definitive management in 20 cases. Cholecystectomy formed the definitive management in the rest of the cases. We successfully managed a middle-aged female patient of cystic artery aneurysm with xanthogranulomatous cholecystitis by open cholecystectomy.
Conclusion
Cystic artery pseudoaneurysms are amenable to successful management with careful evaluation and timely cholecystectomy or angioembolization or a combination of both.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Glaiberman CB, Darcy MD (2006) Embolisation of visceral arterial aneurysms. In: Golzarian J, Sun S, Sharafuddin MJ (eds) Vascular embolotherapy. Springer, Berlin, pp 99–116
Al’Aref SJ, Abdel-Rahman H, Hussain N (2008) Idiopathic cystic artery aneurysm complicated with hemobilia and acute pancreatitis. Hepatobiliary Pancreat Dis Int 7:547–550
Chadha M, Ahuja C (2009) Visceral artery aneurysms: diagnosis and percutaneous management. Semin Intervent Radiol 26(3):196–206
Fujimoto Y, Tomimaru Y, Hatano H, Noguchi K, Nagase H, Atsushi H et al (2018) Ruptured cystic artery pseudoaneurysm successfully treated with urgent cholecystectomy: a case report and literature review. Am J Case Rep 19:187–193
Kaman L, Kumar S, Behera A, Katariya RN (1998) Pseudoaneurysm of the cystic artery: a rare cause of hemobilia. Am J Gastroenterol 93(9):1535–1537
Proença AL, Gomes FV, Costa N, Bilhim T, Luz JH, Coimbra É (2020) Transarterial embolization of iatrogenic cystic artery pseudoaneurysm. GE Port J Gastroenterol 27(2):115–118
Anand U, Thakur SK, Kumar S, Jha A, Prakash V (2011) Idiopathic cystic artery aneurysm complicated with hemobilia. Annal Gastroenterol 24(2):134
Saluja S, Ray S, Gulati M, Pal S, Sahni P, Chattopadhyay TK (2007) Acute cholecystitis with massive upper gastrointestinal bleed: a case report and review of the literature. BMC Gastroenterol 7(1):12
Akatsu T, Tanabe M, Shimizu T et al (2007) Pseudoaneurysm of the cystic artery secondary to cholecystitis as a cause of hemobilia: report of a case. Surg Today 37(5):412–417
England RE, Marsh PJ, Ashleigh R, Martin DF (1998) Pseudoaneurysm of the cystic artery: a rare cause of hemobilia. Clin Radiol 53:72–75
Glaysher MA, Cruttenden-Wood D, Szentpali K (2014) A rare cause of upper gastrointestinal haemorrhage: ruptured cystic artery pseudoaneurysm with concurrent cholecystojejunal fistula. Int J Surg Case Rep 5:1–4
Chun KA, Ha HK, Yu ES, Shinn KS, Kim KW, Lee DH, Kang SW, Auh YH (1997) Xanthogranulomatous cholecystitis: CT features with emphasis on differentiation from gallbladder carcinoma. Radiology 203(1):93–97
Shimada K, Sakamoto Y, Esaki M, Kosuge T (2008) Pseudoaneurysm of the cystic artery associated with xanthogranulomatous cholecystitis. Dig Surg 25(1):8–9
Ahmed I, Tanveer UH, Sajjad Z, Munazza B, Azeem UD, Basit S (2010) Cystic artery pseudo-aneurysm: a complication of xanthogranulomatous cholecystitis. Br J Radiol 83(992):e165–e167
Siddiqui NA, Chawla T, Nadeem M (2011) Cystic artery pseudoaneurysm secondary to acute cholecystitis as a cause of hemobilia. BMJ Case Rep. https://doi.org/10.1136/bcr.07.2011.4480
Fung AK, Vosough A, Olson S, Aly EH, Binnie NR (2013) An unusual cause of acute internal haemorrhage: cystic artery pseudoaneurysm secondary to acute cholecystitis. Scott Med J 58(2):e23–e26
Muñoz-Villafranca C, García-Kamirruaga Í, Góme-García P, Atín-del-Campo V, Bárcena-Robredo V, Aguinaga-Alesanco A, Calderón-García Á (2015) Pseudoaneurysm of the cystic artery: an uncommon cause of upper gastrointestinal bleeding in a case of xanthogranulomatous cholecystitis. Rev Esp Enferm Dig 107(6):375
Lee JW, Kim MY, Kim YJ, Suh CH (2006) CT of acute lower GI bleeding in chronic cholecystitis: concomitant pseudoaneurysm of cystic artery and cholecystocolonic fistula. Clin Radiol 61(7):634–636
Sibulesky L, Ridlen M, Pricolo VE (2006) Hemobilia due to cystic artery pseudoaneurysm. Am J Surg 191:797–798
