Abstract
Background
The key to successful rectal cancer resection is to perform complete total mesorectal excision (TME). Laparoscopic TME can be challenging, especially in the narrow confines of the pelvis. Robotic-assisted surgery can overcome these limitations through superior three-dimensional (3-D) visualization and the increased range of movements provided by the endowrist function. To date, all totally robotic resections of the rectum have been described using da Vinci® S or Si systems. Due to the limitations of the standard system, only hybrid procedures have been described so far.
Aim
To evaluate the feasibility and short-term outcomes of performing totally robotic-assisted laparoscopic colorectal resections using the standard da Vinci® system with a fourth arm extension.
Methods
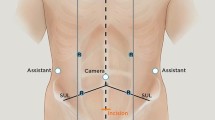
The standard system was docked from the patient’s left hip. Four 8-mm robotic trocars were inserted. Upon completion of phase 1 (pedicle ligation, colonic mobilization, splenic flexure takedown), the two left-sided arms are repositioned to allow phase 2 (pelvic dissection), enabling the entire procedure except for the distal transection and anastomosis to be performed robotically.
Results
Twenty-one robotic procedures were performed from August 2008 to September 2009. The mean age of the patients was 61 years (13 males). The procedures performed included seven anterior resections, seven low anterior resections, five ultralow anterior resections, one abdominoperineal resection, and one resection rectopexy. The majority of the cases were performed in patients with colon or rectal cancer. Operative time ranged from 232 to 444 (mean 316) min. Postoperative morbidity occurred in three patients (14.3%) with no mortalities or conversions. Average hospital stay was 6.4 days. Mean lymph node yield for the cases with cancer was 17.8.
Conclusions
The standard da Vinci® system with four arms can be used to perform totally robotic-assisted colorectal procedures for the left colon and rectum with short-term outcomes similar to those of conventional laparoscopic techniques.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Nagtegaal ID, Quirke P (2008) What is the role for the circumferential margin in the modern treatment of rectal cancer? J Clin Oncol 26(2):303–312
Breukink S, Piere J, Wiggers T (2006) Laparoscopic versus open total mesorectal excision for rectal cancer. Cochrane Database Syst Rev 18(4):CD005200
Weiser MR, Milsom JW (2000) Laparoscopic total mesorectal excision with autonomic nerve preservation. Semin Surg Oncol 19(4):396–403
Tsang WWC, Chung CC, Kwok SY, Li MKW (2005) Minimally invasive surgery for rectal cancer. Surg Clin North Am 85:61–73
Patriti A, Ceccarelli G, Bartoli A, Spaziani A, Lapalorcia LM, Casciola L (2009) Laparoscopic and robot-assisted one-stage resection of colorectal cancer with synchronous liver metastases: a pilot study. J Hepatobiliary Pancreat Surg 16(4):450–457
Pigazzi A, Ellenhorn JD, Ballantyne GH, Paz IB (2006) Robotic-assisted laparoscopic low anterior resection with total mesorectal excision for rectal cancer. Surg Endosc 20(10):1521–1525
Baik SH, Ko YT, Kang CM, Lee WJ, Kim NK, Sohn SK, Chi HS, Cho CH (2008) Robotic tumor-specific mesorectal excision of rectal cancer: short-term outcome of a pilot randomized trial. Surg Endosc 22(7):1601–1608
DeNoto G, Rubach E, Ravikumar TS (2006) A standardized technique for robotically performed sigmoid colectomy. J Laparoendosc Adv Surg Tech A 16(6):551–556
Hellan M, Stein H, Pigazzi A (2009) Totally robotic low anterior resection with total mesorectal excision and splenic flexure mobilization. Surg Endosc 23:447–451
Choi DJ, Kim SH, Lee PJ, Kim J, Woo SU (2009) Single-stage totally robotic dissection for rectal cancer surgery: technique and short-term outcome in 50 consecutive patients. Dis Colon Rectum 52(11):1824–1830
Baik SH, Lee WJ, Rha KH, Kim NK, Sohn SK, Chi HS, Cho CH, Lee SK, Cheon JH, Ahn JB, Kim WH (2008) Robotic total mesorectal excision for rectal cancer using four robotic arms. Surg Endosc 22(3):792–797
Luca F, Cenciarelli S, Valvo M, Pozzi S, Faso FL, Ravizza D, Zampino G, Sonzogni A, Biffi R (2009) Full robotic left colon and rectal cancer resection: technique and early outcome. Ann Surg Oncol 16(5):1274–1278
Acknowledgements
The authors wish to thank Ms Sunitha Nair for her assistance in data management and analysis.
Disclosures
Dean Chi-Siong Koh, Charles Bih-Shou Tsang and Seon-Hahn Kim have no conflicts of interest or financial ties to disclosure.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Koh, D.CS., Tsang, C.BS. & Kim, SH. A new application of the four-arm standard da Vinci® surgical system: totally robotic-assisted left-sided colon or rectal resection. Surg Endosc 25, 1945–1952 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00464-010-1492-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00464-010-1492-1