Abstract
Background
The immunologic function of the spleen and its important role in immune defense has led to splenic-preserving surgery. This study aimed to evaluate whether laparoscopic partial splenectomy is safe.
Methods
Data on consecutive patients presenting with localized benign or malignant disease of the spleen were included in a prospective database. The surgical technique consisted of six steps: patient positioning and trocar placement, mobilization of the spleen, vascular dissection, parenchymal resection, sealing/tamponading of the transected edge, and removal of the specimen.
Results
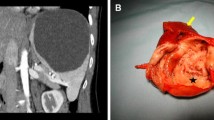
From 1994 to 2005, 38 patients underwent laparoscopic partial splenectomy. The indications included splenomegaly of unknown origin, splenic cysts, benign tumors (hamartoma), and metastasis from ovarian carcinoma and schwannoma. The median operating time was 110 min (range, 65–148 min). The median length of hospital stay was 5 days (range, 4–7 days). There was no postoperative mortality. Postoperative pleural effusion occurred in two patients. There were no reoperations. Three patients required blood transfusions.
Conclusion
Laparoscopic partial splenectomy is safe for patients with localized benign or malignant disease of the spleen.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bonanomi G, Prince JM, McSteen F, Schauer PR, Hamad GG (2004) Sealing effect of fibrin glue on the healing of gastrointestinal anastomoses: implications for the endoscopic treatment of leaks. Surg Endosc 18: 1620–1624
Carroll BJ, Phillips EH, Semel CJ, Fallas M, Morgenstern L (1992) Laparoscopic splenectomy. Surg Endosc 6: 183–185
Delaitre B (1991) Splenectomy by the laparoscopic approach: report of a case. Presse Med 20: 2263
Singer DB (1973) Postsplenectomy sepsis. Perspect Pediatr Pathol 1: 285–311
Sylla P, Kirman I, Whelan RL (2005) Immunological advantages of advanced laparoscopy. Surg Clin North Am 85: 1–18
Targarona EM, Espert JJ, Balague C, Piulachs J, Artigas V, Trias M (1998) Splenomegaly should not be considered a contraindication for laparoscopic splenectomy. Ann Surg 228: 35–39
Uranues S, Alimoglu O (2005) Laparoscopic surgery of the spleen. Surg Clin North Am 85: 75–90
Uranues S, Kronberger L, Kraft-Kine J (1994) Partial splenic resection using the TA-stapler. Am J Surg 168: 49–53
Uranüs S (1995) Physiology of splenic function. In: Uranüs S (ed) Current spleen surgery. W Zuckschwerdt Verlag, München-Bern-Wien-NewYork pp 11–13
Uranüs S, Fingerhut A, Kronberger L, Pfeifer J, Mischinger HJ (1999). Splenic trauma. Eur Surg 31: 75–78
Uranüs S, Pfeifer J (2001) Nonoperative treatment of blunt splenic injury. World J Surg 25: 1405–1407
Uranüs S, Pfeifer J, Schauer C, Kronberger L, Rabl H, Ranftl G, Hauser H, Bahadori K (1995) Laparoscopic partial splenic resection. Surg Laparosc Endosc 5: 133–136
Van Wyck DB, Witte MH, Witte CL, Thies AC Jr (1980) Critical splenic mass for survival from experimental pneumococcemia. J Surg Res 28: 14–17
Wolf HM, Eibl MM, Georgi E, Samstag A, Spatz M, Uranüs S, Passl R (1999) Long-term decrease of CD4+CD45RA+ T cells and impaired primary immune response after posttraumatic splenectomy. Br J Haematol 107: 55–68
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Uranues, S., Grossman, D., Ludwig, L. et al. Laparoscopic partial splenectomy. Surg Endosc 21, 57–60 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00464-006-0124-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00464-006-0124-2