Abstract
Background
The newest trend in the field of thoracic surgery, thoracic natural orifice transluminal endoscopic surgery (NOTES), is still in the early stages of development and limited to animal experiments. Transumbilical endoscopic surgery could work as a viable intermediate step before pure NOTES. We describe our experiences performing transumbilical–diaphragmatic thoracic sympathectomy with an ultrathin flexible endoscope for palmar and axillary hyperhidrosis in human patients.
Methods
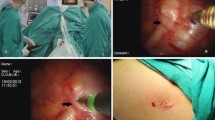
From April 2010 to January 2012, a total of 38 patients underwent transumbilical–diaphragmatic thoracic sympathectomy. Through the incision in the umbilicus, a newly developed long trocar was inserted into the abdominal cavity. An ultrathin endoscope was introduced through the long trocar and then passed through the rigid incision made in the left and right diaphragm and into the thoracic cavity. The ganglion was ablated at the desired thoracic level.
Results
Sympathectomy was performed successfully in all patients. Mean operation time was 68 ± 16 (range, 48–107) minutes. There was no mortality and no conversion to open surgery during the operation of any patient. At a median follow-up of 11 (range, 4–12) months after surgery, no diaphragmatic hernia was observed. The rate of palmar hyperhidrosis and axillary hyperhidrosis resolution was 100 and 75 %, respectively.
Conclusions
Transumbilical endoscopic thoracic sympathectomy is technically feasible and safe, which has the possible advantages of pure NOTES and can be performed in routine clinical practice.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Krasna MJ (2008) Thoracoscopic sympathectomy: a standardized approach to therapy for hyperhidrosis. Ann Thorac Surg 85:764–767
Cerfolio RJ, De Campos JR, Bryant AS, Connery CP, Miller DL, DeCamp MM, McKenna RJ, Krasna MJ (2011) The Society of Thoracic Surgeons expert consensus for the surgical treatment of hyperhidrosis. Ann Thorac Surg 91:1642–1648
Turner BG, Gee DW, Cizginer S, Konuk Y, Karaca C, Willingham F, Mino-Kenudson M, Morse C, Rattner DW, Brugge WR (2010) Feasibility of endoscopic transesophageal thoracic sympathectomy. Gastrointest Endosc 71:171–175
Lima E, Henriques-Coelho T, Rolanda C, Pêgo JM, Silva D, Carvalho JL, Correia-Pinto J (2007) Transvesical thoracoscopy: a natural orifice translumenal endoscopic approach for thoracic surgery. Surg Endosc 21:854–858
Fritscher-Ravens A, Patel K, Ghanbari A, Kahle E, von Herbay A, Fritscher T, Niemann H, Koehler P (2007) Natural orifice transluminal endoscopic surgery (NOTES) in the mediastinum: long-term survival animal experiments in transesophageal access, including minor surgical procedures. Endoscopy 39:870–875
Liu YH, Liu HP, Wu YC, Ko PJ (2010) Feasibility of transtracheal thoracoscopy (natural orifice transluminal endoscopic surgery). J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg 139:1349–1350
Fritscher-Ravens A, Cuming T, Olagbaiye F, Holland C, Milla P, Seehusen F, Hadeler KG, Arlt A, Mannur K (2011) Endoscopic transesophageal vs thoracoscopic removal of mediastinal lymph nodes: a prospective randomized trial in a long term animal survival model. Endoscopy 43:1090–1096
Rolanda C, Silva D, Branco C, Moreira I, Macedo G, Correia-Pinto J (2011) Peroral esophageal segmentectomy and anastomosis with single transthoracic trocar: a step forward in thoracic NOTES. Endoscopy 43:14–20
Ko PJ, Chu Y, Wu YC, Liu CY, Hsieh MJ, Chen TP, Chao YK, Wu CY, Yuan HC, Liu YH, Liu HP (2012) Feasibility of endoscopic transoral thoracic surgical lung biopsy and pericardial window creation. J Surg Res 175:207–214
Desai MM, Stein R, Rao P, Canes D, Aron M, Rao PP, Haber GP, Fergany A, Kaouk J, Gill IS (2009) Embryonic natural orifice transumbilical endoscopic surgery (E-NOTES) for advanced reconstruction: initial experience. Urology 73:182–187
Sohn DK, Jeong SY, Park JW, Kim JS, Hwang JH, Kim DW, Kang SB, Oh JH (2011) Comparative study of NOTES rectosigmoidectomy in a swine model: E-NOTES vs P-NOTES. Endoscopy 43:526–532
Chang S, Tan S, Kok YO (2012) Early experience in single-site laparoscopic cholecystectomy. Singapore Med J 53:377–380
Liu YH, Liu HP, Wu YC, Ko PJ (2010) Feasibility of transtracheal surgical lung biopsy in a canine animal model. Eur J Cardiothorac Surg 37:1235–1236
