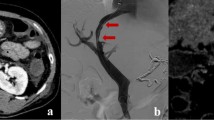
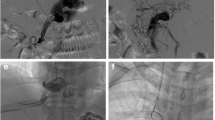
Abstract
Background
The aim of the present study was to compare elective transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt (TIPS) and laparoscopic splenectomy (LS) plus preoperative endoscopic varices ligation (EVL) in their efficacy in preventing recurrent bleeding and improving the long-term liver function in patients with liver cirrhosis and portal hypertension.
Methods
Between January 2009 and March 2012, we enrolled 83 patients (55 with TIPS, defined as the TIPS group, and 28 with LS plus preoperative EVL, defined as the LS group) with portal hypertension and a history of gastroesophageal variceal bleeding resulting from liver cirrhosis. The clinical characteristics, perioperative outcomes, and follow-up were recorded.
Results
No significant differences were observed between the two treatment groups with respect to the patients’ characteristics and preoperative variables. Within 30 days after surgery, one patient in the TIPS group died of multiple organ dysfunction syndrome, whereas no patient in the LS group died. Complications occurred in 14 patients in the TIPS group, which included rebleeding, encephalopathy, ascites, bleeding from a pseudoaneurysm of the thoracoabdominal aorta, and pulmonary infection, compared with 5 patients in the LS group, which included pulmonary effusion, pancreatic leakage, and portal vein thrombosis. During a mean follow-up of 13.6 months in the TIPS group and 12.3 months in the LS group, the actuarial survival was 85.5 % in the TIPS group versus 100 % in the LS group. The long-term complications included rebleeding and encephalopathy in the TIPS group.
Conclusions
LS plus EVL was superior to TIPS in the prevention of gastroesophageal variceal rebleeding in cirrhotic patients. This treatment was associated with a low rate of portosystemic encephalopathy and improvements in the long-term liver function.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bari K, Garcia-Tsao G (2012) Treatment of portal hypertension. World J Gastroenterol 18:1166–1175
Garcia-Pagán JC, Di Pascoli M, Caca K, Laleman W, Bureau C, Appenrodt B, Luca A, Zipprich A, Abraldes JG, Nevens F, Vinel JP, Sauerbruch T, Bosch J, Early TIPS (transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt) Cooperative Study Group (2010) Early use of TIPS In patients with cirrhosis and variceal bleeding. N Engl J Med 362:2370–2379
Jalan R, Hayes PC (2000) UK guidelines on the management of variceal haemorrhage in cirrhotic patients. Gut 46(suppl 3–4):III1–III15
Wong F, Blendis L (2000) An advance in the treatment of portal hypertension. Gastroenterology 118:802–803
Singh P, Pooran N, Indaram A, Bank S (2002) Combined ligation and sclerotherapy versus ligation alone for secondary prophylaxis of esophageal variceal bleeding: a meta-analysis. Am J Gastroenterol 97:623–629
Sahagun G, Benner KG, Saxon R, Barton RE, Rabkin J, Keller FS, Rosch J (1997) Outcome of 100 patients after transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt (TIPS) for variceal hemorrhage. Am J Gastroenterol 92:1444–1452
Boyer TD (2003) Transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt: current status. Gastroenterology 124:1700–1710
Colombato L (2007) The role of transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt (TIPS) in the management of portal hypertension. J Clin Gastroenterol 41(suppl 3):S344–S351
Rosemurgy AS, Frohman HA, Teta AF, Luberice K, Ross SB (2012) Prosthetic H-Graft Portacaval shunts vs transjugular intrahepatic portasystemic stent shunts: 18-year follow up of a randomized trial. J Am Coll Surg 214:445–455
Clark W, Hernandez J, McKeon B, Villadolid D, Al-Saadi S, Mullinax J, Ross SB, Rosemurgy AS 2nd (2010) Surgical shunting versus transjugular intrahepatic portasystemic shunting for bleeding varices resulting from portal hypertension and cirrhosis: a meta-analysis. Am Surg 76:857–864
