Abstract
Background
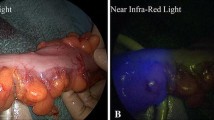
Although indocyanine green (ICG) fluorescence imaging has been reported to be useful for assessing colorectal perfusion, unstable quantification remains an issue. We performed ICG fluorescence observation from the luminal side and examined the usefulness of the transanal approach.
Methods
A total of 69 patients who underwent left-side colon surgery were enrolled in this cohort study. After the anastomosis had been constructed, ICG 0.2 mg/kg was injected intravenously. The anastomotic site was then observed by a scope inserted transanally. The following items were examined in the areas of the anastomotic site with the highest- and lowest-fluorescence intensity: maximum fluorescence (Fmax), time from ICG injection to Fmax (Tmax), time from start of dyeing to Fmax (ΔT), and the contrast pattern of the mucosa.
Results
Anastomotic leakage (AL) occurred in nine cases. Tmax and ΔT values of the lowest-fluorescence area in the distal intestine showed significant differences in the cases with AL (P = 0.015 and P = 0.040, respectively). Regarding the contrast pattern of the mucosa of the lowest-fluorescence area in the proximal and distal intestine, the patients in whom the vessels were not depicted in the area had a significantly higher incidence of AL than those in whom vessels were depicted in the area (P = 0.031 and P = 0.030, respectively). Some of the areas in which vessels were not depicted by ICG fluorescence observation from the luminal side corresponded to the points of leakage. There were heterogeneous changes that might not be grasped by observation from the serosal side.
Conclusion
Transanal ICG fluorescence imaging can evaluate perfusion over the entire circumference of the anastomosis in detail and aid in assessing the risk of AL. Therefore, the examination of the detailed low-perfusion area enables us to take measures for AL and to search for safer operative managements.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
National Cancer Center. Cancer Registry and Statistics. Tokyo, Japan. Available at: https://ganjoho.jp/en/professional/statistics/table_download.html. Accessed 6 Dec 2018
Ministry of Health, Labour and Welfare. Patient Survey, 2014. Tokyo, Japan. Available at: https://www.e-stat.go.jp/dbview?sid=0003128799. Accessed 6 Dec 2018
Mirnezami A, Mirnezami R, Chandrakumaran K, Sasapu K, Sagar P, Finan P (2011) Increased local recurrence and reduced survival from colorectal cancer following anastomotic leak: systematic review and meta-analysis. Ann Surg 253:890–899
Branagan G, Finnis D (2005) Prognosis after anastomotic leakage in colorectal surgery. Dis Colon Rectum 48:1021–1026
Kingham TP, Pachter HL (2009) Colonic anastomotic leak: risk factors, diagnosis, and treatment. J Am Coll Surg 208:269–278
Shiomi A, Ito M, Maeda K, Kinugasa Y, Ota M, Yamaue H, Shiozawa M, Horie H, Kuriu Y, Saito N (2015) Effects of a diverting stoma on symptomatic anastomotic leakage after low anterior resection for rectal cancer: a propensity score matching analysis of 1014 consecutive patients. J Am Coll Surg 220:186–194
Qu H, Liu Y, Bi DS (2015) Clinical risk factors for anastomotic leakage after laparoscopic anterior resection for rectal cancer: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Surg Endosc 29:3608–3617
Kang CY, Halabi WJ, Chaudhry OO, Nguyen V, Pigazzi A, Carmichael JC, Mills S, Stamos MJ (2013) Risk factors for anastomotic leakage after anterior resection for rectal cancer. JAMA Surg 148:65–71
Matsubara N, Miyata H, Gotoh M, Tomita N, Baba H, Kimura W, Nakagoe T, Simada M, Kitagawa Y, Sugihara K, Mori M (2014) Mortality after common rectal surgery in Japan: a study on low anterior resection from a newly established nationwide large-scale clinical database. Dis Colon Rectum 57:1075–1081
Kawada K, Sakai Y (2016) Preoperative, intraoperative and postoperative risk factors for anastomotic leakage after laparoscopic low anterior resection with double stapling technique anastomosis. World J Gastroenterol 22:5718–5727
Boni L, Fingerhut A, Marzorati A, Rausei S, Dionigi G, Cassinotti E (2017) Indocyanine green fluorescence angiography during laparoscopic low anterior resection: results of a case-matched study. Surg Endosc 31:1836–1840