Moreira-Pinto J, Ferreira A, Miranda A, Rolanda C, Correia-Pinto J (2012) Transesophageal pulmonary lobectomy with single transthoracic port assistance: study with survival assessment in a porcine model. Endoscopy 44:354–361
De Palma GD, Siciliano S, Addeo P, Salvatori F, Persico M, Masone S, Rega M, Maione F, Coppola Bottazzi E, Serrao E, Adamo M, Persico G (2010) A NOTES approach for thoracic surgery: transgastric thoracoscopy via a diaphragmatic incision in a survival porcine model. Minerva Chir 65:11–15
Rao PP, Rao PP, Bhagwat S (2011) Single-incision laparoscopic surgery—current status and controversies. J Minim Access Surg 7:6–16
Zornig C, Mofid H, Siemssen L, Emmermann A, Alm M, von Waldenfels HA, Felixmüller C (2009) Transvaginal NOTES hybrid cholecystectomy: feasibility results in 68 cases with mid-term follow-up. Endoscopy 41:391–394
Hassan AM, Hedaya MS, Nasr MM, Nafeh AI, Elsebae MM (2011) Single incision tans-umbilical laparoscopic cholecystectomy using conventional laparoscopic instruments: initial experience of single institute. J Egypt Soc Parasitol 41:675–684
Linke GR, Tarantino I, Hoetzel R, Warschkow R, Lange J, Lachat R, Zerz A (2010) Transvaginal rigid-hybrid NOTES cholecystectomy: evaluation in routine clinical practice. Endoscopy 42:571–575
Noguera JF, Dolz C, Cuadrado A, Olea J, García J (in press) Flexible single-incision surgery: a fusion technique. Surg Innov
Goh PM, Cheah WK, De Costa M, Sim EK (2000) Needlescopic thoracic sympathectomy: treatment for palmar hyperhidrosis. Ann Thorac Surg 70:240–242
Rodríguez PM, Freixinet JL, Hussein M, Valencia JM, Gil RM, Herrero J, Caballero-Hidalgo A (2008) Side effects, complications and outcome of thoracoscopic sympathectomy for palmar and axillary hyperhidrosis in 406 patients. Eur J Cardiothorac Surg 34:514–519
Liu Y, Yang J, Liu J, Yang F, Jiang G, Li J, Huang Y, Wang J (2009) Surgical treatment of primary palmar hyperhidrosis: a prospective randomized study comparing T3 and T4 sympathicotomy. Eur J Cardiothorac Surg 35:398–402
Lesèche G, Castier Y, Thabut G, Petit MD, Combes M, Cerceau O, Besnard M (2003) Endoscopic transthoracic sympathectomy for upper limb hyperhidrosis: limited sympathectomy does not reduce postoperative compensatory sweating. J Vasc Surg 37:124–128
Lyra Rde M, Campos JR, Kang DW, Loureiro Mde P, Furian MB, Costa MG, Coelho Mde S (2008) Guidelines for the prevention, diagnosis and treatment of compensatory hyperhidrosis. J Bras Pneumol 34:967–977
Sugimura H, Spratt EH, Compeau CG, Kattail D, Shargall Y (2009) Thoracoscopic sympathetic clipping for hyperhidrosis: longterm results and reversibility. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg 137:1376–1377
Krasna MJ (2011) The role of surgical treatment of hyperhidrosis. Mayo Clin Proc 86:717–718
Gossot D, Galetta D, Pascal A, Debrosse D, Caliandro R, Girard P, Stern JB, Grunenwald D (2003) Long-term results of endoscopic thoracic sympathectomy for upper limb hyperhidrosis. Ann Thorac Surg 75:1075–1079
Yazbek G, Wolosker N, de Campos JR, Kauffman P, Ishy A, Puech-Leão P (2005) Palmar hyperhidrosis—which is the best level of denervation using video-assisted thoracoscopic sympathectomy? T2 or T3 ganglion? J Vasc Surg 42:281–285
Acknowledgments
Supported in part by the Key Project of Science and Technology of Fujian Province (Grant 2010I0011). The authors thank Professor Philip Wai Yan Chiu (Department of Surgery, Prince of Wales Hospital, Chinese University of Hong Kong) for his critical review.
Disclosures
Li-Huan Zhu, Wen Wang, Shengsheng Yang, Dazhou Li, Zhijian Zhang, Shengping Chen, Xianjin Cheng, Long Chen, and Weisheng Chen have no conflicts of interest or financial ties to disclose.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Li-Huan Zhu and Wen Wang contributed equally to this study, and both should be considered first author.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhu, LH., Wang, W., Yang, S. et al. Transumbilical thoracic sympathectomy with an ultrathin flexible endoscope in a series of 38 patients. Surg Endosc 27, 2149–2155 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00464-012-2732-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00464-012-2732-3