Maleux G, Perez-Gutierrez NA, Evrard S, Mroue A, Le Moine O, Laleman W, Nevens F (2010) Covered stents are better than uncovered stents for transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunts in cirrhotic patients with refractory ascites: a retrospective cohort study. Acta Gastroenterol Belg 73:336–341
Punamiya S, Amarapurker DN (2011) Role of TIPS in improving survival of patients with decompensated liver disease. Intern J Hematol 2011:398291
Rössle M, Haag K, Ochs A, Sellinger M, Nöldge G, Perarnau JM, Berger E, Blum U, Gabelmann A, Hauenstein K et al (1994) The transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic stent-shunt procedure for variceal bleeding. N Engl J Med 330:165–171
Rosemurgy AS, Bloomston M, Clark WC, Thometz DP, Zervos EE (2005) H-graft portacaval shunts versus TIPS: ten-year follow-up of a randomized trial with comparison to predicted survivals. Ann Surg 241:238–246
Goykhman Y, Ben-Haim M, Rosen G, Carmiel-Haggai M, Oren R, Nakache R, Szold O, Klausner J, Kori I (2010) Transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt: current indications, patients selection and results. Isr Med Assoc J 12:687–691
Xiao T, Chen L, Chen W, Xu B, Long Q, Li R, Li L, Peng Z, Fang D, Wang R (2011) Comparison of transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt alone versus TIPS combined with embolotherapy in advanced cirrhosis: a retrospective study. J Clin Gastroenterol 45:643–650
Lunderquist A, Vang J (1974) Transhepatic catheterization and obliteration of the coronary vein in patients with portalhypertension and esophageal varices. N Engl J Med 291:646–649
Zhou Zhou J, Wu Z, Pankaj P, Peng B (2012) Long-term post-operative outcomes of hypersplenism: laparoscopic versus open splenectomy secondary to liver cirrhosis. Surg Endosc 26(12):3391–3400
Anegawa G, Kawanaka H, Uehara H, Akahoshi T, Konishi K, Yoshida D, Kinjo N, Hashimoto N, Tomikawa M, Hashizume M, Maehara Y (2009) Effect of laparoscopic splenectomy on portal hypertensive gastropathy in cirrhotic patients with portal hypertension. J Gastroenterol Hepatol 24:1554–1558
Rosemurgy AS, Serafini FM, Zweibel BR, Black TJ, Kudryk BT, Nord HJ, Goode SE (2000) Transjugular intrahepatic porto-systemic shunt versus small-diameter prosthetic H-graft portacaval shunt: extended follow-up of an expanded randomized prospective trial. J Gastrointest Surg 4:589–597
Ferenci P, Lockwood A, Mullen K, Tarter R, Weissenborn K, Blei AT (2002) Hepatic encephalopathy-definition, nomenclature, diagnosis, and quantification: final report of the working party at the 11th World Congresses of Gastroenterology, Vienna, 1998. Hepatology 3:716–721
Ripoll C, Groszmann R, Garcia-Tsao G, Grace N, Burroughs A, Planas R, Escorsell A, Garcia-Pagan JC, Makuch R, Patch D, Matloff DS, Bosch J (2007) Hepatic venous pressure gradient predictsclinical decompensation in patients with compensatedcirrhosis. Gastroenterology 133:481–488
Yoshida H, Mamada Y, Taniai N, Yamamoto K, Kawano Y, Mizuguchi Y, Shimizu T, Takahashi T, Tajiri T (2005) A randomized control trial of bimonthly versus biweekly endoscopic variceal ligation of esophageal varices. Am J Gastroenterol 100:2005–2009
Zhang CQ, Liu FL, Liang B, Xu HW, Xu L, Feng K, Liu ZC (2009) A modified percutaneous transhepatic varices embolization with 2-octyl cyanoacrylate in the treatment of bleeding esophageal varices. J Clin Gastroenterol 43:463–469
Cai YQ, Zhou J, Chen XD, Wang YC, Wu Z, Peng B (2011) Laparoscopic splenectomy is an effective and safe intervention for hypersplenism secondary to liver cirrhosis. Surg Endosc 25:3791–3797
Vangeli M, Patch D, Terreni N, Tibballs J, Watkinson A, Davies N, Burroughs AK (2004) Bleeding ectopic varices treatment with transjugular intrahepatic porto-systemic shunt (TIPS) and embolization. J Hepatol 41:560–566
Kochar N, Tripathi D, McAvoy NC, Ireland H, Redhead DN, Hayes PC (2008) Bleeding ectopic varices in cirrhosis: the role of transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic stent shunts. Aliment Pharmacol Ther 28:294–303