Kim JC, Lee JL, Yoon YS, Alotaibi AM, Kim J (2016) Utility of indocyanine-green fluorescent imaging during robot-assisted sphincter-saving surgery on rectal cancer patients. Int J Med Robot Comput Assist Surg 12:710–717
Jafari MD, Lee KH, Halabi WJ, Mills SD, Carmichael JC, Stamos MJ, Pigazzi A (2013) The use of indocyanine green fluorescence to assess anastomotic perfusion during robotic assisted laparoscopic rectal surgery. Surg Endosc 27:3003–3008
Kudszus S, Roesel C, Schachtrupp A, Höer JJ (2010) Intraoperative laser fluorescence angiography in colorectal surgery: a noninvasive analysis to reduce the rate of anastomotic leakage. Langenbecks Arch Surg 395:1025–1030
Muto Y, Miyauchi H, Ohira G, Hayano K, Narushima K, Suzuki K, Matsubara H (2018) Evaluation of the anastomotic blood flow with near-infrared ICG fluorescence angiography with intraoperative transanal endoscopy to predict anastomotic leakage after colorectal surgery. Chiba Med J 94:25–31
Son YJ, Kim JE, Park SB, Lee SH, Chung YS, Yang HJ (2013) Quantitative analysis of intraoperative indocyanine green video angiography in aneurysm surgery. J Cerebrovasc Endovasc Neurosurg 15:76–84
Li H, Zhou J, Chi C, Mao Y, Yang F, Tian J, Wang J (2016) Clinical application of near-infrared thoracoscope with indocyanine green in video-assisted thoracoscopic bullectomy. J Thorac Dis 8:1841–1845
Paiella S, De Pastena M, Landoni L, Esposito A, Casetti L, Miotto M, Ramera M, Salvia R, Secchettin E, Bonamini D, Manzini G, D’Onofrio M, Marchegiani G, Bassi C (2017) Is there a role for near-infrared technology in laparoscopic resection of pancreatic neuroendocrine tumor? Results of the COLPAN “colour-and-resect the pancreas” study. Surg Endosc 31:4478–4484
Barnes TG, Penna M, Hompes R, Cunningham C (2017) Fluorescence to highlight the urethra: a human cadaveric study. Tech Coloproctol 21:439–444
Vignali A, Gianotti L, Braga M, Radaelli G, Malvezzi L, Di Carlo V (2000) Altered microperfusion at the rectal stump is predictive for rectal anastomotic leak. Dis Colon Rectum 43:76–82
Kologlu M, Yorganci K, Renda N, Sayek I (2000) Effect of local and remote ischemia-reperfusion injury on healing of colonic anastomoses. Surgery 128:99–104
Sheridan WG, Lowndes RH, Young HL (1987) Tissue oxygen tension as a predictor of colonic anastomotic healing. Dis Colon Rectum 30:867–871
Ris F, Liot E, Buchs NC, Kraus R, Ismael G, Belfontali V, Douissard J, Cunningham C, Lindsey I, Guy R, Jones O, George B, Morel P, Mortensen NJ, Hompes R, Cahill RA, Near-Infrared Anastomotic Perfusion Assessment Network VOIR (2018) Multicentre phase II trial of near-infrared imaging in elective colorectal surgery. Br J Surg 105(10):1359–1367
Wada T, Kawada K, Takahashi R, Yoshitomi M, Hida K, Hasegawa S, Sakai Y (2017) ICG fluorescence imaging for quantitative evaluation of colonic perfusion in laparoscopic colorectal surgery. Surg Endosc 31:4184
Son GM, Kwon MS, Kim Y, Kim J, Kim SH, Lee JW (2018) Quantitative analysis of colon perfusion pattern using indocyanine green (ICG) angiography in laparoscopic colorectal surgery. Surg Endosc 33(5):1640–1649
Kamiya K, Unno N, Miyazaki S, Sano M, Kikuchi H, Hiramatsu Y, Ohta M, Yamatodani T, Mineta H, Konno H (2015) Quantitative assessment of the free jejunal graft perfusion. J Surg Res 194:394–399
Sherwinter DA, Gallagher J, Donkar T (2013) Intra-operative transanal near infrared imaging of colorectal anastomotic perfusion: a feasibility study. Colorectal Dis 15:91–96
Acknowledgements
The authors thank Chiba Medical Journal for providing the figure data (Fig. 1). We thank Editage (www.editage.jp) for English language editing. This work was supported by JSPS KAKENHI Grant Number JP 18K16343.
Funding
This work was supported by JSPS KAKENHI Grant Number JP 18K16343.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Disclosure
Hiroyuki Amagai, Hideaki Miyauchi, Yorihiko Muto, Masaya Uesato, Gaku Ohira, Shunsuke Imanishi, Tetsuro Maruyama, Toru Tochigi, Koichiro Okada, Michihiro Maruyama, and Hisahiro Matsubara have no conflicts of interest or financial ties to disclose.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Amagai, H., Miyauchi, H., Muto, Y. et al. Clinical utility of transanal indocyanine green near-infrared fluorescence imaging for evaluation of colorectal anastomotic perfusion. Surg Endosc 34, 5283–5293 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00464-019-07315-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00464-019-07315-7