Joyce MR (2006) Pseudoaneurysm of the cystic artery: a diagnostic dilemma and rare cause of haemobilia. Ir J Med Sci 175:81
Lin C, Lee R, Chiang J, Wang K (2007) Pseudoaneurysm of the cystic artery in acalculouscholecystitis successfully treated by transcatheter arterial embolization: a case report. Chin J Radiol Taipei 32(1):41
Delgadillo X, Berney T, de Perrot M, Didier D, Morel P (1999) Successful treatment of a pseudoaneurysm of the cystic artery with microcoil embolization. JVIR 10(6):789
Thillai M, Sethi P, Menon RN, Kader NP (2017) Cystic artery psuedonaeurysm following acute necrotizing pancreatitis. BMJ Case Rep. https://doi.org/10.1136/bcr-2016-218891
Dewachter L, Dewaele T, Rosseel F, Cervits I, Aerts P (2012) Acute cholecystitis with pseudoaneurysm of the cystic artery. JBR-BTR 95:136–137
Tapnio RH, Kolber MK, Shukla PA, Berkowitz E (2017) Transcatheter embolization of cystic artery pseudoaneurysms secondary to acute cholecystitis. Vasc Endovasc Surg 51(7):498–500
Loizides S, Ali A, Newton R, Singh KK (2015) Laparoscopic management of a cystic artery pseudoaneurysm in a patient with calculus cholecystitis. Int J Surg Case Rep 14:182–185
Machida H, Ueno E, Shiozawa S, Fujimura M, Akira T, Kim D et al (2008) Unrupturedpseudoaneurysm of the cystic artery with acute calculouscholecystitis incidentally detected by computed tomography. Radiat Med 26(6):384–387
Alis D, Ferahman S, Demiryas S, Samanci C, Ustabasioglu FE (2016) Laparoscopic management of a very rare case: cystic artery pseudoaneurysm secondary to acute cholecystitis. Case Rep Surg 2016:1–3
Song SY (2010) Celiac axis and common hepatic variation in 5002 patients: systematic analysis with spiral CT and DSA. Radiology 255(278e):288
Suzuki M (2000) Laparoscopic cholecystectomy, Calot’s triangle and variations in cystic arterial supply. Surg Endosc 14:141–144
Nakajima M, Hoshino H, Hayashi E et al (1996) Pseudoaneurysm of the cystic artery associated with upper gastrointestinal bleeding. J Gastroenterol 31:750–754
She WH, Tsang S, Poon R, Cheung TT (2017) Gastrointestinal bleeding of obscured origin due to cystic artery pseudoaneurysm. Asian J Surg 40(4):320–323
Maeda A, Kunou T, Saeki S (2002) Pseudoaneurysm of the cystic artery with hemobilia treated by arterial embolization and elective cholecystectomy. J Hepatobiliary Pancreat Surg 9(6):755–758
Sunkara PRVPK, Shah PK, Rakshit K, Choudhary SR, Bohidar NP, Dubey SK (2018) Rupture of cystic artery pseudoaneurysm: a rare complication of acute cholecystitis. Indian J Surg 80(1):87–89
Ernst O, Bulois P, Saint-Drenant S, Leroy C, Paris JC, Sergent G (2003) Helical CT in acute lower gastrointestinal bleeding. Eur Radiol 13:114–117
Desai AU, Saunder MP, Anderson HJ, Howlett DC (2010) Successful transcatheter embolization of a cystic artery psuedoaneurysm secondary to calculus cholecystitis: a case report. J Radiol Case Rep 4(2):18–22
Kulkarni V, Deshmukh H, Gupta R (2014) Pseudoaneurysm of anomalous cystic artery due to calculous cholecystitis. BMJ Case Rep. https://doi.org/10.1136/bcr-2014-207069
Funding
No source of support.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Disclosures
The authors Viniyendra Pamecha, Nilesh Sadashiv Patil, Anubhav Pawar, Piyush Kumar Sinha, Nihar Mohapatra, Tharun Gattu, and Sanyam Falari have no conflict of interest or financial ties to disclose.
Ethical approval
Not applicable.
Informed consent
Written informed consent was obtained from the patient for publication of her clinical details and accompanying images.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Patil, N.S., Kumar, A.H., Pamecha, V. et al. Cystic artery pseudoaneurysm—a rare complication of acute cholecystitis: review of literature. Surg Endosc 36, 871–880 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00464-021-08796-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00464-021-08796-1