Abstract
Background
Postoperative pain is the dominant complaint and the most common cause of delayed discharge after laparoscopic cholecystectomy. The aim of this study is to evaluate the potential of preoperative administration of pregabalin to reduce postoperative pain and opioid consumption.
Methods
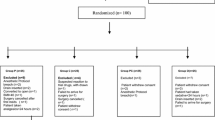
Fifty American Society of Anesthesiologists (ASA) I and II adult patients with symptomatic gallstone disease scheduled for elective laparoscopic cholecystectomy were randomized into two groups: group I patients (n = 25) were given 600 mg pregabalin per os divided in two doses, the night before surgery and 1 h preoperatively, respectively, while group II patients (n = 25) received a matching to pregabalin placebo at the same scheme. Postoperative pain, morphine consumption, and complications were compared between the two groups.
Results
Postoperative pain (static and dynamic assessment) was significantly less at 0, 1, 8, 16, and 24 h (p < 0.001) after the procedure for group I (pregabalin) compared with the placebo group. Postoperative patient-controlled morphine consumption during hospital stay was also significantly less in the pregabalin group compared with the placebo group. Side-effects were similar in both groups expect for dizziness, which was significantly higher (p < 0.0001) in the pregabalin group.
Conclusions
Administration of 600 mg pregabalin per os, divided in two preoperative doses, significantly reduces postoperative pain as well as opioid consumption in patients undergoing laparoscopic cholecystectomy, at the cost of increased incidence of dizziness.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bisgaard T (2006) Analgesic treatment after laparoscopic cholecystectomy. A critical assessment of the evidence. Anesthesiology 104:835–846
Bisgaard T, Kehlet H, Rosenberg J (2001) Pain and convalescence after laparoscopic cholecystectomy. Eur J Surg 167:84–96
Gajraj NM (2007) Pregabalin: its pharmacology and use in pain management. Anesth Analg 105:1805–1815
Abhishek B, Anurag T, Shuchit AlkaG (2009) Pregabalin: pharmacology and use in pain management. J Anaesth Clin Pharmacol 25:321–326
Guay DR (2005) Pregabalin in neuropathic pain: a more ‘pharmaceutically elegant’ gabapentin? Am J Geriatr Pharmacother 3:274–287
Przesmycki K, Wiater-Kozioł E, Kotarski J, Czuczwar M, Jaskowiak R et al (2011) Effect of pre-emptive pregabalin on pain intensity and morphine requirement after hysterectomy. Anestezjol Intens Ter 43:14–17
Gianesello L, Pavoni V, Barboni E, Galeotti I, Nella A (2011) Perioperative pregabalin for postoperative pain control and quality of life after major spinal surgery. J Neurosurg Anesthesiol 24(2):121–126
Gonano C, Latzke D, Sabeti-Aschraf M, Kettner SC, Chiari A, Gustorff B (2011) The anxiolytic effect of pregabalin in outpatients undergoing minor orthopaedic surgery. J Psychopharmacol 25:249–253
Jokela R, Ahonen J, Tallgren M, Haanpää M, Korttila K (2008) A randomized controlled trial of perioperative administration of pregabalin for pain after laparoscopic hysterectomy. Pain 134:106–112
White PF, Tufanogullari B, Taylor J, Klein K (2009) The effect of pregablin on preoperative anxiety and sedation levels: a dose ranging study. Anesth Analg 108:1140–1145
Chang SH, Lee HW, Kim SH, Kim DK (2009) An evaluation of perioperative pregabalin for prevention and attenuation of postoperative shoulder pain after laparoscopic cholecystectomy. Anesth Analg 109:1284–1286
Mathiesen O, Rasmussen ML, Dierking G, Lech K, Hilsted KL, Fomsgaard JS et al (2009) Pregabalin and dexamethasone in combination with paracetamol for postoperative pain control after abdominal hysterectomy. A randomized clinical trial. Acta Anaesthesiol Scand 53:227–235
Paech MJ, Goy R et al (2007) A randomized, placebo-controlled trial of preoperative oral pregabalin for postoperative pain relief after minor gynecological surgery. Anesth Analg 105:1449–1453