Papatheodoridis GV, Goulis J, Leandro G, Patch D, Burroughs AK (1999) Transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt compared with endoscopic treatment for prevention of variceal rebleeding: a meta-analysis. Hepatology 30:612–622
Cabrera J, Maynar M, Granados R, Gorriz E, Reyes R, Pulido-Duque JM, Rodriguez SanRoman JL, Guerra C, Kravetz D (1996) Transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt versus sclerotherapy in the elective treatment of variceal haemorrhage. Gastroenterology 110:832–839
Popovic P, Stabuc B, Skok P, Surlan M (2010) Transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt versus endoscopic clerotherapy in the elective treatment of recurrent variceal bleeding. J Intern Med Res 38:1121–1133
Arroyo V, Ginès P, Gerbes AL, Dudley FJ, Gentilini P, Laffi G, Reynolds TB, Ring-Larsen H, Schölmerich J (1996) Definition and diagnostic criteria of refractory ascites and hepatorenal syndrome in cirrhosis. International ascites club. Hepatology 23:164–176
Boyer TD, Haskal ZJ (2005) American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases Practice Guidelines: the role of transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt creation in the management of portal hypertension. J Vasc Interv Radiol 16:615–629
Angermayr B, Cejna M, Koenig F, Karnel F, Hackl F, Gangl A, Peck-Radosavljevic M (2003) Survival in patients undergoing transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt: ePTFE-covered stentgrafts versus bare stents. Hepatology 38:1043–1050
Cello JP, Ring EJ, Olcott EW, Koch J, Gordon R, Sandhu J, Morgan DR, Ostroff JW, Rockey DC, Bacchetti P, LaBerge J, Lake JR, Somberg K, Doherty C, Davila M, McQuaid K, Wall SD (1997) Endoscopic sclerotherapy compared with percutaneous transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt after initial sclerotherapy in patients with acute variceal haemorrhage. A randomized controlled trial. Ann Intern Med 126:858–865
Sauer P, Theilmann L, Stremmel W, Benz C, Richter GM, Stiehl A (1997) Transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt versus sclerotherapy plus propranolol for variceal rebleeding. Gastroenterology 113:1623–1631
Garcia-Tsao G, Sanyal AJ, Grace ND, Carey WD (2007) Prevention and management of gastroesophageal varices and variceal hemorrhage in cirrhosis. Am J Gastroenterol 102:2086–2102
Rössle M, Deibert P, Haag K, Ochs A, Olschewski M, Siegerstetter V, Hauenstein KH, Geiger R, Stiepak C, Keller W, Blum HE (1997) Randomised trial of transjugular-intrahepatic-portosystemic shunt versus endoscopy plus propranolol for the prevention of variceal rebleeding. Lancet 349:1043–1049
Blei IA, Coradoba J (2001) Hepatic encephalopathy. Am J Gastroenterol 96:1968–1976
Bai M, Qi X, Yang Z, Yin Z, Nie Y, Yuan S, Wu K, Han G, Fan D (2011) Predictors of hepatic encephalopathy after transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt in cirrhotic patients: a systematic review. J Gastroenterol Hepatol 26:943–951
Wu Z, Zhou J, Prsoon P, Peng B (2012) Comparative treatment and literature review for laparoscopic splenectomy alone versus preoperative splenic artery embolization splenectomy. Surg Endosc 26(10):2758–2766
Ikeda M, Sekimoto M, Takiguchi S, Yasui M, Danno K, Fujie Y, Kitani K, Seki Y, Hata T, Shingai T, Takemasa I, Ikenaga M, Yamamoto H, Ohue M, Monden M (2007) Total splenic vein thrombosis after laparoscopic splenectomy: a possible candidate for treatment. Am J Surg 193:21–25
Disclosures
Drs. Bing Peng, Zhong Wu, Jin Zhou, and Junchao Wu have no conflicts of interest or financial ties to disclose.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Drs. Jin Zhou and Zhong Wu contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhou, J., Wu, Z., Wu, J. et al. Transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt (TIPS) versus laparoscopic splenectomy (LS) plus preoperative endoscopic varices ligation (EVL) in the treatment of recurrent variceal bleeding. Surg Endosc 27, 2712–2720 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00464-013-2810-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00464-013-2810-1