Abstract
Background
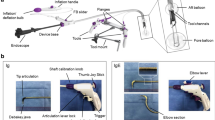
No reliable pure natural orifice transluminal endoscopic surgery (NOTES) mechanical counter traction (MCT) device for the flexible endoscope to obtain a sufficient surgical endoscopic field has yet been developed. Our experience with 10 cases of hybrid NOTES prompted the realization of the importance of an MCT device for the flexible endoscope and inspired us to establish innovative noninsufflation endoscopic full-thickness resection (EFTR) with an MCT device.
Methods
We performed 40 EFTR 40 mm in diameter on excised whole porcine stomachs. Twenty were resected by an MCT device to obtain a surgical field (MCT group), and another 20 were resected with a conventional endoscopic attachment (control group). We evaluated the successful resection rates of EFTR and procedure times between two groups. Next, we implemented EFTR with a custom prototype MCT device in three cases of stomach pseudotumors in female dogs. Gastric pseudotumors ~40 mm in diameter were marked within the open surgical field created by the MCT device. After resecting the pseudotumors, we conducted full-thickness suturing using over-the-scope clips.
Results
In the MCT group, all 20 cases were completely resected. On the other hand, in the control group, only 8 cases were performed via EFTR (P < 0.01). The mean ± standard deviation EFTR procedure times for the MCT and control groups were 4.13 ± 0.824 and 36.26 ± 8.67 min, respectively (P = 0.001). In three dogs, sufficient surgical working spaces were obtained up to 78 mm (range, 65–78 mm), and full-thickness resections were performed safely and sutured with over-the-scope clips.
Conclusions
Our new prototype MCT device effectively obtains a sufficient surgical endoscopic field during EFTR. We are developing a new MCT with a bending function to perform EFTR in any location in the stomach.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kalloo AN, Singh VK, Jagannath SB, Niiyama H, Hill SL, Vaughn CA, Magee CA, Kantsevoy SV (2004) Flexible transgastric peritoneoscopy: a novel approach to diagnostic and therapeutic interventions in the peritoneal cavity. Gastrointest Endosc 60(1):114–117
Autorino R, Haber GP, White MA (2010) Pure and hybrid natural orifice transluminal endoscopic surgery (NOTES): current clinical experience in urology. BJU Int 106:919–922
Voermans RP, van Berge Henegouwen MI, Bemelman WA (2011) Hybrid NOTES transgastric cholecystectomy with reliable gastric closure: an animal survival study. Surg Endosc 25:728–736
Kaouk JH, Haber GP, Goel RK (2010) Pure natural orifice translumenal endoscopic surgery (NOTES) transvaginal nephrectomy. Eur Urol 57:723–726
Isayama H, Kogure H, Koike K (2011) Endoscopic transgastric pure NOTES cholecystectomy with naso-gallbladder drainage tube placement and injection of a hyaluronic acid mixture (with video). J Hepatobiliary Pancreat Sci 18:106–111
Jeong SH, Lee YJ, Lee EH (2010) Gastric lymphatic basin dissection for sentinel node biopsy using hybrid natural orifice transluminal endoscopic surgery (NOTES). Minim Invasive Ther Allied Technol 19:299–303
Abe N, Takeuchi H, Yanagida O (2009) Endoscopic full-thickness resection with laparoscopic assistance as hybrid NOTES for gastric submucosal tumor. Surg Endosc 23:1908–1913
Isariyawongse JP, McGee MF, Rosen MJ (2008) Pure natural orifice transluminal endoscopic surgery (NOTES) nephrectomy using standard laparoscopic instruments in the porcine model. J Endourol 22:1087–1091
Mori H, Kobara H, Masaki T (2011) Establishment of pure NOTES procedure using a conventional flexible endoscope: review of six cases of gastric gastrointestinal stromal tumors. Endoscopy 43:631–634
Mori H, Kobara H, Masaki T (2012) New technique for safer endoscopic submucosal dissection using the duodenal balloon occlusion method. J Gastroenterol Hepatol 27:81–85
Nijhawan S, Barajas-Gamboa JS, Majid S, Jacobsen GR, Sedrak MF, Sandler BJ, Talamini MA, Horgan S (2012) NOTES transvaginal hybrid cholecystectomy: the United States human experience. Surg Endosc (Epub ahead of print). doi:10.1007/s00464-012-2470-6
Shinoda M, Makino A, Wada M (2010) Successful endoscopic submucosal dissection for mucosal cancer of the duodenum. Dig Endosc 22:49–52
Honda T, Yamamoto H, Osawa H (2009) Endoscopic submucosal dissection for superficial duodenal neoplasms. Dig Endosc 21:270–274
Takahashi T, Ando T, Kabeshima Y (2009) Borderline cases between benignancy and malignancy of the duodenum diagnosed successfully by endoscopic submucosal dissection. Scand J Gastroenterol 44:1377–1383
Bernhardt J, Köhler P, Rieber F (2012) Pure NOTES sigmoid resection in an animal survival model. Endoscopy 44:265–269
Hagen ME, Wagner OJ, Swain P (2008) Hybrid natural orifice transluminal endoscopic surgery (NOTES) for Roux-en-Y gastric bypass: an experimental surgical study in human cadavers. Endoscopy 40:918–924
Madan AK, Tichansky DS, Khan KA (2008) Natural orifice transluminal endoscopic gastric bypass performed in a cadaver. Obes Surg 18:1192–1199
Nau P, Anderson J, Happel L (2011) Safe alternative transgastric peritoneal access in humans: NOTES. Surgery 149:147–152
Ikeda K, Sumiyama K, Tajiri H (2011) Evaluation of a new multitasking platform for endoscopic full-thickness resection. Gastrointest Endosc 73:117–122
Dray X, Giday SA, Buscaglia JM (2009) Omentoplasty for gastrotomy closure after natural orifice transluminal endoscopic surgery procedures (with video). Gastrointest Endosc 70:131–140
Disclosures
Drs. Hirohito Mori, Kazi Rafiq, Hideki Kobara, Shintaro Fujihara, Noriko Nishiyama, Makoto Oryuu, Yasuyuki Suzuki, and Tsutomu Masaki have no conflicts of interest or financial ties to disclose.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Supplementary material 1 (WMV 17280 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mori, H., Rafiq, K., Kobara, H. et al. Innovative noninsufflation EFTR: sufficient endoscopic operative field by mechanical counter traction device. Surg Endosc 27, 3028–3034 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00464-013-2846-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00464-013-2846-2