Balaban F, Yağar S, Özgök A, Koç M (2012) Güllapoğlu H. A randomized, placebo-controlled study of pregabalin for postoperative pain intensity after laparoscopic cholecystectomy J Clin Anesth 24:175–178
Pesonen A, Suojaranta-Ylinen R (2011) Hammare‘n E, Kontinen V.K., Raivio P, et al. Pregabalin has an opioid-sparing effect in elderly patients after cardiac surgery: a randomized placebo-controlled trial. Br J Anaesth 106:873–881
Kim SY, Jeong JJ, Chung WY, Kim HJ, Nam KH, Shim YH (2010) Perioperative administration of pregabalin for pain after robot-assisted endoscopic thyroidectomy: a randomized clinical trial. Surg Endosc 24:2776–2781
Schulmeyer MC, Maza J, Ovalle C, Farias CI (2009) Analgesic effects of a single preoperative dose of pregabalin after laparoscopic sleeve gastrectomy. Οbes Surg 20:168–1678
Ittichaikulthol W et al (2009) Effects of pregabalin on post operative morphine consumption and pain after abdominal hysterectomy with/without salphingo-oophorectomy: a randomized, double-blind trial. J Med Assoc Thai 92:1318–1323
Agarwal A, Gautam S, Gupta D, Agarwal S, Singh PK, Singh U (2008) Evaluation of a single preoperative dose of pregabalin for attenuation of postoperative pain after laparoscopic cholecystectomy. Br J Anaesth 101:700–704
Freedman BM, O’Hara E (2008) Pregabalin has opioid sparing-effects following augmentation mammaplasty. Aesthet Surg J 28:421–424
Peng PW, Li C, Farcas E, Haley A, Wong W, Bender J, Chung F (2010) Use of low-dose pregabalin in patients undergoing laparoscopic cholecystectomy. Br J Anaesth 105:155–161
Jokela R, Ahonen J, Tallgren M, Haanpaa M, Korttila K (2008) A randomized controlled trial of perioperative administration of pregabalin for pain after laparoscopic hysterectomy. Pain 134:106–112
Jokela R, Ahonen J, Tallgren M, Haanpa M, Korttila K (2008) Premedication with pregabalin 75 or 150 mg with ibuprofen to control pain after day-case gynaecological laparoscopic surgery. Br J Anaesth 100:834–840
Mathiesen O, Jacobsen LS, Holm HE, Randall S, Adamiec-Malmstroem L, Graungaard BK, Holst PE, Hilsted KL, Dahl JB (2008) Pregabalin and dexamethasone for postoperative pain control: a randomized controlled study in hip arthroplasty. Br J Anaesth 101:535–541
Trabulsi EJ, Patel J, Viscusi ER, Gomella LG, Lallas C (2010) Preemptive multimodal pain regimen reduces opioid analgesia for patients undergoing robotic-assisted laparoscopic radical prostatectomy. Urology 76:1122–1124
Gilron I (2007) Gabapentin and pregabalin for chronic neuropathic and early postsurgical pain: current evidence and future directions. Curr Opin Anaesthesiol 20:456–472
Kindler CH, Harms C, Amsler F, Scholl T, Scheidegger D (2000) The visual analog scale allows effective measurement of preoperative anxiety and detection of patients’ anesthetic concerns. Anesth Analg 90:706–712
Zhang J, Ho K-Y, Wang Y (2011) Efficacy of pregabalin in acute postoperative pain: a meta-analysis. Br J Anaesth 106:454–462
Romundstad L, Breivik H, Roald H et al (2006) Methylprednisolone reduces pain, emesis, and fatigue after breast augmentation surgery: a single-dose, randomized, parallel-group study with methylprednisolone 125 mg, parecoxib 40 mg, and placebo. Anesth Analg 102:418–425
Bisgaard T, Klarskov B, Rosenberg J, Kehlet H (2001) Characteristics and prediction of early pain after laparoscopic cholecystectomy. Pain 90:261–269
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sarakatsianou, C., Theodorou, E., Georgopoulou, S. et al. Effect of pre-emptive pregabalin on pain intensity and postoperative morphine consumption after laparoscopic cholecystectomy. Surg Endosc 27, 2504–2511 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00464-012-2769-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00464-012-2769-3