Abstract
Background and objectives
Laparoscopic surgery in pregnancy remains debated, especially in cases of suspected appendicitis. Cases of suspected appendicitis treated by the laparoscopic approach in a single institution over a 10-year period were reviewed (1997–2007). The objectives were to evaluate the immediate complications of the procedure and the outcome of pregnancies including foetal loss and preterm delivery.
Results
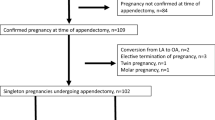
Retrospective analysis of 45 consecutive cases of suspected appendicitis during pregnancy was carried out. Forty-two patients (93%) had a preoperative ultrasound, of which 13 (33%) confirmed an acute appendicitis. Out of 45 cases, 15 (33%) had the surgical procedure during the first trimester, 22 (49%) in the second and 8 (18%) in the third. Two (4%) patients had major complications (intra-abdominal abscess and uterine perforation) and two others (4%) had minor complications (cystitis and ileus). No patients underwent delivery in the month following surgery and there was no foetal loss in the follow-up. Three (8.1%) patients delivered prior to 35 weeks’ gestation and 18.1% delivered before term (<37 weeks). As previously reported, a high rate of normal appendix (33%) was found at surgery. No significant differences were found in rates of preterm delivery, adverse outcome or operative time between trimesters of pregnancy at the time of surgery. Mean operative time was 49 ± 19 min.
Discussion
This large series from a single institution shows a low rate of preterm delivery and absence of foetal loss after laparoscopic appendectomy. Regardless of trimester, the low rate of complication makes it a valuable option for pregnant patients with suspicion of acute appendicitis. The rate of normal appendectomies remaining high, efforts have to be made towards new diagnostic modalities to lower the negative appendectomy rate in this specific population.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Mazze RI, Kallen B (1991) Appendectomy during pregnancy: a Swedish registry study of 778 cases. Obstet Gynecol 77(6):835–840
Wu JM, Chen KH, Lin HF, Tseng LM, Tseng SH, Huang SH (2005) Laparoscopic appendectomy in pregnancy. J Laparoendosc Adv Surg Tech A 15(5):447–450
de Perrot M, Jenny A, Morales M, Kohlik M, Morel P (2000) Laparoscopic appendectomy during pregnancy. Surg Laparosc Endosc Percutan Tech 10(6):368–371
Halkic N, Tempia-Caliera AA, Ksontini R, Suter M, Delaloye JF, Vuilleumier H (2006) Laparoscopic management of appendicitis and symptomatic cholelithiasis during pregnancy. Langenbecks Arch Surg 391(5):467–471; Epub 2006 Aug 15
Moreno-Sanz C, Pascual-Pedreño A, Picazo-Yeste JS, Seoane-Gonzalez JB (2007) Laparoscopic appendectomy during pregnancy: between personal experiences and scientific evidence. J Am Coll Surg 205(1):37–42
Palanivelu C, Rangarajan M, Parthasarathi R (2006) Laparoscopic appendectomy in pregnancy: a case series of seven patients. JSLS 10(3):321–325
Affleck DG, Handrahan DL, Egger MJ, Price RR (1999) The laparoscopic management of appendicitis and cholelithiasis during pregnancy. Am J Surg 178(6):523–529
Rollins MD, Chan KJ, Price RR (2004) Laparoscopy for appendicitis and cholelithiasis during pregnancy: a new standard of care. Surg Endosc 18(2):237–241; Epub 2003 Dec 29
Reedy MB, Källén B, Kuehl TJ (1997) Laparoscopy during pregnancy: a study of five fetal outcome parameters with use of the Swedish Health Registry. Am J Obstet Gynecol 177(3):673–679
Barnes SL, Shane MD, Schoemann MB, Bernard AC, Boulanger BR (2004) Laparoscopic appendectomy after 30 weeks pregnancy: report of two cases and description of technique. Am Surg 70(8):733–736
Upadhyay A, Stanten S, Kazantsev G, Horoupian R, Stanten A (2007) Laparoscopic management of a nonobstetric emergency in the third trimester of pregnancy. Surg Endosc 21(8):1344–1348; Epub 2007 Feb 7
Pastore PA, Loomis DM, Sauret J (2006) Appendicitis in pregnancy. J Am Board Fam Med 19(6):621–626
Yilmaz HG, Akgun Y, Bac B, Celik Y (2007) Acute appendicitis in pregnancy—risk factors associated with principal outcomes: a case control study. Int J Surg 5(3):192–197; Epub 2006 Jun 21
McGory ML, Zingmond DL, Tillou A, Hiatt JR, Ko CY, Kryer JM (2007) Negative appendectomy in pregnant women is associated with a substantial risk of fetal loss. J Am Coll Surg 205(4):534–540
Cohen-Kerem R, Railton C, Oren D, Lishner M, Koren G (2005) Pregnancy outcome following non-obstetric surgical intervention. Am J Surg 190(3):467–473
Mourad J, Elliot JP, Erickson L, Lisboa L (2000) Appendicitis in pregnancy: new information that contradicts long-held clinical beliefs. Am J Obstet Gynecol 182:1027–1029
Hée P, Viktrup L (1999) The diagnosis of appendicitis during pregnancy and maternal and fetal outcome after appendectomy. Int J Gynaecol Obstet 65:129–135
Friedman JD, Ramsey PS, Ramin KD, Berry C (2002) Pneumoamnion and pregnancy loss after second-trimester laparoscopic surgery. Obstet Gynecol 99(3):512–513
Society of American Gastrointestinal Endoscopic Surgeons (SAGES) (1998) Guidelines for laparoscopic surgery during pregnancy. Surg Endosc 12(2):189–190; Updated October 2000
Augustin G, Majerovic M (2007) Non-obstetrical acute abdomen during pregnancy. Eur J Obstet Gynecol Reprod Biol 131(1):4–12; Epub 2006 Sep 18
Acknowledgements
Dr. Louis Beland, Dr. Yves-Marie Dion, Dr. Jean-Pierre Gagne, Dr. Roger C. Gregoire, Dr. Jean Peloquin, Dr. Claude Thibault, Dr. Claude A. Rouleau and Dr. Guy Roy are acknowledged for contributing cases to the study. The editorial assistance of Ovid M. Da Silva is acknowledged. Dr. Bujold holds a Clinician-Scientist Award from the Canadian Institute for Health Research and the Jeanne et Jean-Louis Lévesque Chair at Laval University.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lemieux, P., Rheaume, P., Levesque, I. et al. Laparoscopic appendectomy in pregnant patients: a review of 45 cases. Surg Endosc 23, 1701–1705 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00464-008-0201-9
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00464-008-0201-9